Manual Muscle Testing: Hip Flexion: Difference between revisions
m (The hip flexor muscle group) |
m (part of introduction, i am still working on it) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
An assessment of [[muscle]] strength is typically performed as part of a patient's [[Outcome Measures|objective assessment]] and is an important component of the physical exam that can reveal information about | An assessment of [[muscle]] strength is typically performed as part of a patient's [[Outcome Measures|objective assessment]] and is an important component of the physical exam that can reveal information about the comparison of the involved leg verses the uninvolved leg. This test can help the therapist determine what strength the patient was at prior to injury or trauma. It is used to evaluate weakness and can be effective in differentiating true weakness from imbalance or poor endurance. See [[Muscle Strength Testing]] | ||
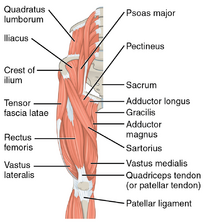
== Muscles Involved == | == Muscles Involved == | ||
[[File:Hip flexors.png|right|frameless|222x222px|alt=|Anterior thigh muscles]] | [[File:Hip flexors.png|right|frameless|222x222px|alt=|Anterior thigh muscles]] | ||
There are | There are four main muscles that flex the hip. There are two joint muscles which are Sartorius, Tensor Fasciae Latae, and Rectus Femoris. There is a one muscle that is a one joint muscle known as Iliopsoas. | ||
* | * Iliopsoas | ||
* | * Tensor Fasciae Latae | ||
* Sartorius | |||
* [[Rectus Femoris|Rectus femoris]] | * [[Rectus Femoris|Rectus femoris]] | ||
Image 1: Anterior hip/thigh muscles. | Image 1: Anterior hip/thigh muscles. | ||
Revision as of 20:53, 21 March 2024
Original Editor - Claire Knott
Top Contributors - Whitney Wagganer, Kaitlyn Carroll, Tony Varela, Claire Knott, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson and Wanda van Niekerk
Welcome to Arkansas Colleges of Health Education School of Physical Therapy Musculoskeletal 1 Project. This space was created by and for the students at Arkansas Colleges of Health Education School in the United States. Please do not edit unless you are involved in this project, but please come back in the near future to check out new information!!
Introduction[edit | edit source]
An assessment of muscle strength is typically performed as part of a patient's objective assessment and is an important component of the physical exam that can reveal information about the comparison of the involved leg verses the uninvolved leg. This test can help the therapist determine what strength the patient was at prior to injury or trauma. It is used to evaluate weakness and can be effective in differentiating true weakness from imbalance or poor endurance. See Muscle Strength Testing
Muscles Involved[edit | edit source]
There are four main muscles that flex the hip. There are two joint muscles which are Sartorius, Tensor Fasciae Latae, and Rectus Femoris. There is a one muscle that is a one joint muscle known as Iliopsoas.
- Iliopsoas
- Tensor Fasciae Latae
- Sartorius
- Rectus femoris
Image 1: Anterior hip/thigh muscles.
Patient Positioning[edit | edit source]
- Grades 3 to 5 - Patient is in short sitting with thighs supported
- Grades 0-2 - Patient is in side lying ('gravity minimal' position)
Therapist Position[edit | edit source]
- Therapist to stand next to test side
- Palpation over hip flexors
To Test[edit | edit source]
- Patient actively flexes the hip
- For grades 4 to 5 apply resistance over the distal femur in a direction opposite to flexion[1]
- To satisfy grade 5 'normal muscle' performance criteria, the patient must have the ability to move through complete range of motion (active resistance testing) OR maintain an end point range (break testing) against maximum resistance.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Hislop H, Avers D, Brown M. Daniels and Worthingham's muscle Testing-E-Book: Techniques of manual examination and performance testing. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013 Sep 27.