Sacroiliac Joint: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
There is limited movement of the SI joint.<br> | There is limited movement of the SI joint.<br> | ||
<u>Nutation and Counternutation</u> - Nutation occurs as the sacrum moves anteriorly and inferiorly while the coccyx moves posteriorly relative to the ilium. | |||
== Ligaments & Joint Capsule<br> == | == Ligaments & Joint Capsule<br> == | ||
Revision as of 00:05, 3 June 2009
Original Editor - Kathleen Nestor and Katie Sheidler
Lead Editors - Your name will be added here if you are a lead editor on this page. Read more.
Description[edit | edit source]
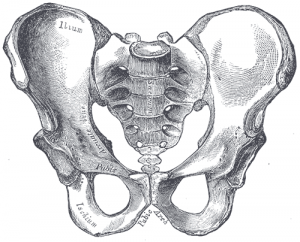
The sacroiliac joint (simply called the SI joint) is the joint connection between the spine and the pelvis. It is a large diathrodial joint made up of the sacrum and the two innominates of the pelvis. Each innominate is formed by the fusion of the three bones of the pelvis: the ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. [1]
Motions Available[edit | edit source]
There is limited movement of the SI joint.
Nutation and Counternutation - Nutation occurs as the sacrum moves anteriorly and inferiorly while the coccyx moves posteriorly relative to the ilium.
Ligaments & Joint Capsule
[edit | edit source]
Muscles[edit | edit source]
There are 35 muscles that attach to the sacrum or innominates which mainly provide stability to the joint rather than producing movements.
Muscles that attach to the sacrum or innominates:
- Adductor brevis
- Adductor longus
- Adductor magnus
- Biceps femoris - long head
- Coccygeus
- Erector spinae
- External oblique
- Gluteus maxiumus
- Gluteus medius
- Gluteus minimus
- Gracilis
- Iliacus
- Inferior gemellus
- Internal oblique
- Latissimus dorsi
- Levator ani
- Multifidus
- Obturator internus
- Obturator externus
- Pectineus
- Piriformis
- Psoas minor
- Pyramidalis
- Quadratus femoris
- Quadratus lumborum
- Rectus abdominis
- Rectus femoris
- Sartorius
- Semimembranosus
- Semitendonosus
- Sphincter urethrae
- Superficial transverse perineal ischiocavernous
- Superior gemellus
- Tensor fascia lata
- Transversus abdominus
Specific Pathologies[edit | edit source]
There are many pathologies that could present at the site of the sacroiliac joint including:
- sacroiliac tuberculosis
- spondyloarthropathy
- crystal and pyogenic arthropathies
- groin pain
- osteitis pubis
- symphysis pubic dysfunction
- osteoarthritis
- stress fracture
Special Tests[edit | edit source]
SI Joint stress tests
- Anterior Gapping test
- Posterior Distraction test
- Pubic Stress test
- Sacrotuberous Ligament Stress test
- Sacral Compression test (POSH test)
- Rotational Stress test
Leg Length tests
- Prone test
- Standing leg length test
- Functional leg length test
Other Special Tests
- Seated Flexion test (Piedallu's Sign)
- Long Sit test
- Sign of the Buttock
- Posterior Pelvic Pain Provocation test
- Gaenslen's test
- Yeoman's test
- FABER (Figure-Four) test
Other Important Information[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ Dutton M. Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw Hill, 2008.