Tibialis Posterior: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
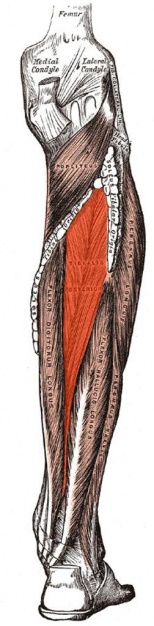
The '''Tibialis Posterior''' is located in the deep compartment of the lower leg, and is a key stabilising muscle, supporting the medial arch of the foot. | |||
=== Origin <ref name=":0">Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. Gray's Anatomy for Students. 2nd Ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, 2010.</ref> === | === Origin <ref name=":0">Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. Gray's Anatomy for Students. 2nd Ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, 2010.</ref> === | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
To plantarflex and invert the ankle. It also plays an important role in stabilising the medial longitudinal arch. | To plantarflex and invert the ankle. It also plays an important role in stabilising the medial longitudinal arch. Tibialis posterior dysfunction can lead to flat feet in adults. | ||
|{{#ev:youtube|9N_eR8Pojuw|400}} <ref>nabil ebraheim. Anatomy Of The Tibialis Posterior Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9N_eR8Pojuw [last accessed: 25/6/18]</ref> | |{{#ev:youtube|9N_eR8Pojuw|400}} <ref>nabil ebraheim. Anatomy Of The Tibialis Posterior Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9N_eR8Pojuw [last accessed: 25/6/18]</ref> | ||
Revision as of 12:57, 25 June 2018
Description[edit | edit source]
The Tibialis Posterior is located in the deep compartment of the lower leg, and is a key stabilising muscle, supporting the medial arch of the foot.
Origin [1][edit | edit source]
Proximal postero-lateral aspect of the tibia.
Proximal postero-medial aspect of the fibula and the interosseous membrane
Mid portion: Situated in the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg and runs proximal to the medial malleoli where it is secured by the flexor retinaculum.
Insertion[1][edit | edit source]
The major insertion is onto the navicula and the plantar slip attatches to the medial cuniform
Nerve[1][edit | edit source]
Tibial Nerve (L4-S3)
Artery[1][edit | edit source]
Tibial Artery
Function[edit | edit source]
To plantarflex and invert the ankle. It also plays an important role in stabilising the medial longitudinal arch. Tibialis posterior dysfunction can lead to flat feet in adults.
|
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Resisted Muscle Test:
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Strengthening exercises for Tibialis Posterior:
| [5]Resources[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. Gray's Anatomy for Students. 2nd Ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, 2010.
- ↑ nabil ebraheim. Anatomy Of The Tibialis Posterior Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9N_eR8Pojuw [last accessed: 25/6/18]
- ↑ Sheena Livingstone. Tibialis Posterior Muscle Test. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7cEJD-9aBTk [last accessed 25/6/18]
- ↑ PolkStatePTA. Tibialis Posterior. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f-vVv59NNBI [last accessed 25/6/18]
- ↑ Physiotutors. Tibialis Posterior Strengthening | Flat Feet Exercise. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XBvfk3zwiiE [last accessed: 25/6/18]