Equipment for individuals with limb deficiency: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
<br>The patient with Amputation will use a walking aid, either temporary or permeant to restore the functional ambulation and independency. The choice is depending on the level of fitness, strength, balance skills, and risk of falls. As well as the walking aid will help to control the allowed weight bearing on the injured leg, compensate the lack of balance, and decrease the risk of fall. | <br>The patient with Amputation will use a walking aid, either temporary or permeant to restore the functional ambulation and independency. The choice is depending on the level of fitness, strength, balance skills, and risk of falls. As well as the walking aid will help to control the allowed weight bearing on the injured leg, compensate the lack of balance, and decrease the risk of fall. | ||
=== <br>Named, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Adjustment === | === <br>Named, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Adjustment === | ||
<br>Watch the video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=inH0rdkTWTI explaining how to choose, use some assistive devices.<br>The table below is explaining the different type of walking aids, the advantages, the disadvantages and the adjustment guide (11, 12).<br> | <br>Watch the video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=inH0rdkTWTI explaining how to choose, use some assistive devices.<br>The table below is explaining the different type of walking aids, the advantages, the disadvantages and the adjustment guide (11, 12).<br> | ||
[[Image:Deambulation.png]] | |||
=== Special Consideration on walking Aids === | |||
<br>Our long term goal with amputee patients it to reach maximum functional independency without walking aids, a special consideration should be taken such as (12, 13):<br>- Some patients can’t achieve this goal due to the age or other medical problem.<br>- The ambulation using a walker is not a must step to shift the patient from parallel bar to crutches or cane if the physical and medical condition allows.<br>- Usually using a single walking aid should be handled at the sound side, and it can be used at the Amputee side if the goal is to shift more weight to this side.<br>- The role to ascend and descend the stair is to ascend with sound leg, and descend with the amputee side (Up good, and down pad).<br>- A proper selection of a walking aid with proper adjustment will speed up the rehabilitation process and improve the quality of the outcomes. | |||
== Other Equipment’s for Physiotherapy Units == | |||
<br>Physiotherapy unit must be supplied by many essential equipment and materials which are important in the implementation of the treatment plan of the physiotherapy and prosthetic/orthotics as well. These materials are necessary before and after the prosthetic rehabilitation as well as in advanced gait training level. <br>The materials and equipment itself are classified into three different categories (14): | |||
[[Image:Equipment.png]]<br><br> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 21:46, 16 May 2015
Introduction [edit | edit source]
it has been defined the amputation is removal of all or part of the extremities, and it cause a decrease of level of activities. The person who had an amputation is in-need to have a proper rehabilitation program as early as possible especially at the time of the hospitalization under special considerations. Also to provide these group with compensatory equipment’s to reach their maximum functional independency.
So far, the patient will need proper external support and equipment to transport, to be mobile, to do their Activity of Daily Living (ADL), and to be involved in the community. However, the prescription of the assistive device and the walking aid will depend on multidisciplinary team after evaluating different factors and involving the patient in this decision.
Risk assessment [edit | edit source]
Risk factor Assessment Tools[edit | edit source]
Falls are happened usually due to certain reasons for different ages that may lead to serious outcomes. Such assessment tools are implemented to demonstrate these risk factors of falls.
Gait and balance assessment (1) such as; Time up and Go (TUG), Berg Balance Scale (BBS), Tinetti Performance Oriented Mobility Assessment (POMA), Dynamic Gait Index, and Get Up and Go test. These assessment tools are reflecting the relation between the balance and the ability of a person to walk in appropriate way. It's explaining and determining for how long the person can keep his balance during gait, as well as to apply few kinds of ADL while moving from point to another, to identify the level of balance effect on gait.
These tools used in the evaluation of the person gait quality, and then it may help to achieve the key factor of falls for the patient, which may help to find out management technique for this patient. Also the previous tools may reflect other aspects that could be affected such as:
- Mental problems.
- Language difficulties.
- Short term verbal memory.
- Construct ability.
