Coronary Artery
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Rania Nasr and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The coronary arteries arise from the coronary sinuses immediately distal (superior) to the aortic valve and supply the myocardium with oxygenated blood
- This is a crucial function for myocardial function and subsequently homeostasis of the body[1].
They branch and encircle the heart to cover its surface with a lacy network, perhaps resembling a slightly crooked crown.[2]
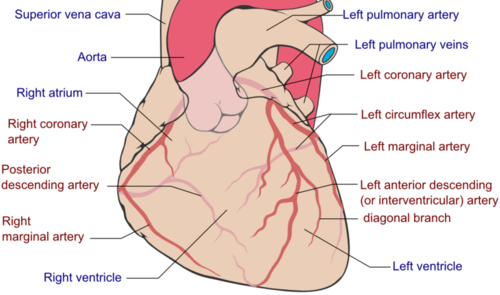
Gross Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The typical configuration consists of two coronary arteries, arising from the left posterior and right anterior aortic or coronary sinuses respectively, in the proximal ascending aorta. These are the only two branches of the ascending aorta.
- Left coronary artery (LMCA)
- Right coronary artery (RCA)
The right coronary artery courses in the right atrioventricular groove to the inferior surface of the heart, whereupon it turns anteriorly at the crux as the posterior descending artery (PDA) in right dominant circulation.
The left coronary artery has a short common stem (and is hence often referred to as the left main coronary artery), that bifurcates into the left circumflex artery (LCx), which courses over the left atrioventricular groove, and the left anterior descending artery (LAD), which passes towards the apex in the anterior interventricular groove.
Occasionally there is a trifurcation (in ~15%), with the third branch, the ramus intermedius, arising inbetween the LAD and LCx. In left dominant hearts, the LCx supplies the posterior descending artery (PDA)[2].
Path[edit | edit source]
The coronary arteries run along the coronary sulcus of the myocardium of the heart[1].
Divisions[edit | edit source]
The RCA and left main coronary artery (LMCA) extend from the aortic root to supply different regions of the heart. The RCA gives rise to the sinoatrial nodal branch of the right coronary artery, posterior descending artery branch of the RCA, and the marginal branch. While the LMCA branches into the circumflex artery (Cx) and the left anterior descending artery (LAD). The Cx gives rise to the left marginal artery and posterior descending artery (in a left-dominant heart). The left anterior descending artery gives off the diagonal branches[1].
Supply[edit | edit source]
The RCA emerges from the anterior ascending aorta and supplies blood to the right atrium, right ventricle, SA node, and AV node. It descends into smaller branches including the right posterior descending artery (PDA) and acute marginal artery. In conjunction with the left anterior descending artery (LADA), the RCA helps supply blood to the septum of the heart[1].
The LMCA gives off two major branches; the left anterior descending (LAD) and the left circumflex (LCx) coronary arteries, which supply blood to the left atrium and left ventricle. The LAD supplies blood to the front and the left side of the heart. The circumflex artery is responsible for blood supply to the left atrium and the posterior-lateral aspect of the left ventricle[1].
Clinical Relevance[edit | edit source]
Coronary artery disease (CAD, also called coronary heart disease, or CHD) is caused by the narrowing of the coronary arteries. Arteries that have become extremely narrow can cause shortness of breath and chest pain during physical activity. If a coronary artery suddenly becomes completely blocked, it can result in a Myocardial Infarct/heart attack[3].
Related pages[edit | edit source]
Physical Activity and Cardiovascular Disease
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Ogobuiro I, Tuma F. Anatomy, Thorax, Heart Coronary Arteries. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019 Jan.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radiopedia Coronary arteries Available from:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/coronary-arteries (last accessed 5.8.2020)
- ↑ InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. Coronary artery disease: Overview. 2013 Feb 13 [Updated 2017 Jul 27].
- ↑ Armando Hasudungan. Cardiology - Coronary Blood Supply. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3wpT-4bSmoU [last accessed 26/9/2019]