Sporting Hand and Wrist - Mobility Strength and Endurance: Difference between revisions
Carin Hunter (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[https://physio-pedia.com/Category:Hand_-_Anatomy The hand anatomy] is efficiently | [https://physio-pedia.com/Category:Hand_-_Anatomy The hand anatomy] is efficiently organised to carry out a variety of complex tasks combining intricate movements and finely controlled force production. The soft tissue structure of the hand is complicated and an injury to any of these structures can alter the overall function of the hand, thereby complicating the therapeutic management.<ref name=":0">Duruoz MT. Hand function. Springer-Verlag New York; 2016</ref> [https://physio-pedia.com/Hand_Function#sts=Functional%20Position%20of%20Hand?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Hand function] and strength are important elements in day to day life and participation in sports.<ref name=":1">Gatt I, Smith-Moore S, Steggles C, Loosemore M. The takei handheld dynamometer: an effective clinical outcome measure tool for hand and wrist function in boxing. HAND. 2018 May;13(3):319-24</ref> Activities of daily living can use up to 70% of your hand motion. In a study conducted by Rainbow et al<ref>Rainbow MJ, Wolff AL, Crisco JJ, Wolfe SW. Functional kinematics of the wrist. Journal of Hand Surgery (European Volume). 2016 Jan;41(1):7-21.</ref> it was found that throughout all motions, the ligaments are always taut. This contributes to the stability in the wrist joint. | ||
In depth understanding of the hand anatomy and biomechanics is crucial for choosing the most effective treatment.<ref>Eschweiler J, Li J, Quack V, Rath B, Baroncini A, Hildebrand F, Migliorini F. [https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/12/2/188 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Loads of the Wrist Joint]. Life. 2022 Jan 27;12(2):188.</ref> Hand function has four important components: | |||
* Mobility | * Mobility | ||
** The maintenance development of movement through a specific range of motion | ** The maintenance or development of movement through a specific range of motion | ||
* Stability or Motor Control | * Stability or Motor Control | ||
** The maintenance or development of kinetic stability during | ** The maintenance or development of kinetic stability during static or dynamic skilled movements | ||
* Endurance or Work Capacity | * Endurance or Work Capacity | ||
** The ability to produce or tolerate variable intensities and duration of work whilst maintaining that motor control | ** The ability to produce or tolerate variable intensities and duration of work whilst maintaining that motor control | ||
* Strength | * Strength | ||
** The ability to produce or tolerate maximal strength | ** The ability to produce or tolerate maximal strength | ||
It is | It is important to know and remember the average range of motion of the [[Wrist and Hand Examination|wrist]] when conducting an assessment: | ||
* Flexion - 70 to 75 degrees | * Flexion - 70 to 75 degrees | ||
* Extension - 70 to 75 degrees | * Extension - 70 to 75 degrees | ||