- Calculation problems.
It's important to initiate those tools of assessing the patients since hospitalization, it will help in better and earlier effective treatment plan. Certain centers and health care institutions are participated to provide and produce several kinds of assessment to evaluate patient's risk to falls in different ages. These assessment tools consider as important part to keep the patient's safety, and to protect him/her from expected injuries.
Falls Risk Assessment and Management Plan (FRAMP):[edit | edit source]
According to the FRAMP (2) which is one of the tools that evaluating the patient's risk to falls since the early stage of hospitalization. FRAMP is passing through three similar stages of assessment during specific period of time which identifying the history of falls, using of walking aids, cognitive impairment and other urinary and fecal problems.
The FRAMP is explaining important practice points for patients who are complaining from (coagulopathy) and under anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy are more vulnerable for intracranial hemorrhage due to recurrent falls, as well as patients with osteoporosis who may develop more fractures as a result of falls.
Moreover, the individualized intervention for specific risks such as:
- Mobility risks.
- Functional ability risks.
- Medication/ Medical condition risks.
- Cognitive state risks.
- Continence/ elimination risks.
Each one of the above risks is assessing the level of patient's ability to perform the test with an appropriate intervention for each problem.
FRAMP has minimum intervention to be applied on ALL kinds of patients and appropriate as well and they are:
- Provision of information for the patients about the environment (Toilet, bed and ward) as well as to explain them about the call bell to facilitate their needs.
- Education of patients about mobility aids and to enable them to use it in proper way.
- Improve their awareness about the conditions that increase the risks of falls in order to prevent it.
- Improve the quality of surrounding environment to reduce the risk of falls (proper lights and remove obstacles).
Wheelchairs[edit | edit source]
Manual Wheel chair[edit | edit source]
The WHO (3) defied the manual wheel chair as: “Wheel Chair propelled by the users or pushed by another person, and it is appropriate when it meet the user needs and environmental condition”.
The manual wheel chairs reached good level of technology, at the same time some challenges to provide the PwDs are exist. According to WHO statistics 2008 (3); 10 % out of 650 million PwDs are in need for a Wheel Chair, that can reflect the huge need of the wheel chair and the access to provide it.
Why the Wheel chair is important for the PwDs?
- To avoid immobility and bed ridden.
- To prevent secondary complications.
- To involve the users in the community activities.
- To increase the opportunity for education, employment, and social interaction.
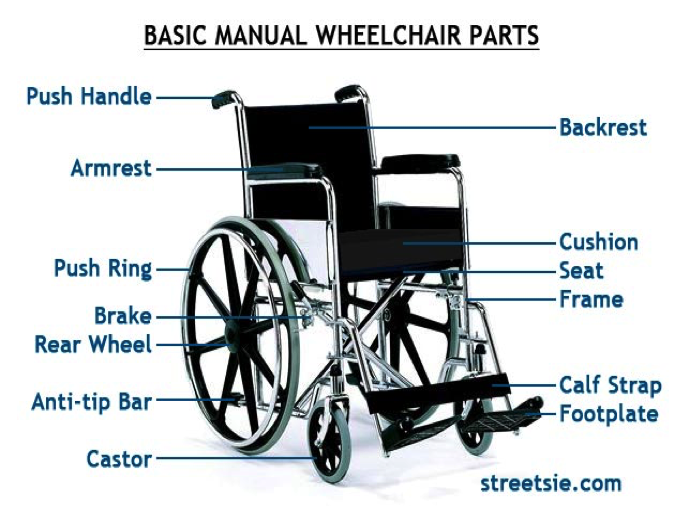
The picture below shows the main component for the wheel chair.
The PwDs have low employment rate, according to the International Labor Organization (3) (ILO) 80 % or more in the development countries are unemployed which make their living condition worse.
The majority of the PwDs are living in developing countries, so the infra-structure and living environment were not prepared to be accessible which make a physical barrier. Also they are lacking for the rehabilitation Services, which make it more difficult to raise the level of alertness, and the education in the community, as well as to involve the users to participate in the wheel chair design, or to choose the most design that matching with their physical and environmental needs.
