Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Lead Editors
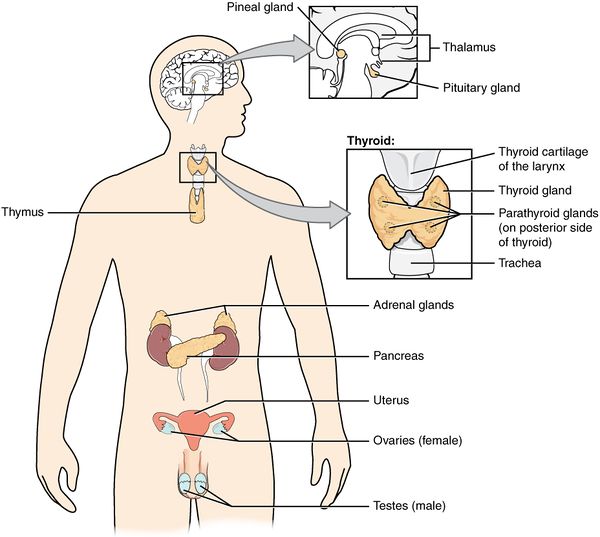
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Endocrine and metabolic diseases span a vast range of conditions. The endocrine system works via chemical messages (hormones) secreted from glands directly into the circulatory system to regulate the function of distant target organ. A negative feedback loop works to maintain the release of these hormones and so maintain homeostasis ie the state of steady conditions vital for life.[1]
The endocrine system involves many organ systems and hormones, many of which are still being investigated.[3]
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the mechanism of injury and/or pathology of the condition
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the clinical presentation of the condition
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to diagnostic tests for the condition
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Resources[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Wikipedia. Endocrine system. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system (last accessed 6.4.2019)
- ↑ Cool facts. How does endocrine system works. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IAXv8Kxt4QU&app=desktop (last accessed 6.4.2019)
- ↑ Better Health. Endocrine system. Available from: https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/hormonal-endocrine-system (last accessed 6.4.2019)