* Radial deviation - 20 degrees | * Radial deviation - 20 degrees | ||
* Ulnar deviation - 35 degrees | * Ulnar deviation - 35 degrees | ||
To determine functionality of the hand movement, therapist must consider the arm and wrist as making a vital contribution to the hand activities.<ref>Liu Y, Jiang L, Liu H, Ming D. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8216684/pdf/fnbot-15-658075.pdf A Systematic Analysis of Hand Movement Functionality: Qualitative Classification and Quantitative Investigation of Hand Grasp Behavior.] Front Neurorobot. 2021 Jun 7;15:658075. </ref> | |||
== Principles of Dosage in Exercise Prescription == | == Principles of Dosage in Exercise Prescription == | ||
=== Dosage === | === Dosage === | ||
There are five aspects to consider when prescribing any exercise regime | There are five aspects to consider when prescribing any exercise regime: | ||
# | # The intention of the program (endurance, strength, stability, mobility) | ||
# Intensity | # Intensity | ||
# Repetitions | # Repetitions | ||
# Sets | # Sets | ||
# Rest | # Rest | ||
The table below shows examples of dosage for endurance rehabilitation and for strength rehabilitation. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Intention | !Intention | ||
!Endurance | !Endurance | ||
!Strength | !Strength | ||
(relative to the individual) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Intensity | |'''Intensity''' | ||
|Low to moderate intensity | |Low to moderate intensity | ||
|High | |High intensity (85-100%) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Repetitions | |'''Repetitions''' | ||
|High repetitions | |High repetitions (15 +) | ||
|Low repetitions | |Low repetitions (1-6 reps) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Sets | |'''Sets''' | ||
| | |2-3 sets | ||
|Increased sets | |Increased sets (2-6 sets) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Rest | |'''Rest''' | ||
|Short rest periods | |Short rest periods | ||
(30 seconds to 1 minute) | |||
|Longer rests periods to allow the recovery | |Longer rests periods to allow the recovery | ||
(2-5 minutes) | |||
|} | |} | ||
== Grip Strength in Day to Day Life == | == Grip Strength in Day to Day Life == | ||
Daily activities require a combination of different movements in the upper limb. Hand function is an important component of these movements. The loss of grip strength is associated with a number of pathologies. [https://physio-pedia.com/Wrist_and_Hand_Osteoarthritis?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Hand Osteoarthritis] is | Daily activities require a combination of different movements in the upper limb. Hand function is an important component of these movements. The loss of grip strength is associated with a number of pathologies. [https://physio-pedia.com/Wrist_and_Hand_Osteoarthritis?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Hand Osteoarthritis] is a common chronic condition involving one or more joints of the thumb and fingers. It is associated with pain, reduced grip strength, loss of range of motion (ROM), and joint stiffness leading to impaired hand function and difficulty with [[Activities of Daily Living|daily activities]]. [https://physio-pedia.com/Stroke:_Hand_Rehabilitation?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Stroke] is another condition that impacts the upper limb and hand function. Addressing these conditions requires an understanding of hand anatomy and [[biomechanics]]. | ||
