Obliquus Capitis Inferior: Difference between revisions
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Category:Cervical_Anatomy" to "Category:Cervical Spine - Anatomy") |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | |||
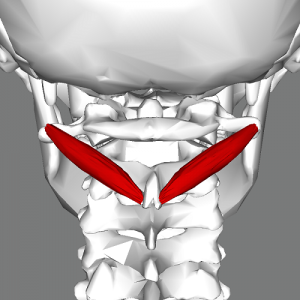
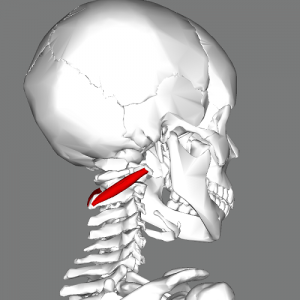
== | Obliquus Capitis Inferior (also known as the Inferior Oblique) is a small muscle that runs posteriorly and inferomedially from C1 to C2. It is situated under the deep cervical vein and comprises the inferior boarder of the suboccipital triangle.<ref name="Grants">Agur AMR, Dalley AF (2012). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy (13th ed). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.</ref> It is the only suboccipital muscle that does not attach to the skull.<ref name="T&S">Travell JG, Simons DG, Simons LS (1998). Travell and Simons' Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual, Volume 1: Upper Half of Body (2nd ed). Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins.</ref> | ||
{| cellpadding="2" border="0;" | |||
|- | |||
! scope="col" width="400" | [[Image:Obliquus capitis inferior muscle posterior view.png|center|300x300px|OCI_post_view]] | |||
! scope="col" width="400" | [[Image:Obliquus capitis inferior muscle right lateral view.png|center|300x300px|OCI_right_lateral_view]] | |||
|} | |||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
Base of | Base of spinous process and adjoining lamina of the axis.<ref name="AE">http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5213/</ref> | ||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
Along the inferior aspect of the tip of the transverse process of the atlas. | Along the inferior aspect of the tip of the transverse process of the atlas.<ref name="AE" /> | ||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1). | Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1).<ref name="AE" /> | ||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
Vertebral artery and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery. | Vertebral artery and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery.<ref name="AE" /> | ||
== Action == | == Action == | ||
Ipsilateral rotation of the atlantoaxial joint.<ref name="Grants" /> | |||
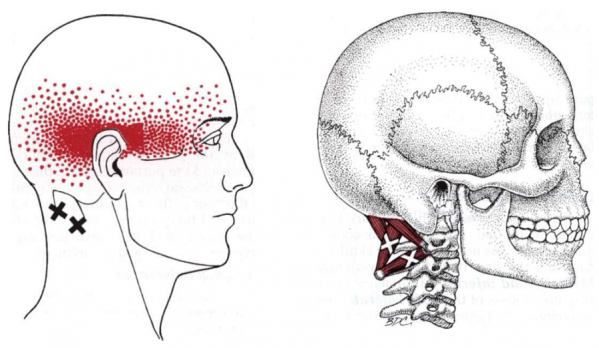
== | == Trigger Point Referral Pattern<ref name="T&S" /> == | ||
[[Image:OCI RCPM TrP Referral.png|center|600x348px|OCI_post_view]]<div class="researchbox"> | |||
<div class="researchbox"> | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Cervical Spine - Anatomy]] [[Category:Muscles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:37, 16 August 2019
Original Editor - Evan Thomas
Lead Editors - Evan Thomas, WikiSysop, Tarina van der Stockt and Kim Jackson
Description[edit | edit source]
Obliquus Capitis Inferior (also known as the Inferior Oblique) is a small muscle that runs posteriorly and inferomedially from C1 to C2. It is situated under the deep cervical vein and comprises the inferior boarder of the suboccipital triangle.[1] It is the only suboccipital muscle that does not attach to the skull.[2]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Base of spinous process and adjoining lamina of the axis.[3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Along the inferior aspect of the tip of the transverse process of the atlas.[3]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1).[3]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Vertebral artery and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery.[3]
Action[edit | edit source]
Ipsilateral rotation of the atlantoaxial joint.[1]
Trigger Point Referral Pattern[2][edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Agur AMR, Dalley AF (2012). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy (13th ed). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Travell JG, Simons DG, Simons LS (1998). Travell and Simons' Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual, Volume 1: Upper Half of Body (2nd ed). Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5213/