Flexor Digitorum Brevis: Difference between revisions
Oyemi Sillo (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Oyemi Sillo (talk | contribs) m (fixed the references) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User: | '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Oyemi Sillo|Oyemi Sillo]] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
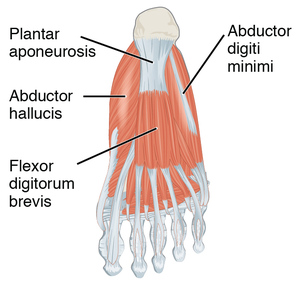
Flexor Digitorum Brevis is the central muscle of the superficial layer of the plantar foot muscles.<ref>Jenkins, D. B. | Flexor Digitorum Brevis is the central muscle of the superficial layer of the plantar foot muscles.<ref>Jenkins, D. B. Hollinshead's functional anatomy of the limbs and back. St. Louis, Mo: Saunders/Elsevier. 2009.</ref> It lies in the middle of the sole, immediately superior to the plantar aponeurosis and inferior to the tendon of Flexor Digitorum Longus.<ref name=":0">Drake, R. L., Vogl, W., Mitchell, A. W. M., Gray, H., & Gray, H. Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. 2010.</ref> | ||
[[File:1124 Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot b.png|thumb]] | [[File:1124 Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot b.png|thumb]] | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
The Flexor Digitorum Brevis muscle originates from the medial process of calcaneal tuberosity and the central part of the plantar aponeurosis.<ref name=":1">Logan, B. M., & Hutchings, R. T. | The Flexor Digitorum Brevis muscle originates from the medial process of calcaneal tuberosity and the central part of the plantar aponeurosis.<ref name=":1">Logan, B. M., & Hutchings, R. T. McMinn's Color Atlas of Foot and Ankle Anatomy E-Book''. 2011.''</ref> | ||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
Flexor Digitorum Brevis is supplied by the medial plantar nerve (S1 & S2), which is a terminal branch of the tibial nerve.<ref name=":2">Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. | Flexor Digitorum Brevis is supplied by the medial plantar nerve (S1 & S2), which is a terminal branch of the tibial nerve.<ref name=":2">Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. Clinically oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health. 2014.</ref> | ||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Muscles]] | [[Category:Muscles]] | ||
[[Category:Foot]] | |||
[[Category:Foot - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Foot - Muscles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:21, 30 November 2020
Original Editor - Oyemi Sillo
Top Contributors - Oyemi Sillo
Description[edit | edit source]
Flexor Digitorum Brevis is the central muscle of the superficial layer of the plantar foot muscles.[1] It lies in the middle of the sole, immediately superior to the plantar aponeurosis and inferior to the tendon of Flexor Digitorum Longus.[2]
Origin[edit | edit source]
The Flexor Digitorum Brevis muscle originates from the medial process of calcaneal tuberosity and the central part of the plantar aponeurosis.[3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
It inserts on the middle phalanges of the lateral four toes by a tendon to each toe.[3]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Flexor Digitorum Brevis is supplied by the medial plantar nerve (S1 & S2), which is a terminal branch of the tibial nerve.[4]
Artery[edit | edit source]
The Flexor Digitorum Brevis is supplied by the medial and lateral plantar arteries.[3]
Function[edit | edit source]
Flexor Digitorum Brevis plantarflexes the four lateral toes at the proximal interphalangeal joint.[2]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
As an intrinsic muscle of the foot, the Flexor Digitorum Brevis plays an important role in stabilising the longitudinal arch of the foot.[4]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Jenkins, D. B. Hollinshead's functional anatomy of the limbs and back. St. Louis, Mo: Saunders/Elsevier. 2009.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Drake, R. L., Vogl, W., Mitchell, A. W. M., Gray, H., & Gray, H. Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. 2010.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Logan, B. M., & Hutchings, R. T. McMinn's Color Atlas of Foot and Ankle Anatomy E-Book. 2011.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. Clinically oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health. 2014.