Peroneus Tertius: Difference between revisions
(Added image of peroneus tertius muscle) |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File:Peroneus tertius.png|thumb|Peroneus tertius muscle]] | [[File:Peroneus tertius.png|thumb|Peroneus tertius muscle]] | ||
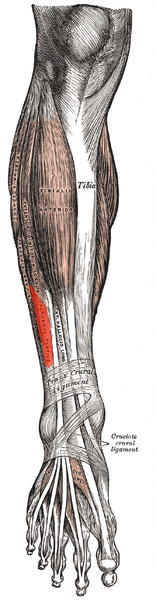
The Peroneus Tertius muscle also called the Fibularis Tertius is one the 3 peroneal muscles ([[ | The Peroneus Tertius muscle also called the Fibularis Tertius is one the 3 peroneal muscles ([[Peroneus (Fibularis) Longus Muscle|peroneus longus]], [[peroneus brevis]]).<ref name=":0">Lippert, Lynn S. Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F A Davis Company; 2016.</ref> It is absent in 5% to 17% of the human white population.<ref name=":1">Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.</ref> | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
Revision as of 16:46, 2 November 2020
Top Contributors - Sai Kripa, Kim Jackson, Patti Cavaleri, Claire Testa, Lilian Ashraf and Oyemi Sillo
Description[edit | edit source]
The Peroneus Tertius muscle also called the Fibularis Tertius is one the 3 peroneal muscles (peroneus longus, peroneus brevis).[1] It is absent in 5% to 17% of the human white population.[2]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Distal half or third of the fibula.[3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Base of the 5th metatarsal.[3]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Deep peroneal nerve.[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
Secondary function in foot dorsiflexion and eversion.[3]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
The strength of eversion and dorsiflexion is not compromised in people who lack the Peroneus Tertius muscle. Peroneus Tertius seems to not provide higher protection against ankle ligamentous injury.[2]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lippert, Lynn S. Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F A Davis Company; 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.