The influence of antidepressant medication on physiologic processes and exercise: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
= Exercise Effects = | = Exercise Effects = | ||
The effects of antidepressants on individuals with high or low aerobic capacity can be assessed to evaluate the time to fatigue. Research was performed on paroxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, to determine its relationship to fatigue. Fatigue can be caused by a higher ratio of serotonin to dopamine in the brain, producing lethargy and lack of motivation. A dosage of 20 milligrams of paroxetine caused a decrease in total time of exercise until fatigue and performance in the individuals with higher aerobic capacity, which makes these individuals more responsive to the activation of serotonin than the low aerobic capacity group.<sup>1 </sup>Therefore, antidepressant medication | The effects of antidepressants on individuals with high or low aerobic capacity can be assessed to evaluate the time to fatigue. Research was performed on paroxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, to determine its relationship to fatigue. Fatigue can be caused by a higher ratio of serotonin to dopamine in the brain, producing lethargy and lack of motivation. A specific dosage of 20 milligrams of paroxetine caused a decrease in total time of exercise until fatigue and performance in the individuals with higher aerobic capacity, which makes these individuals more responsive to the activation of serotonin than the low aerobic capacity group.<sup>1 </sup>Therefore, antidepressant medication may be able to influence time to fatigue and exercise performance in individuals with high aerobic capacity. However, because of the variability of outcomes with dosage amounts, more reseach needs to be done before results can be accepted as conclusive. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
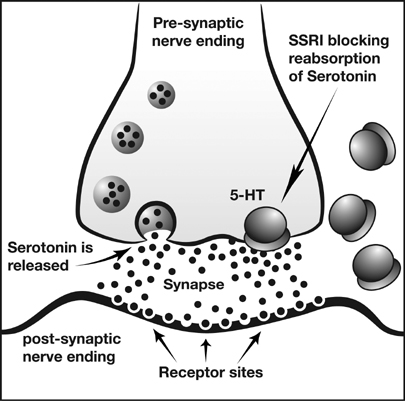
Antidepressants can have effects on the functional outcomes and the recovery process. The effects are dependent on the type of anitdepressant consumed. Research has compared the effects of fluoxetine and maprotiline used with and without rehabilitation therapy on individuals who have experience a stroke to evaluate the effectiveness of the antidepressant medications. Fluoxetine, a drug that inhibits the reuptake of serotonin, increased good outcomes during the recovery process; whereas maprotiline, a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, caused the least amount of improvements.<sup>2</sup><sup> </sup><sup></sup><sup></sup>While both medications lowered depression, only fluoxetine combined with rehabilitation therapy was more beneficial than rehabilitation alone. Maprotiline was less beneficial, which could have been due to its hinderance of recovery. Long-term treatment of fluoxetine could increase the spread of serotonin by blocking 5-HT sites to cause an increase in motor function and recovery.<sup>3 </sup>Serotonergic antidepressants combined with rehabilitation therapy could assist in the recovery process and lead to better outcomes. | Antidepressants can have effects on the functional outcomes and the recovery process. The effects are dependent on the type of anitdepressant consumed. Research has compared the effects of fluoxetine and maprotiline used with and without rehabilitation therapy on individuals who have experience a stroke to evaluate the effectiveness of the antidepressant medications. Fluoxetine, a drug that inhibits the reuptake of serotonin, increased good outcomes during the recovery process; whereas maprotiline, a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, caused the least amount of improvements.<sup>2</sup><sup> </sup><sup></sup><sup></sup>While both medications lowered depression, only fluoxetine combined with rehabilitation therapy was more beneficial than rehabilitation alone. Maprotiline was less beneficial, which could have been due to its hinderance of recovery. Long-term treatment of fluoxetine could increase the spread of serotonin by blocking 5-HT sites to cause an increase in motor function and recovery.<sup>3 </sup>Serotonergic antidepressants combined with rehabilitation therapy could assist in the recovery process and lead to better outcomes. | ||
<br> | |||
[[Image:Serotonin synapse.jpg]] | [[Image:Serotonin synapse.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 04:09, 11 November 2015
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Antidepressants are used to treat, relieve, and prevent psychic depression. When used with exercise, different physiologic responses can occur.
Exercise Effects[edit | edit source]
The effects of antidepressants on individuals with high or low aerobic capacity can be assessed to evaluate the time to fatigue. Research was performed on paroxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, to determine its relationship to fatigue. Fatigue can be caused by a higher ratio of serotonin to dopamine in the brain, producing lethargy and lack of motivation. A specific dosage of 20 milligrams of paroxetine caused a decrease in total time of exercise until fatigue and performance in the individuals with higher aerobic capacity, which makes these individuals more responsive to the activation of serotonin than the low aerobic capacity group.1 Therefore, antidepressant medication may be able to influence time to fatigue and exercise performance in individuals with high aerobic capacity. However, because of the variability of outcomes with dosage amounts, more reseach needs to be done before results can be accepted as conclusive.
Antidepressants can have effects on the functional outcomes and the recovery process. The effects are dependent on the type of anitdepressant consumed. Research has compared the effects of fluoxetine and maprotiline used with and without rehabilitation therapy on individuals who have experience a stroke to evaluate the effectiveness of the antidepressant medications. Fluoxetine, a drug that inhibits the reuptake of serotonin, increased good outcomes during the recovery process; whereas maprotiline, a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, caused the least amount of improvements.2 While both medications lowered depression, only fluoxetine combined with rehabilitation therapy was more beneficial than rehabilitation alone. Maprotiline was less beneficial, which could have been due to its hinderance of recovery. Long-term treatment of fluoxetine could increase the spread of serotonin by blocking 5-HT sites to cause an increase in motor function and recovery.3 Serotonergic antidepressants combined with rehabilitation therapy could assist in the recovery process and lead to better outcomes.
Cardiovascular System
[edit | edit source]
Pulmonary System[edit | edit source]
Metabolic System[edit | edit source]
Neurological Effects[edit | edit source]
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
1. Teixeira-Coelho, F., Uendeles-Pinto, J., Serafim, A., Wanner, S., Coelho, M., & Soares, D. (2014). The paroxetine effect on exercise performance depends on the aerobic capacity of exercising individuals. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 13, 232-243.
2. Dam, M., Tonin, P., De Boni, A., Pizzolato, G., Casson, S., Ermani, M., . . . Battistin, L. (1996). Effects of fluoxetine and maprotiline on functional recovery in postroke hemiplegic patients under rehabilitation therapy. Stroke, 27(7), 1211-1214. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.27.7.1211
3. Dam, M., Tonin, P., De Boni, A., Pizzolato, G., Casson, S., Ermani, M., . . . Battistin, L. (1996). Effects of fluoxetine and maprotiline on functional recovery in postroke hemiplegic patients under rehabilitation therapy. Stroke, 27(7), 1211-1214. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.27.7.1211