There are numerous factors such as sex, age, and hand preference that contribute to | There are numerous factors such as sex, age, and hand preference that contribute to [[Grip Strength|grip strength]] and they should be considered when making clinical decisions. The average grip strength of women is approximately 60% that of men, and for both sexes, grip strength reaches a maximum during the fourth decade of life and declined thereafter with increasing age. | ||
Cold weather causes reduced muscle contraction and affects grip strength and function | Cold weather causes reduced muscle contraction and affects grip strength and hand function.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
It is believed that the difference between the dominant and non-dominant hand in strength is 10% (known as the 10% rule). This applies to right-handed people. For | It is believed that the difference between the dominant and non-dominant hand in strength is 10% (known as the 10% rule). This applies to right-handed people. For left-handed individuals, grip strength is considered equivalent in both hands.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Measuring Grip Strength == | == Measuring Grip Strength == | ||
Measuring grip strength is commonly used in research and sports to measure the efficacy of an intervention. It is a useful practice to implement in hand rehabilitation | Measuring grip strength is commonly used in research and sports to measure the efficacy of an intervention. It is a useful practice to implement in hand rehabilitation as it can aid decision making and reporting outcomes. | ||
'''Dynamometers'''<ref name=":1" /> | '''Dynamometers:'''<ref name=":1" /> The Jamar and the Takei are the most commonly studied dynamometers. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Jamar | !Jamar | ||
| Line 73: | Line 79: | ||
|Digital or analogue display | |Digital or analogue display | ||
|} | |} | ||
Important points to consider when testing grip strength<ref name=":2" | Important points to consider when testing grip strength:<ref name=":2">Gatt I. Sporting Hand & Wrist - Why Power & Pinch Grips Matter. Plus Course 2020</ref> | ||
* Note the associated symptoms such as pain or instability. The timing of the symptoms also matters - i.e. whether they accompany the movement or start after the testing | |||
* The difference between the right and left hands. Consider the element of chronicity that could lead to weakness due to reciprocal inhibition. | |||
* Repeat the test 3 times starting with the non-painful side before moving on to the other hand. Alternate the testing between hands three times | |||
* Look for the peak force (the best number that can be achieved on testing). Some people might be able to generate a high number on the strength test, but this number may then lower due to fatigue, Alternatively, they may take a few repetitions to generate the force | |||
