Levator Scapulae: Difference between revisions
m (typo, deleted pubmed) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description<br> == | == Description<br> == | ||
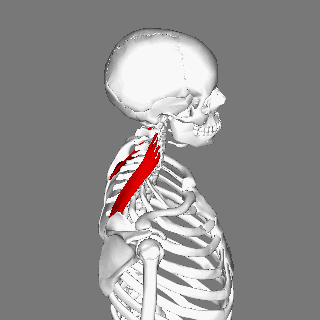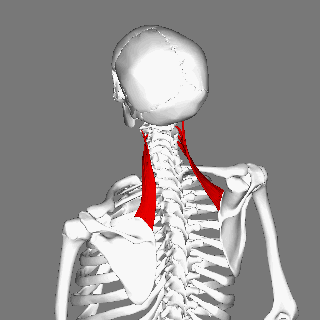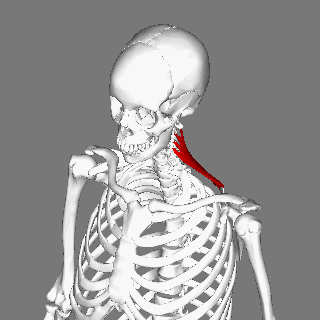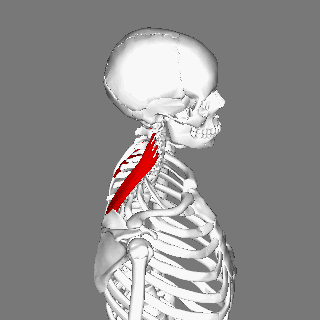
Levator scapulae connects the upper limb to the vertebral column and lies in the posterior triangle of the neck | Levator scapulae connects the upper limb to the vertebral column and lies in the posterior triangle of the neck. | ||
The superior aspect of the levator scapulae is covered by [[sternocleidomastoid]], and its inferior part by [[trapezius]]. | |||
[[Image:Levator scapulae muscle animation small2.gif|center]] | [[Image:Levator scapulae muscle animation small2.gif|center]] | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
The levator scapulae originates on the or tubercle of transverse process of [[Cervical Vertebrae|Cervical Vertebrae]] 1 to 4<ref name="p1">http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5502/</ref> | |||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
Revision as of 20:13, 4 July 2018
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Eric Henderson, SULEIMAN USMAN, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton, Wendy Walker, WikiSysop, Admin, Evan Thomas, Oyemi Sillo, Tarina van der Stockt and Joao Costa
Description
[edit | edit source]
Levator scapulae connects the upper limb to the vertebral column and lies in the posterior triangle of the neck.
The superior aspect of the levator scapulae is covered by sternocleidomastoid, and its inferior part by trapezius.
Origin[edit | edit source]
The levator scapulae originates on the or tubercle of transverse process of Cervical Vertebrae 1 to 4[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Vertebral margin of the scapula, between the superior angle and the root of the spine[2]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
C3 to 5
Cervical nerve (C3, C4) and dorsal scapular nerve (C5)[3]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Descending scapular artery[4]
Action[edit | edit source]
Elevation and rotation of the scapula[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
Elevation of the scapula, and rotation of it inferior angle medially, in movements such as elevation of the upper limb
If the scapula is fixed, it helps produce cervical side flexion[2]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5502/
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/levator_scapula
- ↑ http://www.bartleby.com/107/121.html
- ↑ Joseph P Iannotti, Richard Parker.fckLRThe Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations: Musculoskeletal System, Volume 6, Part I - Upper Limb. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2012