Type of Wheel Chairs:[edit | edit source]
There are huge variation in the type of the wheel chairs, and no single wheel chair can fit all users, although considering the physical and environmental needs. The proper wheel chair is the wheel chair which can to provide a good safety and comfort that responding to the user’s physical and environmental needs to become mobile, healthy, and participate in the community.
For example a foldable wheel chair is used when the transporting activity can have space for small mass. Also a modify wheel chair with an extra support padding or cushions can be used for postural need. And the wheel chair that will be used in-door will be different from the one need to be used out door.
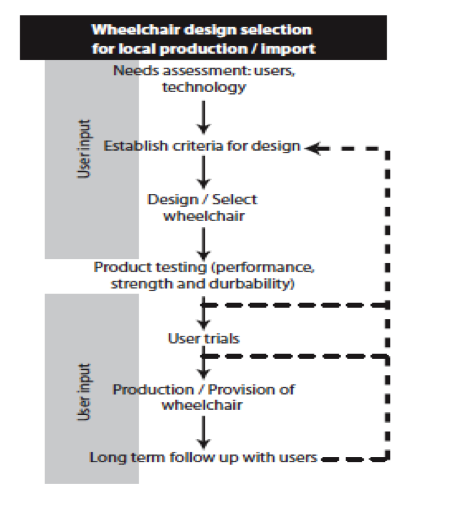
Wheel Chair Provision[edit | edit source]
According to the “Guidelines on the provision of Manual Wheel chairs in less resourced settings” (3) the wheel chair provision is depend on 4 components:
- Design.
- Production.
- Supply.
- Services and Delivery.
A proper design for wheel chair should match with the Physical and environmental needs for the users, to be able to match the stander through the production procedure, at the same time to facilitate an access for the users to have reliable supply for wheel chair and its spare parts, at the end the users have to be provided with services which include; participation in the wheel chair design, selecting, producing and training. The Diagram below can explain the wheel chair design process (4).
The design to produce a wheel chair or imported should be taken after answering the following questions:
- Do we have skilled manpower for production?
- Is the spare part and the material available?
- Is the machine and equipment for production available?
Functional Performance[edit | edit source]
What is the Functional Performance?
It is how a wheel chair perform depending on the users need, and its environment (4). So it is the performance of the wheel chair according to the different user in different Environment.
The evaluation of wheel chair design in functional performance include an evaluation for the wheel chair Static and dynamic stability, evaluating the rolling capacity and the resistance, evaluating the access for repair and spare part, and evaluating overall dimension, mass, and turning space.
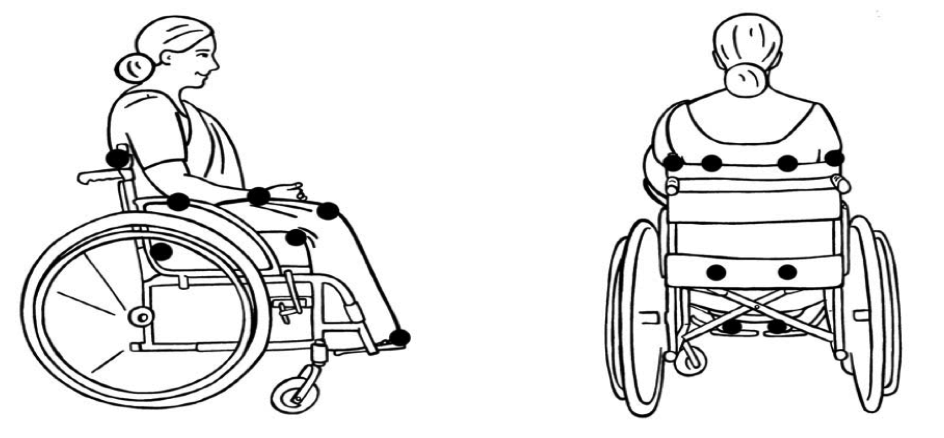
As an example for the stability evaluation: when the PwD has bilateral above knee amputation his Centre of Gravity will change so to adjust the rear wheel through moving it farther behind the center of gravity for the user.
