Machado-Joseph Disease (Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3): Difference between revisions
Kyle Seagram (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Casey Goheen (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
= Clinical Presentation<br> = | = Clinical Presentation<br> = | ||
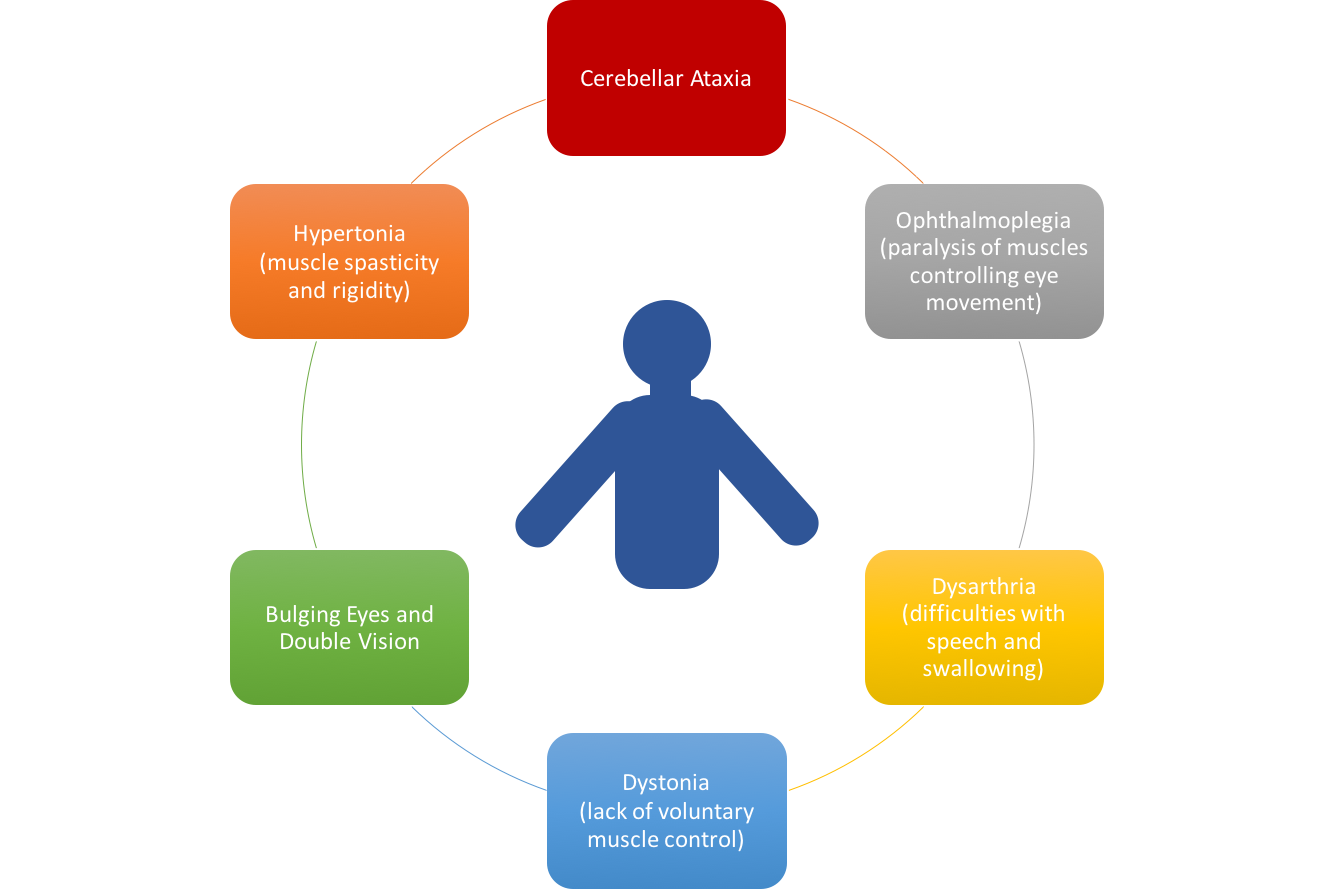
[[Image:Man.png]] | |||
= Diagnostic Procedures<br> = | = Diagnostic Procedures<br> = | ||
Revision as of 02:47, 8 May 2017
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process
[edit | edit source]
Clinical Presentation
[edit | edit source]
Diagnostic Procedures
[edit | edit source]
Genetic testing revealing CAG repeats are indicative of MJD diagnosis (1). The number of these repeats correlates with severity of the disease; increasing number of repeats corresponds with increased reflexes and mortality rate, and vise versa with decreased number of repeats (2). Type 3 MJD is specifically characterized by fasciculations (3). Health care practitioners must be cautious to rule out amyotrophic lateral sclerolsis (ALS), as the involvement of motor neurons causes the two conditions to present similarly (1).
Upon autopsy, the following findings may be present; encephalon of decreased mass, pale-coloured substantia nigra, atrophied cerebellum, medulla oblongata and pons, as well as a decreased number of neuron bodies in the dentate nucleus, substantia nigra and anterior horn of the spinal cord (1).
Outcome Measures
[edit | edit source]
In order to assess the severity of MJD several scales specific to ataxia can be used. The International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (CARS) and Scale for the Assessment of Rating of Ataxia (SARA) have been shown to be both reliable and effective when used with MJD. (Zhou et al, 2011).
Common assessment measures that are not specific to MJD but may be useful outcome measures for core symptoms include:
- Berg Balance Scale (BBS),
- Romberg Test
- Ashworth Scale
- Tardieu Scale/Modified Tardieu Scale
- Functional Independence Measure (FIM)
- 6 Minute Walk Test
- Time Up and Go (TUG)
- Psychological General Well-being (PGWB) Index
Management / Interventions
[edit | edit source]
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
The clinical presentation of MJD can often appear like other neurodegenerative diseases that affect movement, the most common differential diagnoses are:
Key Evidence
[edit | edit source]
Resources
[edit | edit source]
Case Studies
[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research
[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]