Gracilis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
In women, the muscular volume of the medial vastus is greater than in men, while the volume of the gracilis muscle (and the sartorius muscle) is smaller. This predisposes females to [[Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction|ACL injury]] compared to males.<ref name=":2" /> | In women, the muscular volume of the medial vastus is greater than in men, while the volume of the gracilis muscle (and the sartorius muscle) is smaller. This predisposes females to [[Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction|ACL injury]] compared to males.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
= | |||
Surgeons may use the gracilis tendon in reconstruction surgery of the ACL<ref name=":2" /> | |||
[[Pes Anserinus Bursitis|Pes anserine bursitis]] there should be a high suspicion of pes anserine bursitis, especially if there is edema present. Pes anserine bursitis is commonly seen in patients who have obese, have osteoarthritis, and female. | |||
== Assessment and Treatment == | |||
See adductor tendinopathy Groin Injuries | |||
{{#ev:youtube|DVfJW72bEAE}} | {{#ev:youtube|DVfJW72bEAE}} | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
See | |||
Injury or surgery to the gracilis can be rehabilitated through a standard progression of isometrics -> isotonics -> tendon loading to improve strength during functional activities. | Injury or surgery to the gracilis can be rehabilitated through a standard progression of isometrics -> isotonics -> tendon loading to improve strength during functional activities. | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 19 January 2022
Original Editor - Eric Henderson
Top Contributors - Eric Henderson, Lucinda hampton, Candace Goh, Joao Costa and Vidya Acharya
Introduction[edit | edit source]
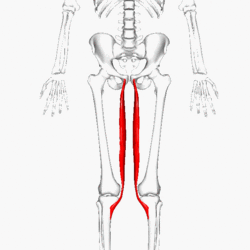
The gracilis is a spiral unipennate muscle in the medial thigh compartment.
The gracilis:
- Assists with hip adduction, knee flexion, and knee internal rotation.
- It is innervated by the anterior branch of the obturator nerve.
- Crosses at both the hip and knee joints.
- The gracilis may is prone to strain injuries, resulting in adductor tendinopathyeg common in soccer, hockey, football, and basketball athletes[1].
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin
The gracilis muscle originates from the inferior ischiopubic ramus, and body of pubis.[2]
Insertion
The gracilis muscle decends almost vertically down the leg and inserts on the medial tibia at the Pes anserinus.[2] The pes anserinus is also the attachment site of the Sartorius and Semitendinosus. The muscles attached here can be remembered by the acronym sargent or "SGT" for Sartorius Gracilis semiTendinosus.
Nerve
The gracilis muscles is innervated by the anterior branch of the obturator nerve (L2-L4). The anterior branch of the obturator nerve also innervates the adductor longus, and sometimes adductor brevis.[2]
There are 5 to 7 muscle fiber bundle compartments in the gracilis muscle, with nerve branches coursing along each compartment, indicating possible independent neuromuscular compartment functioning.[1]
Artery
The gracilis muscle receives blood supply from the medial circumflex femoral artery.[2]
Function[edit | edit source]
Due to it's attachment on the tibia, the gracilis flexes the knee, adducts the thigh, and medially rotate the tibia on the femur.[3]
Physiotherapy Relevance[edit | edit source]
Groin strain/adductor tendinopathy commonly occur in high impact sports that involve ballistic movements or stretching eg soccer, hockey, baseball. Tearing of the muscles usually occur at proximal region near bony attachments at the pelvis[4]
In women, the muscular volume of the medial vastus is greater than in men, while the volume of the gracilis muscle (and the sartorius muscle) is smaller. This predisposes females to ACL injury compared to males.[1]
Surgeons may use the gracilis tendon in reconstruction surgery of the ACL[1]
Pes anserine bursitis there should be a high suspicion of pes anserine bursitis, especially if there is edema present. Pes anserine bursitis is commonly seen in patients who have obese, have osteoarthritis, and female.
Assessment and Treatment[edit | edit source]
See adductor tendinopathy Groin Injuries
Treatment[edit | edit source]
See
Injury or surgery to the gracilis can be rehabilitated through a standard progression of isometrics -> isotonics -> tendon loading to improve strength during functional activities.
Resources[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Bordoni B, Varacallo M. Anatomy, bony pelvis and lower limb, thigh quadriceps muscle. Available:https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/22380 (accessed 19.1.2022)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Human anatomy & physiology. 10th ed. Boston, Ma: Pearson; 2016.
- ↑ Gracilis. Available from: https://rad.washington.edu/muscle-atlas/gracilis/ (accessed 15 May 2018).
- ↑ Teach Me Anatomy. Muscles in the Medial Compartment of the Thigh. Available from: https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/muscles/thigh/medial-compartment/ (Accessed on 19 May 2020)