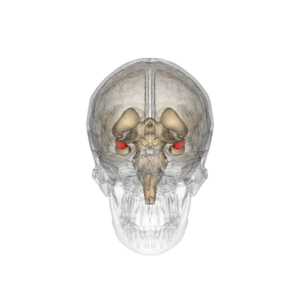
Amygdala
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton and Sai Kripa
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The amygdala is a collection of nuclei found deep within the temporal lobe. There are two amygdala, one in each cerebral hemisphere. The amygdala is recognized as a component of the limbic system, and is thought to play important roles in emotion and behavior. It is best known for its role in the processing of fear however this is an oversimplified perspective on amygdala function[1].
Function[edit | edit source]
Early humans were exposed to the constant threat eg being killed by wild animals or other tribes. To improve the chances of survival, the fight- or-flight response evolved ie an automatic response to physical danger that allows you to react quickly without thinking.
- This response is triggered by emotions like fear, anxiety, aggression, and anger.
- The amygdalae are most functional in immediate fear situations. Whenever our senses detect a change in our surroundings that could be dangerous, the amygdalae are responsible for preparing the body for escape or defense. This is part of what is known as the startle circuit of the brain, which controls our response to being startled,
- The amygdala helps to store memories of events and emotions so that an individual may be able to recognize similar events in the future.
- The size of the amygdala is positively correlated with increased aggression and physical behavior.
- The amygdala in humans also plays a role in sexual activity and libido, or sex drive. It can change in size and shape based on the age, hormonal activity, and gender of the individual. For example, males who have low testosterone, or who may have been castrated, (had their testicles removed), tend to have smaller amygdalae, and, in turn, may also have a lower sex drive.
- The amygdalae are most functional in immediate fear situations. Whenever our senses detect a change in our surroundings that could be dangerous, the amygdalae are responsible for preparing the body for escape or defense. This is part of what is known as the startle circuit of the brain, which controls our response to being startled[2].
- Destroying an animal’s amygdala has disastrous effects on its natural alarm system. But that does not make the amygdala the “fear centre”, because the amygdala also has connections coming in from and going out to several other parts of the brain, all of which also are needed to manifest fear[3].
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Neuroscientifically challenged Amygdala Available from:https://www.neuroscientificallychallenged.com/blog/know-your-brain-amygdala (accessed 30.12.2020)
- ↑ study.com Amygdala Available from:https://study.com/academy/lesson/the-amygdala-definition-role-function.html (accessed 30.12.2020)
- ↑ McGill The Brain Available from:https://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_04/d_04_cr/d_04_cr_peu/d_04_cr_peu.html (accessed 30.12.2020)