Longissimus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
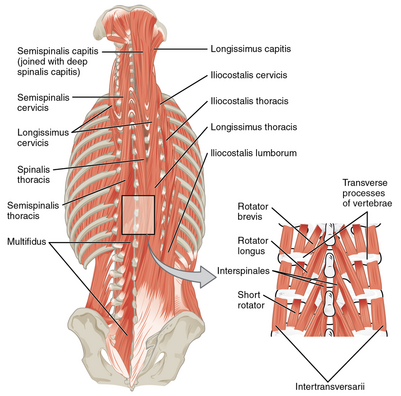
The longissimus muscle is a long intrinsic muscle of the back. Along with spinalis and iliocostalis, these three muscles comprise the erector spinae group. | [[File:Muscles of the Back.png|thumb|401x401px|Back Muscles]] | ||
The longissimus muscle is a long intrinsic [[Back Muscles|muscle of the back]]. Along with [[spinalis]] and iliocostalis, these three muscles comprise the [[Erector Spinae|erector spinae]] group. Longissimus is the longest, thickest and most central erector spinae muscle. | |||
The longissimus muscle is not one muscle, but a collection of three separate muscles that run up nearly the entire length of both sides of the spinal column, from the lower back up to the neck. These three muscles include: | |||
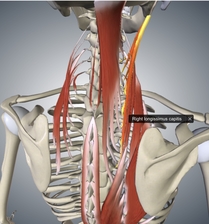
# [[Longissimus Capitis|Longissimus capitis]] | |||
# Longissimus cervicis | |||
# [[Longissimus Thoracis|Longissimus thoracis]]<ref>Study.com Longissimus Available:https://study.com/academy/lesson/longissimus-muscle-origin-insertion-function.html (accessed 5.2.2022)</ref> | |||
== | The erector spinae muscles, including longissimus, are the most powerful extensors of the vertebral column. Their main actions include spine extension and lateral flexion. Longissimus capitis also rotates the head<ref>Ken Hub Longissimus Available:https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/longissimus-muscle (accessed 5.2.2022)</ref>. | ||
== Anatomy == | |||
[[File:Longissimus capitis origin.jpg|thumb|Longissimus capitis]] | |||
For the 3 muscles of Longissimus see links above. | |||
Relations | |||
# Longissimus is found on either sides of the vertebral bodies, running superficial to the transversospinalis and spinalis thoracis muscles. | |||
# Longissimus is located deep to the splenius capitis, splenius colli, iliocostalis thoracis, iliocostalis lumborum muscles, and erector spinae aponeurosis. | |||
Nerve Supply: The various parts of longissimus muscle are innervated by branches of the posterior rami of the corresponding regional [[Thoracic Spinal Nerves|spinal nerves]]. | |||
== Sub Heading 3 == | == Sub Heading 3 == | ||
Revision as of 06:34, 5 February 2022
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton and Wendy Snyders
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The longissimus muscle is a long intrinsic muscle of the back. Along with spinalis and iliocostalis, these three muscles comprise the erector spinae group. Longissimus is the longest, thickest and most central erector spinae muscle.
The longissimus muscle is not one muscle, but a collection of three separate muscles that run up nearly the entire length of both sides of the spinal column, from the lower back up to the neck. These three muscles include:
- Longissimus capitis
- Longissimus cervicis
- Longissimus thoracis[1]
The erector spinae muscles, including longissimus, are the most powerful extensors of the vertebral column. Their main actions include spine extension and lateral flexion. Longissimus capitis also rotates the head[2].
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
For the 3 muscles of Longissimus see links above.
Relations
- Longissimus is found on either sides of the vertebral bodies, running superficial to the transversospinalis and spinalis thoracis muscles.
- Longissimus is located deep to the splenius capitis, splenius colli, iliocostalis thoracis, iliocostalis lumborum muscles, and erector spinae aponeurosis.
Nerve Supply: The various parts of longissimus muscle are innervated by branches of the posterior rami of the corresponding regional spinal nerves.
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Study.com Longissimus Available:https://study.com/academy/lesson/longissimus-muscle-origin-insertion-function.html (accessed 5.2.2022)
- ↑ Ken Hub Longissimus Available:https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/longissimus-muscle (accessed 5.2.2022)