Pressure Relief[edit | edit source]
As an early stage for the rehabilitation of amputee patients postoperatively and especially with bilateral amputees, they will need to depend on the wheel chair, therefore they will might use it for long period during the day which might put them at the risk of pressure sore if they didn’t follow the instructions and did the exercises.
So, what is the most sensitive area for the pressure sore (4)?</i>
How we can do the Pressure relief exercises (5)?
To use a proper modify wheel chair with proper cushion can help in both decreasing the risk and practicing the exercises. The most techniques used are:
o Independent push up.
o Leaning from side to side.
o Leaning forward.
Very Important: Don’t forget to instruct the patient to lock the break.
The video below can demonstrate the pressure relief exercises (6):
http://www.naric.com/?q=en/content/pressure-relief-techniques-manual-wheelchair
Manual Handling Equipment[edit | edit source]
Equipment of manual handling (7)[edit | edit source]
When it’s difficult to avoid manual handling task it’s possible to reduce the complications and risk by converting working environment or system for the patient and caregiver good.
The provision of different types of equipment will functions and personnel who are playing an important roles in keeping safer handling for both carriers and patient.
These materials and handling equipment may in usage from one person to another due to the disability, age, severity of the case and socioeconomic status. These materials such as: transferring board, wheel chair, transferring sheet, stretcher, shower and bath equipment, standing hoist, transfer belt and other equipment.
The main group of the patients moving and handling tasks are:
- Sitting, standing and walking.
- Bed mobility.
- Lateral Transfer.
- Hoisting.
Handling and safety[edit | edit source]
The handling process it’s in direct relation with other consequences that appears during time of transferring and shifting of PwDs, the carriers, nurses or the caregivers maybe affected as a result for this continues handling process and this will lead to serious injuries like: LBP, disc problems and muscles strain.
According to the Health and Safety Authorities 2011 (7), to keep the safety for both patient and the caregiver a lot of issues should be under consideration:
- The surrounding environment, ergonomic and workplace design should match the needs for both, to decrease the incidence of injuries that usually results.
- Provision of appropriate manual handling equipment, the patient’s situation and degree of disability are determining the kind of equipment that it will be in the handling process.
- Qualified staff and trainees that assisting in the process of shifting and transferring techniques will increase better result achievement.
- Management committee to safer manual handling in the workplace: staff must follow the guidance that maintaining safer manual handling.
Early walking Aid (EWA)[edit | edit source]
The early working aid (EWA) is a temporary socket mainly made of inflatable bag, supported by metallic frame with padded safely rings and prosthetic or rocker foot (8).
The EWA has been used to help in the patient assessment and to start the treatment. One of the most important objective of the EWA is to help the patient to be ambulated in upright posture as early as the wound condition get stable which will reflect on the patient psychological status. Also the EWA can accelerate the rehabilitation process through starting the gait training and facilitate the prosthesis fitting.
The EWA help to improve the balance, the posture, and the sensory integration. The provided pressure from the air bag is playing a big role in controlling the oedema, and decreasing the pain.
• Types of EWA (9) :
- Pneumatic using air bag.
- Vacuum Technique as LIC Tulip.
- Preformed Plastic Socket as LIC Femorett, LIC LEMA, and Hexilite temporary patellar tendon Weight bearing.
- Local Variations.
plastic socket EVA pneumatic using airbag
• Application of EWA (8,9,10):
According to (Enstgrom and Van de Ven 1999) (10); the training with Pneumatic EWA can start 7 to 10 days postoperatively, with gradual increasing of the pressure and considering the wound condition.
Special consideration during the application:
- Usually starting the air inflation with 15 to 25 mmHg.
- Gradual increase of the pressure and it should not be inflated with air more than 40 mmHg.
