Gemellus Superior: Difference between revisions
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The gemelli muscles act to externally (laterally) rotate the hip and to extend the hip. | The gemelli muscles act to externally (laterally) rotate the hip and to extend the hip. | ||
{{#ev:youtube|v=SWuoa-XJPXg}}<ref>Kenhub - Learn human anatomy. Functions of the gemelli muscles (preview) - 3D Human Anatomy | Kenhub. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SWuoa-XJPXg [last accessed 25/07/2019]</ref> | |||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 23 January 2020
Original Editor -
Top Contributors - Abbey Wright
Description[edit | edit source]
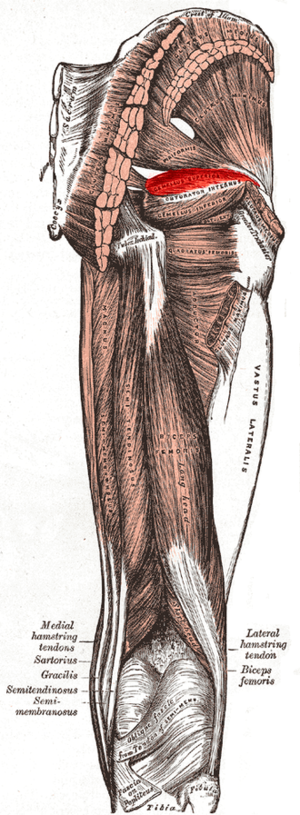
Gemellus superior is a small muscle in the posterio-latereal portion of the hip. It works with gemellus inferior and obturator internus, to form the triceps coxae, to externally rotate and extend the hip[1].
Origin[edit | edit source]
Gemellus superior originates from the outer (gluteal) surface of the spine of the ischium[2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
It has a blended insertion with the upper part of the tendon of the Obturator internus.[2]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
L5, S1, and S2
Artery[edit | edit source]
Function[edit | edit source]
The gemelli muscles act to externally (laterally) rotate the hip and to extend the hip.
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Palastanga, NIgel; Soames, Roger (November 2011). Physiotherapy Essentials : Anatomy and Human Movement : Structure and Function (6th ed.). London, GBR: Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 235
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Palastanga, NIgel; Soames, Roger (November 2011). Physiotherapy Essentials : Anatomy and Human Movement : Structure and Function (6th ed.). London, GBR: Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 237.
- ↑ Kenhub - Learn human anatomy. Functions of the gemelli muscles (preview) - 3D Human Anatomy | Kenhub. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SWuoa-XJPXg [last accessed 25/07/2019]