Tibialis Posterior: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:User Name|Michelle Lee]] '''Top Contributors''' - [[User:User Name|Jenny Lim]] </div> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:User Name|Michelle Lee]] '''Top Contributors''' - [[User:User Name|Jenny Lim]] </div> | ||
[[File:Tibialis-posterior-location.jpg|right|frameless|626x626px]] | |||
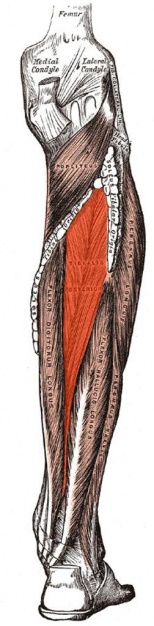
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
Tibialis Posterior Rupture | [[Tibialis Posterior Rupture]] | ||
Shin Splints | [[Shin Splints]] | ||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
Revision as of 12:10, 25 June 2018
Description[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Proximal postero-lateral aspect of the tibia.
Proximal postero-medial aspect of the fibula and the interosseous membrane
Mid portion: Situated in the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg and runs proximal to the medial malleoli where it is secured by the flexor retinaculum.
Insertion[edit | edit source]
The major insertion is onto the navicula and the plantar slip attatches to the medial cuniform
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Tibial Nerve (L4-S3)
Artery[edit | edit source]
Tibial Artery
Function[edit | edit source]
To plantarflex and invert the ankle. It also plays an important role in stabilising the medial longitudinal arch.