Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
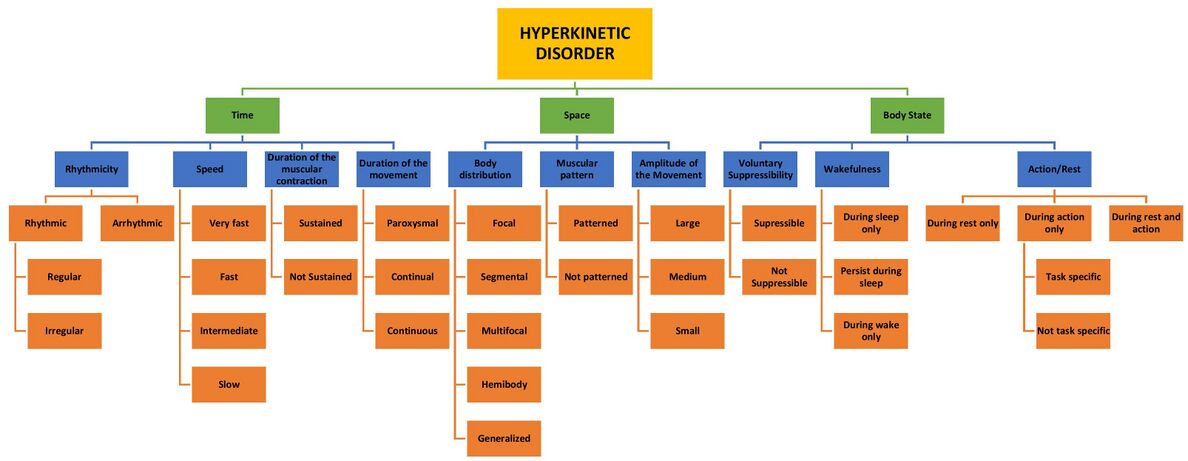
Hyperkinetic movement disorders can be grouped according to distinct cardinal features, which can be described in terms of | Hyperkinetic movement disorders can be grouped according to distinct cardinal features, which can be described in terms of | ||
* | * Time | ||
* | * Space distribution | ||
* | * Body state’s impact. | ||
[[File:Hyperkinetic disorder relationship chart.jpg|center|frameless|1188x1188px]] | [[File:Hyperkinetic disorder relationship chart.jpg|center|frameless|1188x1188px]] | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 23 September 2022
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Hyperkinetic movement disorders also referred to as Dyskinesias are characterized by abnormal, often repetitive, involuntary movements overlapped to normal motor activity. Its 5 major types are Tremors, Chorea, Dystonia, Myoclonus and Tics.
Etiology[edit | edit source]
Common etiologies seen in this condition
- Genetic abnormalities
- Neurodegenerative diseases
- Structural lesions
- Infection
- Drugs
- Psychogenic problems
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
Among all HMDs there appears to be decreased neural firing rates in the inhibitory output nuclei of the basal ganglia leading to a subsequent disinhibition of thalamocortical activity. Sensory abnormalities may also have a role.
Cardinal Features[edit | edit source]
Hyperkinetic movement disorders can be grouped according to distinct cardinal features, which can be described in terms of
- Time
- Space distribution
- Body state’s impact.
Classification[edit | edit source]
There are 5 types of tremors