Extensor Hallucis Brevis: Difference between revisions
Leana Louw (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Leana Louw (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
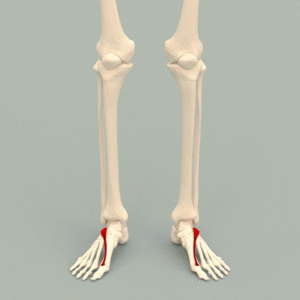
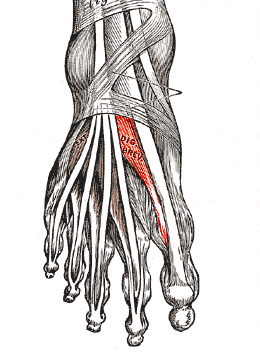
Extensor hallucis brevis (EHB) is a thin, broad muscle on the top of the foot that assists in extending the big toe. It is essentially the medial part of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle.<ref>Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.</ref> | Extensor hallucis brevis (EHB) is a thin, broad muscle on the top of the foot that assists in extending the big toe. It is essentially the medial part of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle.<ref name=":0">Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.</ref> | ||
{| border="0" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | {| border="0" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|[[File:Extensor hallucis brevis.png|thumb]] | |[[File:Extensor hallucis brevis.png|thumb]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Origin === | |||
Distal part of superior and lateral surface of the [[calcaneus]], lateral talocalcaneal ligament and apex of inferior extensor retinaculum.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Insertion === | |||
Dorsal surface of the base of the proximal phalanx of the big toe.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Nerve === | |||
Deep peroneal nerve (L5 or S1 or both).<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Artery === | |||
* Perforating branch of the peroneal artery | |||
* Anterior lateral malleolar artery | |||
* Lateral tarsal arteries | |||
* Dorsalis pedis artery | |||
* Arcuate artery | |||
* First dorsal metatarsal artery | |||
* Dorsal digital arteries<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Assists extensor hallucis longus with big toe extension of the metatarsophalangeal joint.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Clinical Significance == | == Clinical Significance == | ||
* Dorsal foot pain | |||
* Entrapment neuropathy of the peroneal nerve caused by extensor hallucis brevis<ref>Kanbe K, Kubota H, Shirakura K, Hasegawa A, Udagawa E. [https://www.jfas.org/article/S1067-2516(09)80078-1/pdf Entrapment neuropathy of the deep peroneal nerve associated with the extensor hallucis brevis.] The Journal of foot and ankle surgery 1995;34(6):560-2.</ref> | |||
* Extensor hallucis brevis tear | |||
* Trigger points | |||
{{#ev:youtube|4Cho3GkVsIE|300}}<ref>Trigger Points 3D. Great Toe Extension - Extensor Digitorum Longus and Brevis - Trigger Point of the Week. </ref> | |||
== Assessment == | |||
* Palpation: The belly of the muscle is palpable on active extension of the big toe. | |||
* Muscle length testing | |||
* Muscle strength testing | |||
{{#ev:youtube|F5eDjBXisCA|300}}<ref>Advanced Massage Techniques School. Extensor Hallucis Longus and Brevis Muscle Test. </ref> | |||
* | |||
Strains of the EHB are common. Some of the symptoms that may help point towards a strain include; pain right at the top of the foot and near the toes, difficulty in raising the foot upwards, feeling of numbness in the foot, big toe pain and deformities (clawtoe or hammertoes). Common causes of a strain are; frequent stubbing of the toes, repetitive kicking and cycling. | Strains of the EHB are common. Some of the symptoms that may help point towards a strain include; pain right at the top of the foot and near the toes, difficulty in raising the foot upwards, feeling of numbness in the foot, big toe pain and deformities (clawtoe or hammertoes). Common causes of a strain are; frequent stubbing of the toes, repetitive kicking and cycling. | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 1 November 2020
Description[edit | edit source]
Extensor hallucis brevis (EHB) is a thin, broad muscle on the top of the foot that assists in extending the big toe. It is essentially the medial part of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle.[1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Distal part of superior and lateral surface of the calcaneus, lateral talocalcaneal ligament and apex of inferior extensor retinaculum.[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Dorsal surface of the base of the proximal phalanx of the big toe.[1]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Deep peroneal nerve (L5 or S1 or both).[1]
Artery[edit | edit source]
- Perforating branch of the peroneal artery
- Anterior lateral malleolar artery
- Lateral tarsal arteries
- Dorsalis pedis artery
- Arcuate artery
- First dorsal metatarsal artery
- Dorsal digital arteries[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
Assists extensor hallucis longus with big toe extension of the metatarsophalangeal joint.[1]
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
- Dorsal foot pain
- Entrapment neuropathy of the peroneal nerve caused by extensor hallucis brevis[2]
- Extensor hallucis brevis tear
- Trigger points
Assessment[edit | edit source]
- Palpation: The belly of the muscle is palpable on active extension of the big toe.
- Muscle length testing
- Muscle strength testing
Strains of the EHB are common. Some of the symptoms that may help point towards a strain include; pain right at the top of the foot and near the toes, difficulty in raising the foot upwards, feeling of numbness in the foot, big toe pain and deformities (clawtoe or hammertoes). Common causes of a strain are; frequent stubbing of the toes, repetitive kicking and cycling.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There is limited research on the treatment of strains of the EHB. Some strategies that are frequently used include;
- PRICE in the acute stage
- Cryotherapy
- Heat therapy - after the acute phase
- Rehabilitation programme to strengthen the extensor muscles
- Ensuring appropriate footwear
- Calf muscle brace and strain
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.
- ↑ Kanbe K, Kubota H, Shirakura K, Hasegawa A, Udagawa E. Entrapment neuropathy of the deep peroneal nerve associated with the extensor hallucis brevis. The Journal of foot and ankle surgery 1995;34(6):560-2.
- ↑ Trigger Points 3D. Great Toe Extension - Extensor Digitorum Longus and Brevis - Trigger Point of the Week.
- ↑ Advanced Massage Techniques School. Extensor Hallucis Longus and Brevis Muscle Test.