Valgus Knee: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
[[File:Normal vs valgus knew.png| | [[File:Normal vs valgus knew.png|alt=|right|frameless]] | ||
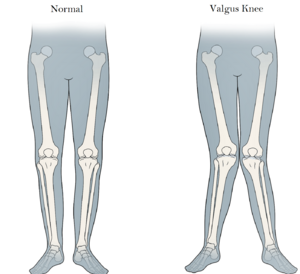
Valgus knee or '''knock knee''' is a lower leg deformity that exists when the bone at the knee joint is angled out and away from the body's midline. This deformity is defined as a valgus angle equal to or greater than 10°<ref>Long WJ, Scuderi GRVarus and Valgus Deformities. In: Lotke PA, Lonner JH, eds. ''Knee Arthroplasty, Masters Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery.'' 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009:111–125</ref> | Valgus knee or '''knock knee''' is a lower leg deformity that exists when the bone at the knee joint is angled out and away from the body's midline. This deformity is defined as a valgus angle equal to or greater than 10°<ref>Long WJ, Scuderi GRVarus and Valgus Deformities. In: Lotke PA, Lonner JH, eds. ''Knee Arthroplasty, Masters Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery.'' 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009:111–125</ref> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
* '''The medial side''', the soft tissue are '''attenuated''', the medial collateral ligament (MCL) . | * '''The medial side''', the soft tissue are '''attenuated''', the medial collateral ligament (MCL) . | ||
== | == Classification: == | ||
There is a lot of number of classification for the knee deformaty that depend on the severiry of deformation and the soft tissue involeved. But the most recent one descibes three grades of valgus deformity<ref>Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, Rasquinha VJ, Rossi R, Babhulkar S. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(Suppl 1(Pt 2)):271–284</ref>: | |||
* Grade I: the deviation is less than 10°, passively correctable, with contracture of the lateral soft tissue but without elongation of the medial collateral ligament. | |||
* Grade II: the axial deviation ranges between 10 and 20°, the lateral structures are contracted and the MCL is elongated but functional. | |||
* Grade III deformity is present in the remaining 5 % of the patients; the axial deformity is greater than 20°, the lateral structures are tight and the medial stabilisers are not functional. | |||
== Sub Heading 3 == | == Sub Heading 3 == | ||
Revision as of 16:08, 25 April 2022
Original Editor - Yesmine Gouddi
Top Contributors - Yesmine Gouddi and Sehriban Ozmen
Definition[edit | edit source]
Valgus knee or knock knee is a lower leg deformity that exists when the bone at the knee joint is angled out and away from the body's midline. This deformity is defined as a valgus angle equal to or greater than 10°[1]
The valgus deformity is resulted of anatomical variations : bone tissue remodelling and soft tissue contraction/elongation.
Bone tissue remodelling:
- Lateral femoral condyle deficiency with external rotation deformity of the tibia and lateral tibial plateau deficiency as well.
- The patellofemoral joint can be affected with lateral subluxation of the patella and trochlear blunting secondary to lateral femoral condylar wear.
Soft tissue contraction/elongation:
- The lateral side is contracted including the lateral collateral ligament (LCL), popliteus tendon, posterolateral capsule, iliotibial band (IT band), and posterior capsule.
- The medial side, the soft tissue are attenuated, the medial collateral ligament (MCL) .
Classification:[edit | edit source]
There is a lot of number of classification for the knee deformaty that depend on the severiry of deformation and the soft tissue involeved. But the most recent one descibes three grades of valgus deformity[2]:
- Grade I: the deviation is less than 10°, passively correctable, with contracture of the lateral soft tissue but without elongation of the medial collateral ligament.
- Grade II: the axial deviation ranges between 10 and 20°, the lateral structures are contracted and the MCL is elongated but functional.
- Grade III deformity is present in the remaining 5 % of the patients; the axial deformity is greater than 20°, the lateral structures are tight and the medial stabilisers are not functional.
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Long WJ, Scuderi GRVarus and Valgus Deformities. In: Lotke PA, Lonner JH, eds. Knee Arthroplasty, Masters Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009:111–125
- ↑ Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, Rasquinha VJ, Rossi R, Babhulkar S. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(Suppl 1(Pt 2)):271–284