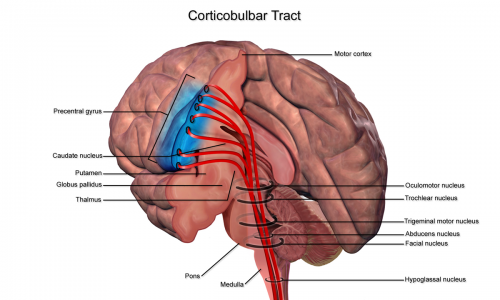
Corticobulbar Tract
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Kate Sampson, Lucinda hampton, Ahmed M Diab, 127.0.0.1, WikiSysop and Kim Jackson
Description[edit | edit source]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Course / Path[edit | edit source]
Function[edit | edit source]
Pathology[edit | edit source]
- Unilateral leisons to the corticobular usually do not redult in any clinical effect on the neck and head muscles as the lower motor neurons of the brain stem recieve bilateral corticobulbar innervation. [1] However there are two exceptions to these rules:
1) Facial nucleus (VII): The muscles of the lower face recieve contralateral input from the opposite motor cortex. Therefore contralateral leisons to the motor cortex/internal capsule results in weakness to the face muscles in the opposite side of the face. However they would still be able to wrinkle their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract. [1]
2) Hypoglossal nucleus (XII): The genioglossus muscle (muscle responsible for sticking out the tongue) receives innervation from the contralateral motor cortex. Therefore lesion involving the right motor cortex/ internal capsule would result in weakness in the left hypoglossal muscle. Therefore due to the weakness in the left side of the tongue, the strong muscle on the right side, pushes the tongue to the left. [1]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=10YYOHVqhl38EZ2KmODZnqbZ98ue2Llh2JVCjrXLfQ98EWWQef|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 HyperBrain. A resource for learning Neuroanatomy. Chapter 10. Lower and Upper Motor Neurons and the Internal Capsule. http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/hyperbrain/syllabus/syllabus10.html (accessed 05/06/2016)
- ↑ Soton Brain Hub. Corticobulbar tract. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GfTDIGoGiY8