Ganglion
Original Editor - lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka and Vidya Acharya
Introduction[edit | edit source]
A ganglion is a collection of neuronal bodies found in the somatic and autonomic branches of the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Ganglia can be thought of as synaptic relay stations between neurons. The information enters the ganglia, excites the neuron in the ganglia and then exits[1].
Among vertebrate animals there are three major groups of ganglia. These include:
- Cranial nerve ganglia that contain the neurons of the cranial nerves
- Dorsal root ganglia or spinal ganglia where the cell bodies of sensory or afferent nerves are located
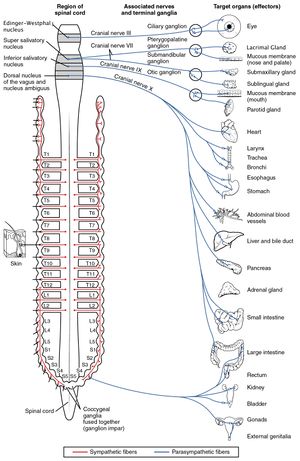
- Autonomic ganglia, which contain the cell bodies of the autonomic nervous system. In this system, nerve fibers that run from the central nervous system to the ganglia are called the preganglionic fibers. The nerve fibers originating in the ganglia that connect to effector organs are termed postganglionic fibers.[2]
Image 1: Shows the Autonomic Ganglia (red SNS, blue PNS)
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ ken Hub Ganglion Available from:https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/nerve-ganglia (accessed 5.2.2021)
- ↑ New Medical Ganglion Available from:https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-a-Ganglion.aspx (accessed 5.2.2021)