* Note the associated symptoms such as pain or instability. The timing of the symptoms also matters whether they accompany the movement or start after the testing | |||
* The difference between the right and left hands. Consider the element of chronicity could lead to weakness due to reciprocal inhibition. | |||
* Repeat the test | |||
* Look for the peak force (the best number that | |||
Testing position: | Testing position: | ||
* Elbow | * Elbow is at a 90-degree angle - this helps to generate the highest peak. However, having the forearm in mid-position can lead to contraction of the brachioradialis muscle and the movement will not be generated purely from the hand | ||
* Testing from straight elbow position and wrist in neutral. This position is recommended by Gatt | * Testing from straight elbow position and wrist in neutral. This position is recommended by Gatt<ref name=":2" /> to isolate the hand muscles | ||
== Rehabilitation of the wrist == | |||
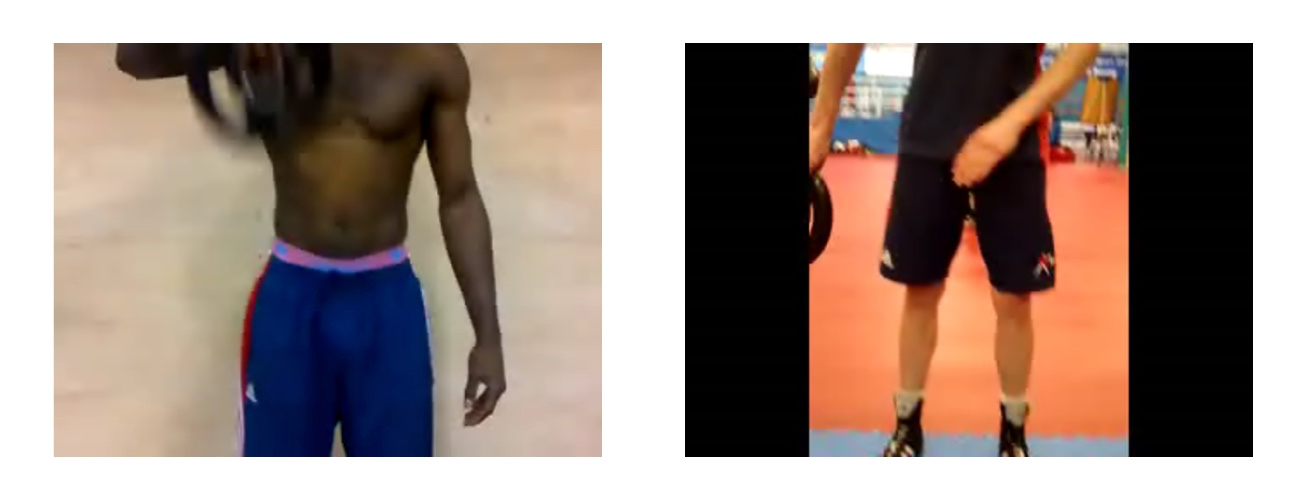
=== 1 - Power grip rehabilitation === | |||
[[File:Strength or endurance4.png|center|frame|Power grip Rehabilitation - Strength or endurance]]1 - Rubber exercise bar, known as Flexbars. Different colours can be deployed for varying strength and to target the wrist and forearm muscles. This exercise helps with wrist mobility, it may also provide a degree of stability, and it will improve strength or endurance. Alter the exercise to incorporate pronation and supination. | |||
2 - Crushes - this is another tool that can be used to improve the power grip. Intensity can be adjusted by the number of springs. Green crushes use a wide grip, or power grip, to improve strength. Wrist stability entails the co-contraction of all the muscles around the wrist - the best position to achieve stability tends to be around 30 degrees of wrist extension | |||
Other exercises using a Flexbar:{{#ev:youtube|viKPwMTJJBA}} | |||
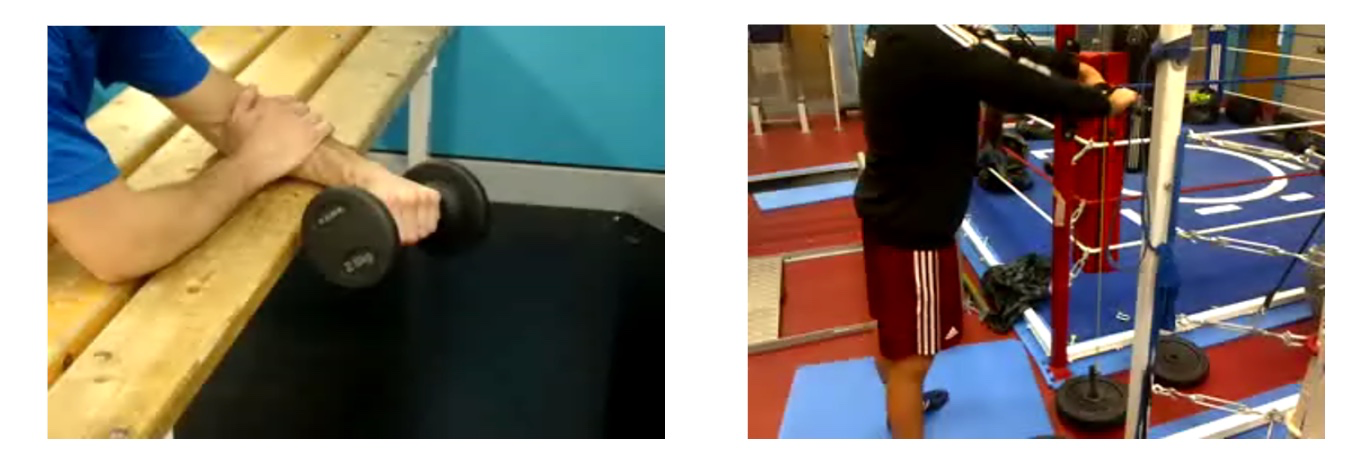
=== 2. Flexion/extension rehabilitation === | |||
[[File:Strength or endurance3.png|center|frame|Flexion/Extension rehabilitation - Strength or endurance]]1 - Wrist curls, in this position (pictured above), focus on extension. In 30 degrees of extension, the power grip in the isometric position is very strong | |||
2 - Horizontal pulley. This works into extension, both concentric (roll-up), and eccentric (roll down) | |||
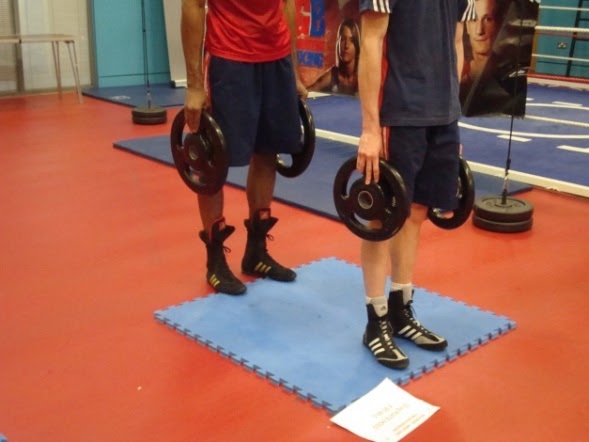
=== 3 - Thumb rehabilitation === | |||
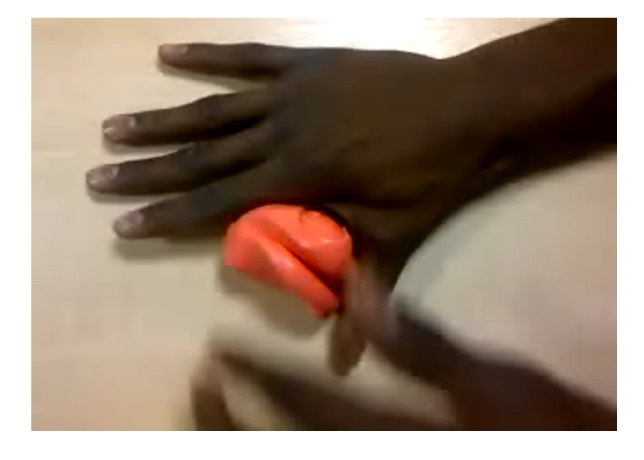
[[File:Strength or endurance2.jpg|center|frame|Thumb rehabilitation - Strength or endurance]]Plate holds - Holding a plate: there are different variations depending on the targeted muscles. The time to hold can be adjusted based on the type of training e.g. conditioning vs endurance, and also can be used to check the difference in the maximum hold between right and left hands. Monitoring the symptoms associated with holding the plate such as pain, the timing of the symptoms and the effect on holding can be useful data in the management.[[File:Strength or endurance.png|center|frame|Thumb rehabilitation - Strength or endurance]]Putty: for pinch or power grip using different variations: | |||
