Posterior atlanto-axial ligament: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
*Rupture | *Rupture | ||
In case of traumatic and non-traumatic atlanto-axial subluxation/dislocation the posterior atlantisaxis ligamente could suffer a rupture. <ref>Hall, Graham C et al. “Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation.” World Journal of Orthopedics 6.2 (2015): 236–243. PMC. Web. 25 Apr. 2017.</ref> | :- In case of traumatic and non-traumatic atlanto-axial subluxation/dislocation the posterior atlantisaxis ligamente could suffer a rupture. <ref>Hall, Graham C et al. “Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation.” World Journal of Orthopedics 6.2 (2015): 236–243. PMC. Web. 25 Apr. 2017.</ref> | ||
*Atlantoaxial instability (AAI) | *Atlantoaxial instability (AAI) | ||
Can originate in a congenital conditions, but in adults, it is primarily seen in the setting of acute trauma or degenerative changes due to the inflammatory pannus of [[Rheumatoid Arthritis|rheumatoid arthritis]] (RA). | :- Can originate in a congenital conditions, but in adults, it is primarily seen in the setting of acute trauma or degenerative changes due to the inflammatory pannus of [[Rheumatoid Arthritis|rheumatoid arthritis]] (RA). | ||
*Ossification | *Ossification | ||
The ossification of the posterior atlantoaxial membrane that led to the development of cervical myelopathy is rare. | :- The ossification of the posterior atlantoaxial membrane that led to the development of cervical myelopathy is rare. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
There is no record of specific treatment of the Atlantoaxial ligament complex. | There is no record of specific treatment of the Atlantoaxial ligament complex. Hovewer, in case of AAI or rupture, the treatment should include the cervical stabilization management . Check this page about [[Cervical Instability|Cervical Instability]] for further information. | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
[[Anterior atlanto-axial ligament|Anterior Atlantoaxial Ligament | [[Anterior atlanto-axial ligament|Anterior Atlantoaxial Ligament]] | ||
[[Anterior atlanto-occipital ligament|Anterior Atlanto-occipital Ligament]] | [[Anterior atlanto-occipital ligament|Anterior Atlanto-occipital Ligament]] | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
[[Posterior atlanto-occipital ligament|Posterior Atlanto-occipital Ligament]]<br> | [[Posterior atlanto-occipital ligament|Posterior Atlanto-occipital Ligament]]<br> | ||
[[Transverse ligament of the atlas|Transverse ligament of the atlas]] | |||
[[Sharp Purser Test|Sharp Purser Test]] | |||
== Recent Related Research (from Pubmed) == | == Recent Related Research (from Pubmed) == | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 30 April 2017
Original Editor - Rachael Lowe
Top Contributors - Kim Jackson, Evan Thomas, Daniele Barilla, Admin, Rachael Lowe and WikiSysop
Description[edit | edit source]
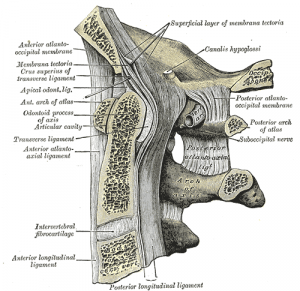
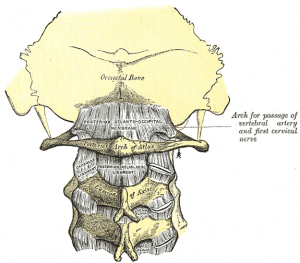
The posterior atlantoaxial ligament is a broad, thin membrane attached, above, to the lower border of the posterior arch of the atlas; below, to the upper edges of the lamina of the axis. It is a continuation of the Ligamentum flavum, and is in relation, behind, with the obliqus capitis inferior muscle. [1]It is part of a ligament complex called Altantoaxial Ligament Complex (Axis). These four ligaments extend from the Atlas to the Axis:
- Anterior Atlantoaxial Ligament
- Posterior Atlantoaxial Ligament
- Lateral Ligaments (2)
Attachments[edit | edit source]
From lower border of atlantal arch (and more superiorly to the occipital bone) and upper borders of lamina of C2.
Function[edit | edit source]
It contributes the stabilization of the atlanto-axial joint movement that overall allows 10-15° of flexion/extension and 30° of axial rotation.
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
- Rupture
- - In case of traumatic and non-traumatic atlanto-axial subluxation/dislocation the posterior atlantisaxis ligamente could suffer a rupture. [2]
- Atlantoaxial instability (AAI)
- - Can originate in a congenital conditions, but in adults, it is primarily seen in the setting of acute trauma or degenerative changes due to the inflammatory pannus of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
- Ossification
- - The ossification of the posterior atlantoaxial membrane that led to the development of cervical myelopathy is rare.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There is no record of specific treatment of the Atlantoaxial ligament complex. Hovewer, in case of AAI or rupture, the treatment should include the cervical stabilization management . Check this page about Cervical Instability for further information.
Resources[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
Anterior Atlantoaxial Ligament
Anterior Atlanto-occipital Ligament
Posterior Atlanto-occipital Ligament
Transverse ligament of the atlas