Pallister Killian Mosaic Syndrome
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Pallister-Killian mosaic syndrome is a developmental disorder that affects many parts of the body. It is a rare chromosomal disorder caused by the presence of at least four copies of the short arm of chromosome 12 instead of the normal two.In 1977, the syndrome was reported independently by Pallister, and again in 1981 by Teschler-Nicola and Killian. However, it wasn’t until 2003 when Pallister performed chromosomal analysis on skin fibroblast that the presence of tetrasomy 12p was found.[1]
Cause[edit | edit source]
Pallister-Killian mosaic syndrome is usually caused by the presence of an abnormal extra chromosome 12 called isochromosome 12p. An isochromosome is a chromosome with two identical arms. Normal chromosomes have one long (q) arm and one short (p) arm, but isochromosomes have either two q arms or two p arms. Isochromosome 12p is a version of chromosome 12 made up of two p arms. Cells normally have two copies of each chromosome, one inherited from each parent. In people with Pallister-Killian mosaic syndrome, cells have the two usual copies of chromosome 12, but some cells also have the isochromosome 12p. These cells have a total of four copies of all the genes on the p arm of chromosome 12. The extra genetic material from the isochromosome disrupts the normal course of development, causing the characteristic features of this disorder
As cells divide during early development, some cells lose the isochromosome 12p, while other cells retain the abnormal chromosome. This situation is called mosaicism. Almost all cases of Pallister-Killian mosaic syndrome are caused by mosaicism for an isochromosome 12p. If all of the body's cells contained the isochromosome, the resulting syndrome would probably not be compatible with life.[2]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
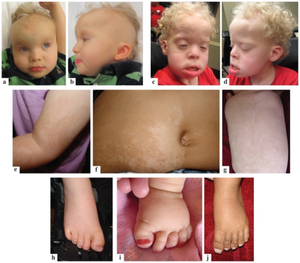
- low muscle tone at birth(can cause difficulty breathing and problems with feeding)
- "coarse" facial appearance that are common to the syndrome-high forehead, broad nasal bridge,short nose, wide space between the eyes,low-set ears
- sparse scalp hair at birth
- high, arched palate or cleft palate
- hypopigmentation
- cognitive and developmental delays
- diaphragmatic hernias(about 40%;this potentially serious birth defect allows the stomach and intestines to move into the chest, where they can crowd the developing heart and lungs)[2]
Additional features-
- hearing loss
- vision impairment
- seizures
- extra nipples
- genital abnormalities
- heart defects.
- Affected individuals may also have skeletal abnormalities such as extra fingers and/or toes, large big toes (halluces), and unusually short arms and legs. [2]
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
Gene Testing-the isochromosome i(12p) can be primarily detected in samples of skin fibroblasts, as well as in chorionic villus and amniotic fluid cell samples.[3]
Pallister-Killian mosaic syndrome can be diagnosed before birth (prenatally) by removing a small amount of fluid that is in the womb during pregnancy (amniocentesis) or by removing a small number of cells from outside the sac where the fetus develops (chorionic villous sampling). Cell cultures may yield a false negative however, and a normal chromosomal analysis does not completely rule out the condition.[4]
Management[edit | edit source]
There is no specific therapy for individuals with Pallister-Killian mosaic syndrome. Affected children may benefit from early intervention programs and special education. Genetic counseling may be of benefit for affected individuals and their families. Other treatment is symptomatic and supportive.[5]
Physiotherapy Intervention[edit | edit source]
With as minimal as 250 cases reported to have the syndrome, physical therapy intervention has not quite been explored in this condition. According to a case report published in 2018[6], the following have shown results-
- Clinical presentation - hypotonia, developmental delay
- Physical assessment - tone, developmental milestones, ROM, deformity/contractures, scoliosis
- Plan of care - educate parents/caregivers, prevent/correct deformity, normalise tone, maintain ROM, monitor normal motor development,
- Intervention - Sensory Intergration Technique(SIT)- vestibular, auditory and visual, Neurodevelopmental Technique(NDT), Positioning and Orthosis(AFO,Boston corset)
- Outcome measures used- Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM-88) and duration of grasping ping pong ball were recorded to determine objective results of his motor level.
- GMFM-88 measures gross motor functions of children in five domains which are lying and rolling, crawling and kneeling, sitting, standing and walk-run-jumping activities. The amount of completion of the movements in the form is scored . Ping pang ball was also used to evaluate the fine motor skill of the case as this is a specific ball type which is commonly used to measure different aspects of motor skills.[6]
Synonyms[edit | edit source]
- chromosome 12, Isochromosome 12p syndrome
- Killian syndrome
- Killian Teschler-Nicola syndrome
- Pallister mosaic syndrome
- Teschler-Nicola Killian syndrome
- PKS
- isochromosome 12p syndrome
- tetrasomy 12p, mosaic[5]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Schinzel A. Tetrasomy 12p (Pallister-Killian syndrome). Journal of medical genetics. 1991 Feb;28(2):122.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Genetics Home Reference. Pallister-Killian mosaic syndrome. Available from: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/pallister-killian-mosaic-syndrome#inheritance (accessed 03/03/2019).
- ↑ Polityko AD, Goncharova E, Shamgina L, Drozdovskaja N, Podleschuk L, Abramchik E, Jaroshevich E, Khurs O, Pisarik I, Pribushenya O, Rumyantseva N. Pallister-Killian syndrome: rapid decrease of isochromosome 12p frequency during amniocyte subculturing. Conclusion for strategy of prenatal cytogenetic diagnostics. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry. 2005 Mar;53(3):361-4.
- ↑ Weaver DD, Brandt IK. Catalog of prenatally diagnosed conditions. JHU Press; 1999.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 2. Pallister Killian Mosaic Syndrome - NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders) [Internet]. NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). 2019 [cited 2 March 2019]. Available from: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/pallister-killian-mosaic-syndrome/
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Topcu ZG, Uzuner S. The effects of physiotherapy and rehabilitation on Pallister-Killian Syndrome: A case report.