1 - Pinch Grip<ref name=":0" />{{#ev:youtube|QxaP5P9CSWc}}2 - Power Grip<ref name=":0" />{{#ev:youtube|DufAYWGidsc}} | |||
[[File:Stability or endurance.png|center|frame|Thumb rehabilitation - Stability or endurance]]Flipping Plates: good exercise to improve thumb and wrist proprioception. {{#ev:youtube|viKPwMTJJBA}}Pendular exercises create stability through compression. | |||
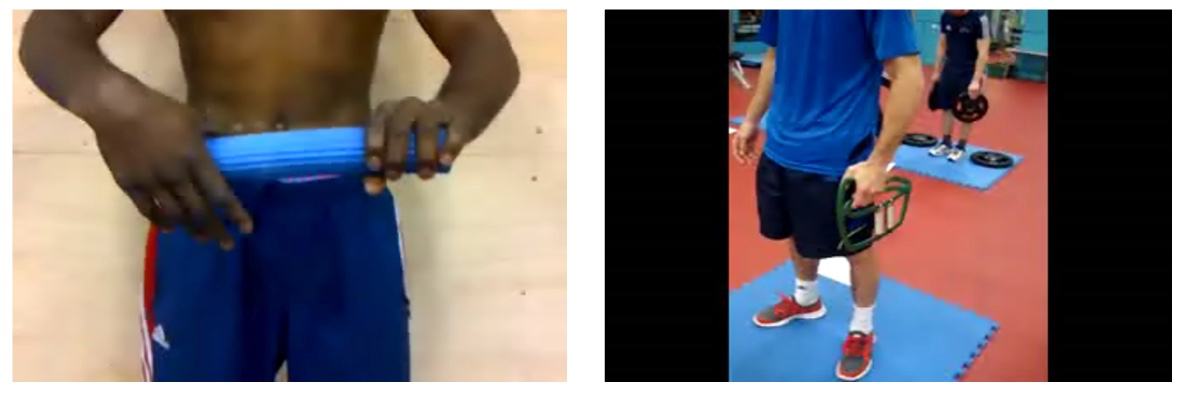
=== 4 - Wrist stability === | |||
[[File:Pertubations 1.jpg|center|frame|Wrist stability - Perturbations]][[Perturbation techniques|Perturbations]]/Vibrations assist with developing wrist stability | |||
=== 5 - Wrist rehabilitation for static stability === | |||
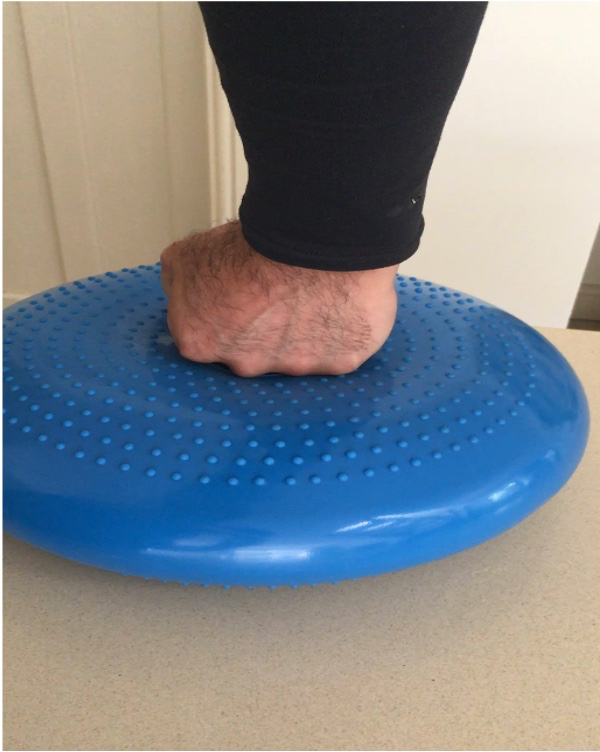
[[File:Static Stability - Push into Bosu ball.png|center|frame|Wrist rehabilitation - Static stability]]Punching into a Bosu ball creates compression to assist with static stability of the wrist. | |||
In a study conducted by Kim et al<ref>Kim GS, Weon JH, Kim MH, Koh EK, Jung DY. Effect of weight-bearing wrist movement with carpal-stabilizing taping on pain and range of motion in subjects with dorsal wrist pain: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Hand Therapy. 2020 Jan 1;33(1):25-33.</ref>, using strapping to assist with stability could be used as a part of your wrist stability intervention. | |||
=== 6. Wrist rehabilitation for Dynamic stability === | |||
[[File:Dynamic Stability - Ball punch.png|left|thumb|Wrist rehabilitation - Dynamic stability]][[File:Dynamic stability - Dumbell pushups.png|center|thumb|Wrist rehabilitation - Dynamic stability]][[File:Dynamic stability - wall push offs.png|thumb|Dynamic Stability. | |||
Wall push offs and Trampoline punch | |||
|center]] | |||
* Physioball punches for dynamic stability | |||
* Dumbbell pushups for dynamic stability | |||
* Trampoline punch | |||
* Wall Push offs - this exercise focuses on the maintenance of the wrist, in a neutral position. The elbow is rigid and maintained in extension. | |||
Variations | |||
* Fist | |||
* Open hand | |||
* Hold onto a rubber ball | |||
* Hold onto a weighted ball | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Course Pages]] | |||
[[Category:Plus Content]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:51, 17 January 2023
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The hand anatomy is efficiently organised to carry out a variety of complex tasks combining intricate movements and finely controlled force production. The soft tissue structure of the hand is complicated and an injury to any of these structures can alter the overall function of the hand, thereby complicating the therapeutic management.[1] Hand function and strength are important elements in day to day life and participation in sports.[2] Activities of daily living can use up to 70% of your hand motion. In a study conducted by Rainbow et al[3] it was found that throughout all motions, the ligaments are always taut. This contributes to the stability in the wrist joint.
