Recognition of Stroke in the Emergency Room (ROSIER) Scale: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "<div class="noeditbox">This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! ({{REVISIONDAY}}/{{REVISIONMONTH}}/{{REVISIONYEAR}})</div>") |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | |||
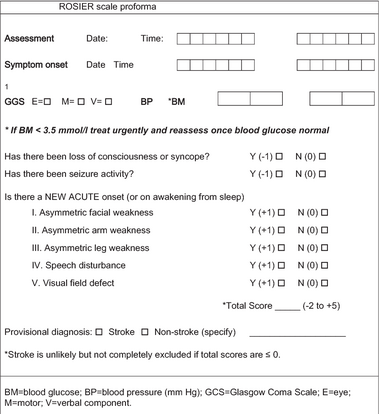
[[File:3-Figure1-1.png|thumb|414x414px|ROSIER scale]] | |||
ROSIER scale is used as a part of stroke early assessment (pre-hospital, emergency or acute stroke units) to help health care professionals diagnose stroke from its mimics in which presentation resembles or may even be indistinguishable from ischemic stroke. It consists of seven yes or no questions. | |||
== Pre - scale data items == | |||
* Assessment date and time. | |||
* Symptoms onset (record date and time). | |||
* Glasgow coma scale (record the 3 sub scores). | |||
* Blood pressure. | |||
* Blood Glucose level (if less than 3.5 mmol/l, treat urgently and reassess). | |||
== Scale categories == | |||
# Loss of consciousness or syncope (score -1 for Yes, zero for No). | |||
# Seizure activity (score -1 for Yes, zero for No). | |||
# Facial weakness asymmetry (score +1 for Yes, zero for No). | |||
# Arm weakness asymmetry (score +1 for Yes, zero for No). | |||
# Leg weakness asymmetry (score +1 for Yes, zero for No). | |||
# Speech disturbance (score +1 for Yes, zero for No). | |||
# Visual field defects (score +1 for Yes, zero for No). | |||
== Results == | |||
Total score ranges from -2 to +5. | |||
If > 0, stroke diagnosis is likely but keep nil orally until water swallow test is applied. | |||
If < 0, stroke diagnosis is not excluded but further medical discussion is needed. | |||
== Validity == | |||
ROSIER is a sensitive tool for stroke provisional diagnosis<ref>Han F, Zuo C, Zheng G. [https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-020-01841-x A systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of recognition of stroke in the emergency department (ROSIER) scale.] BMC Neurology [Internet]. 2020 Aug 18;20(1). Available from: <nowiki>https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-020-01841-x</nowiki></ref>. However, the ROSIER solely cannot be used to confidently rule out or identify stroke as a diagnosis. The comprehensive clinical assessment and further examination or imaging for potential stroke patients are still irreplaceable. <ref>Zhixin W, Lianda L, Jinfang F, Mingfeng H, Qihong G, Yanbin Y. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3424796/ Validation of the use of the ROSIER scale in prehospital assessment of stroke.] Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology [Internet]. 2012;15(3):191. Available from: <nowiki>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3424796/</nowiki></ref> | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:14, 16 February 2024
Introduction[edit | edit source]
ROSIER scale is used as a part of stroke early assessment (pre-hospital, emergency or acute stroke units) to help health care professionals diagnose stroke from its mimics in which presentation resembles or may even be indistinguishable from ischemic stroke. It consists of seven yes or no questions.
Pre - scale data items[edit | edit source]
- Assessment date and time.
- Symptoms onset (record date and time).
- Glasgow coma scale (record the 3 sub scores).
- Blood pressure.
- Blood Glucose level (if less than 3.5 mmol/l, treat urgently and reassess).
Scale categories[edit | edit source]
- Loss of consciousness or syncope (score -1 for Yes, zero for No).
- Seizure activity (score -1 for Yes, zero for No).
- Facial weakness asymmetry (score +1 for Yes, zero for No).
- Arm weakness asymmetry (score +1 for Yes, zero for No).
- Leg weakness asymmetry (score +1 for Yes, zero for No).
- Speech disturbance (score +1 for Yes, zero for No).
- Visual field defects (score +1 for Yes, zero for No).
Results[edit | edit source]
Total score ranges from -2 to +5.
If > 0, stroke diagnosis is likely but keep nil orally until water swallow test is applied.
If < 0, stroke diagnosis is not excluded but further medical discussion is needed.
Validity[edit | edit source]
ROSIER is a sensitive tool for stroke provisional diagnosis[1]. However, the ROSIER solely cannot be used to confidently rule out or identify stroke as a diagnosis. The comprehensive clinical assessment and further examination or imaging for potential stroke patients are still irreplaceable. [2]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Han F, Zuo C, Zheng G. A systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of recognition of stroke in the emergency department (ROSIER) scale. BMC Neurology [Internet]. 2020 Aug 18;20(1). Available from: https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-020-01841-x
- ↑ Zhixin W, Lianda L, Jinfang F, Mingfeng H, Qihong G, Yanbin Y. Validation of the use of the ROSIER scale in prehospital assessment of stroke. Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology [Internet]. 2012;15(3):191. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3424796/