- The patients’ attitude to amputation, stability, recovery, and comfort to adapt the pressure.
- Continue inspection and observation of the wound is needed.
- Weight bearing should be restricted to the physician order.
Prostheses:[edit | edit source]
The prostheses prescription, type, component and production are passing through multidisciplinary team without forgetting to involve the patient according to specific factors. It had been explained in details at the Prostheses section of this course: http://www.physio-pedia.com/Prosthetics.
Walking Aids[edit | edit source]
The patient with Amputation will use a walking aid, either temporary or permeant to restore the functional ambulation and independency. The choice is depending on the level of fitness, strength, balance skills, and risk of falls. As well as the walking aid will help to control the allowed weight bearing on the injured leg, compensate the lack of balance, and decrease the risk of fall.
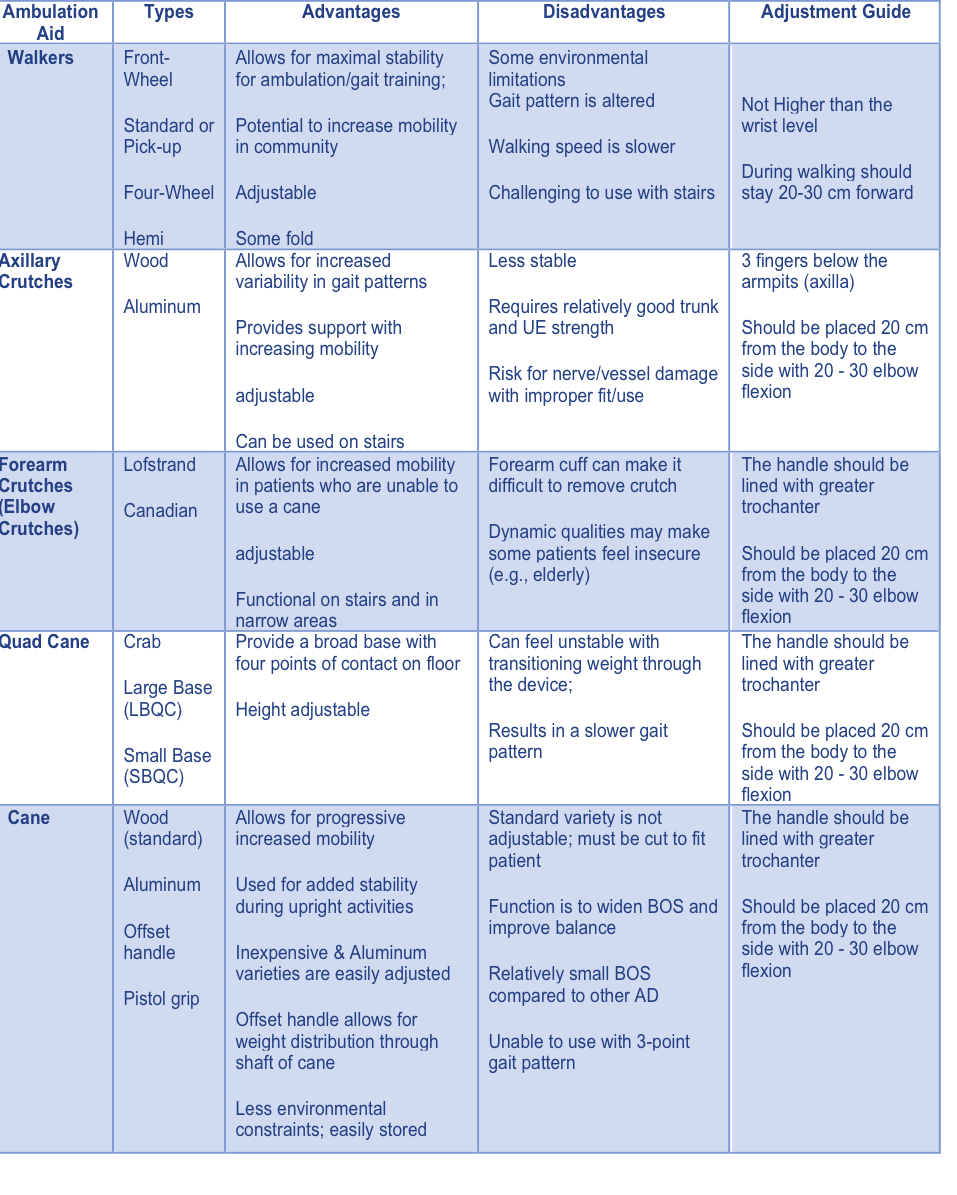
Named, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Adjustment[edit | edit source]
Watch the video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=inH0rdkTWTI explaining how to choose, use some assistive devices.