In depth understanding of the hand anatomy and biomechanics is crucial for choosing the most effective treatment.[4] Hand function has four important components:
- Mobility
- The maintenance or development of movement through a specific range of motion
- Stability or Motor Control
- The maintenance or development of kinetic stability during static or dynamic skilled movements
- Endurance or Work Capacity
- The ability to produce or tolerate variable intensities and duration of work whilst maintaining that motor control
- Strength
- The ability to produce or tolerate maximal strength
It is important to know and remember the average range of motion of the wrist when conducting an assessment:
- Flexion - 70 to 75 degrees
- Extension - 70 to 75 degrees
- Radial deviation - 20 degrees
- Ulnar deviation - 35 degrees
To determine functionality of the hand movement, therapist must consider the arm and wrist as making a vital contribution to the hand activities.[5]
Principles of Dosage in Exercise Prescription[edit | edit source]
Dosage[edit | edit source]
There are five aspects to consider when prescribing any exercise regime:
- The intention of the program (endurance, strength, stability, mobility)
- Intensity
- Repetitions
- Sets
- Rest
The table below shows examples of dosage for endurance rehabilitation and for strength rehabilitation.
| Intention | Endurance | Strength
(relative to the individual) |
|---|---|---|
| Intensity | Low to moderate intensity | High intensity (85-100%) |
| Repetitions | High repetitions (15 +) | Low repetitions (1-6 reps) |
| Sets | 2-3 sets | Increased sets (2-6 sets) |
| Rest | Short rest periods
(30 seconds to 1 minute) |
Longer rests periods to allow the recovery
(2-5 minutes) |
Grip Strength in Day to Day Life[edit | edit source]
Daily activities require a combination of different movements in the upper limb. Hand function is an important component of these movements. The loss of grip strength is associated with a number of pathologies. Hand Osteoarthritis is a common chronic condition involving one or more joints of the thumb and fingers. It is associated with pain, reduced grip strength, loss of range of motion (ROM), and joint stiffness leading to impaired hand function and difficulty with daily activities. Stroke is another condition that impacts the upper limb and hand function. Addressing these conditions requires an understanding of hand anatomy and biomechanics.
There are numerous factors such as sex, age, and hand preference that contribute to grip strength and they should be considered when making clinical decisions. The average grip strength of women is approximately 60% that of men, and for both sexes, grip strength reaches a maximum during the fourth decade of life and declined thereafter with increasing age.
Cold weather causes reduced muscle contraction and affects grip strength and hand function.[1]
It is believed that the difference between the dominant and non-dominant hand in strength is 10% (known as the 10% rule). This applies to right-handed people. For left-handed individuals, grip strength is considered equivalent in both hands.[1]
Measuring Grip Strength[edit | edit source]
Measuring grip strength is commonly used in research and sports to measure the efficacy of an intervention. It is a useful practice to implement in hand rehabilitation as it can aid decision making and reporting outcomes.
Dynamometers:[2] The Jamar and the Takei are the most commonly studied dynamometers.
| Jamar | Takei |
|---|---|
| Gold standard for documenting manual grip strength | Valid and reliable tool to measure power grip |
| Adjustable anatomical rigid handle | Complacent handle shape |
| Hydraulic system | Electromechanical system |
| Analogue display | Digital or analogue display |
Important points to consider when testing grip strength:[6]
- Note the associated symptoms such as pain or instability. The timing of the symptoms also matters - i.e. whether they accompany the movement or start after the testing
- The difference between the right and left hands. Consider the element of chronicity that could lead to weakness due to reciprocal inhibition.
