28-Item General Health Questionnaire: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Objective<br> == | == Objective<br> == | ||
The General Health Questionnaire (GHQ) is a screening device for identifying minor psychiatric disorders in the general population and within community or non-psychiatric clinical settings such as primary care or general medical out-patients. Suitable for all ages from adolescent upwards – not children, it assesses the respondent’s current state and asks if that differs from his or her usual state. It is therefore sensitive to short-term psychiatric disorders but not to long-standing attributes of the respondent. | The General Health Questionnaire (GHQ) is a screening device for identifying minor psychiatric disorders in the general population and within community or non-psychiatric clinical settings such as primary care or general medical out-patients. Suitable for all ages from adolescent upwards – not children, it assesses the respondent’s current state and asks if that differs from his or her usual state. It is therefore sensitive to short-term psychiatric disorders but not to long-standing attributes of the respondent. | ||
== Intended Population<br> == | == Intended Population<br> == | ||
The self-administered questionnaire focuses on two major areas: | The self-administered questionnaire focuses on two major areas: | ||
The inability to carry out normal functions | The inability to carry out normal functions | ||
The appearance of new and distressing phenomena. | |||
<br> | |||
== Method of Use == | == Method of Use == | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
GHQ28 4/5* (max score 28) | GHQ28 4/5* (max score 28) | ||
[[Image:GHQ.jpg|center]] | [[Image:GHQ.jpg|center]] | ||
== Reference<br> == | == Reference<br> == | ||
Michele Sterling, General Health Questionnaire 28; Journal of Physiotherapy Vol 57, 2011-59. Clinimetrics Appraisal | |||
== Evidence == | == Evidence == | ||
[[Image:Reliability GHQ 28.JPG|center]] | [[Image:Reliability GHQ 28.JPG|center]] | ||
== Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 7 June 2014
Original Editor - Ajay Upadhyay
Top Contributors - Ajay Upadhyay, Kim Jackson, Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop and Claire Knott
Objective
[edit | edit source]
The General Health Questionnaire (GHQ) is a screening device for identifying minor psychiatric disorders in the general population and within community or non-psychiatric clinical settings such as primary care or general medical out-patients. Suitable for all ages from adolescent upwards – not children, it assesses the respondent’s current state and asks if that differs from his or her usual state. It is therefore sensitive to short-term psychiatric disorders but not to long-standing attributes of the respondent.
Intended Population
[edit | edit source]
The self-administered questionnaire focuses on two major areas:
The inability to carry out normal functions The appearance of new and distressing phenomena.
Method of Use[edit | edit source]
The self-administered questionnaire is an ideal screening device for identifying non-psychotic and minor psychiatric disorders to help inform further intervention.
GHQ-28: a 28 item scaled version – assesses somatic symptoms, anxiety and insomnia, social dysfunction and severe depression.
GHQ28 4/5* (max score 28)
Reference
[edit | edit source]
Michele Sterling, General Health Questionnaire 28; Journal of Physiotherapy Vol 57, 2011-59. Clinimetrics Appraisal
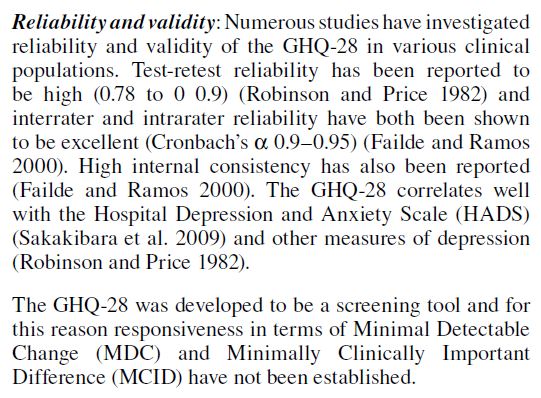
Evidence[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1rMwxYmtBPsqhR8LmyilawKlf4DG9hGXanLxpVb2aHFsX_bUvH|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.