Bunnell-Littler Test: Difference between revisions
Jon DeVaul (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Jon DeVaul (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Technique<br> == | == Technique<br> == | ||
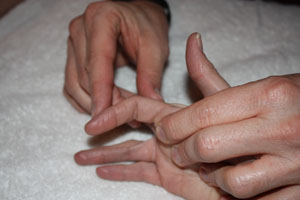
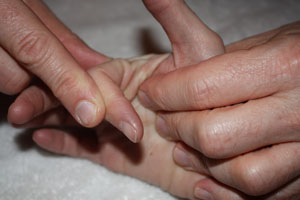
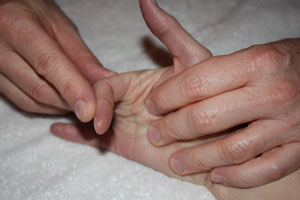
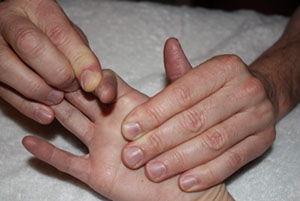
The MCP is held in an extended position and the therapist passively flexes the PIP making note of the available range. The test is then repeated with the MCP flexed. If no change in motion is detected between the two tests, then capsular restriction at the PIP joint is implicated. If the motion increases when the MCP is flexed, then lumbricale muscle tightness is implicated. | The MCP is held in an extended position and the therapist passively flexes the PIP making note of the available range. The test is then repeated with the MCP flexed. If no change in motion is detected between the two tests, then capsular restriction at the PIP joint is implicated. If the motion increases when the MCP is flexed, then lumbricale muscle tightness is implicated. | ||
Scroll over the pictures below for captions.<br><br> | Scroll over the pictures below for captions.<br><br> | ||
[[Image:B l test start.jpg|+ test finding for PIP restriction]] [[Image: | [[Image:B l test start.jpg|+ test finding for PIP restriction]] [[Image:B l end intrinsic.jpg|increased PIP flexion with MCP flexion implies intrinsic restriction]] | ||
<br> | |||
[[Image:B l end capsular.jpg|no increase in PIP flexion with MCP flexion implies capsular restriction]] [[Image:B l normal.jpg|full PIP flexion with MCP extension is a normal (-) test finding]] | |||
[[Image: | |||
== Evidence == | == Evidence == | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Orthopaedic Physical Therapy by Donatelli and Wooden. 4th edition | Orthopaedic Physical Therapy by Donatelli and Wooden. 4th edition | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 21:16, 6 December 2009
Purpose
[edit | edit source]
This test evaluates the source of PIP flexion motion limitation by differentiating between intrinsic muscle or capsular tightness in the affected digit. A typical patient presentation may include pain located in the distal intermetacarpal space and with prolonged gripping or making a fist. Symptoms are most often seen in the ring and long finger.
Technique
[edit | edit source]
The MCP is held in an extended position and the therapist passively flexes the PIP making note of the available range. The test is then repeated with the MCP flexed. If no change in motion is detected between the two tests, then capsular restriction at the PIP joint is implicated. If the motion increases when the MCP is flexed, then lumbricale muscle tightness is implicated.
Scroll over the pictures below for captions.
Evidence[edit | edit source]
Provide the evidence for this technique here
Resources[edit | edit source]
Orthopaedic Physical Therapy by Donatelli and Wooden. 4th edition
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.