- Repeat the test 3 times starting with the non-painful side before moving on to the other hand. Alternate the testing between hands three times
- Look for the peak force (the best number that can be achieved on testing). Some people might be able to generate a high number on the strength test, but this number may then lower due to fatigue, Alternatively, they may take a few repetitions to generate the force
Testing position:
- Elbow is at a 90-degree angle - this helps to generate the highest peak. However, having the forearm in mid-position can lead to contraction of the brachioradialis muscle and the movement will not be generated purely from the hand
- Testing from straight elbow position and wrist in neutral. This position is recommended by Gatt[6] to isolate the hand muscles
Rehabilitation of the wrist[edit | edit source]
1 - Power grip rehabilitation[edit | edit source]
1 - Rubber exercise bar, known as Flexbars. Different colours can be deployed for varying strength and to target the wrist and forearm muscles. This exercise helps with wrist mobility, it may also provide a degree of stability, and it will improve strength or endurance. Alter the exercise to incorporate pronation and supination.
2 - Crushes - this is another tool that can be used to improve the power grip. Intensity can be adjusted by the number of springs. Green crushes use a wide grip, or power grip, to improve strength. Wrist stability entails the co-contraction of all the muscles around the wrist - the best position to achieve stability tends to be around 30 degrees of wrist extension
Other exercises using a Flexbar:
2. Flexion/extension rehabilitation[edit | edit source]
1 - Wrist curls, in this position (pictured above), focus on extension. In 30 degrees of extension, the power grip in the isometric position is very strong
2 - Horizontal pulley. This works into extension, both concentric (roll-up), and eccentric (roll down)
3 - Thumb rehabilitation[edit | edit source]
Plate holds - Holding a plate: there are different variations depending on the targeted muscles. The time to hold can be adjusted based on the type of training e.g. conditioning vs endurance, and also can be used to check the difference in the maximum hold between right and left hands. Monitoring the symptoms associated with holding the plate such as pain, the timing of the symptoms and the effect on holding can be useful data in the management.
Putty: for pinch or power grip using different variations: 1 - Pinch Grip[1]
2 - Power Grip[1]
Flipping Plates: good exercise to improve thumb and wrist proprioception.
Pendular exercises create stability through compression.
4 - Wrist stability[edit | edit source]
Perturbations/Vibrations assist with developing wrist stability
5 - Wrist rehabilitation for static stability[edit | edit source]
Punching into a Bosu ball creates compression to assist with static stability of the wrist.
In a study conducted by Kim et al[7], using strapping to assist with stability could be used as a part of your wrist stability intervention.
6. Wrist rehabilitation for Dynamic stability[edit | edit source]
- Physioball punches for dynamic stability
- Dumbbell pushups for dynamic stability
- Trampoline punch
- Wall Push offs - this exercise focuses on the maintenance of the wrist, in a neutral position. The elbow is rigid and maintained in extension.
Variations
- Fist
- Open hand
- Hold onto a rubber ball
- Hold onto a weighted ball
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Duruoz MT. Hand function. Springer-Verlag New York; 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Gatt I, Smith-Moore S, Steggles C, Loosemore M. The takei handheld dynamometer: an effective clinical outcome measure tool for hand and wrist function in boxing. HAND. 2018 May;13(3):319-24
- ↑ Rainbow MJ, Wolff AL, Crisco JJ, Wolfe SW. Functional kinematics of the wrist. Journal of Hand Surgery (European Volume). 2016 Jan;41(1):7-21.
- ↑ Eschweiler J, Li J, Quack V, Rath B, Baroncini A, Hildebrand F, Migliorini F. Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Loads of the Wrist Joint. Life. 2022 Jan 27;12(2):188.
- ↑ Liu Y, Jiang L, Liu H, Ming D. A Systematic Analysis of Hand Movement Functionality: Qualitative Classification and Quantitative Investigation of Hand Grasp Behavior. Front Neurorobot. 2021 Jun 7;15:658075.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Gatt I. Sporting Hand & Wrist - Why Power & Pinch Grips Matter. Plus Course 2020
- ↑ Kim GS, Weon JH, Kim MH, Koh EK, Jung DY. Effect of weight-bearing wrist movement with carpal-stabilizing taping on pain and range of motion in subjects with dorsal wrist pain: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Hand Therapy. 2020 Jan 1;33(1):25-33.