The table below is explaining the different type of walking aids, the advantages, the disadvantages and the adjustment guide (11, 12).
Special Consideration on walking Aids[edit | edit source]
Our long term goal with amputee patients it to reach maximum functional independency without walking aids, a special consideration should be taken such as (12, 13):
- Some patients can’t achieve this goal due to the age or other medical problem.
- The ambulation using a walker is not a must step to shift the patient from parallel bar to crutches or cane if the physical and medical condition allows.
- Usually using a single walking aid should be handled at the sound side, and it can be used at the Amputee side if the goal is to shift more weight to this side.
- The role to ascend and descend the stair is to ascend with sound leg, and descend with the amputee side (Up good, and down pad).
- A proper selection of a walking aid with proper adjustment will speed up the rehabilitation process and improve the quality of the outcomes.
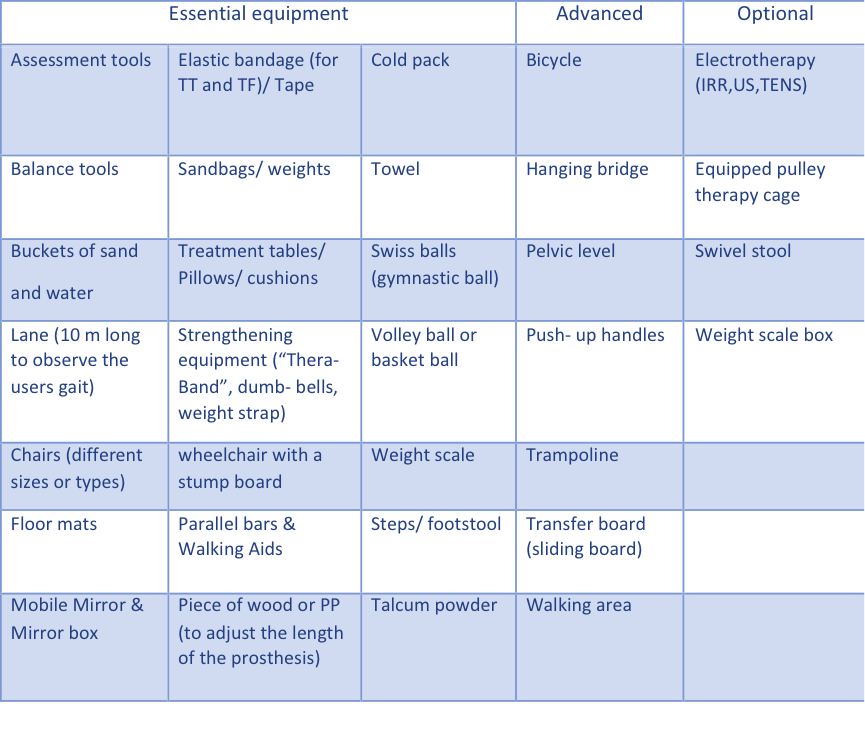
Other Equipment’s for Physiotherapy Units[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapy unit must be supplied by many essential equipment and materials which are important in the implementation of the treatment plan of the physiotherapy and prosthetic/orthotics as well. These materials are necessary before and after the prosthetic rehabilitation as well as in advanced gait training level.
The materials and equipment itself are classified into three different categories (14):
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.