Posterior atlanto-axial ligament: Difference between revisions
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[Image:Upper cervical ligaments.png|thumb|right]] | [[Image:Upper cervical ligaments.png|thumb|right]] | ||
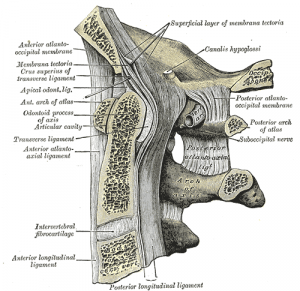
The posterior atlantoaxial ligament is a broad, thin membrane attached, above, to the lower border of the posterior arch of the atlas; below, to the upper edges of the | The posterior atlantoaxial ligament is a broad, thin membrane attached, above, to the lower border of the posterior arch of the atlas; below, to the upper edges of the lamina of the axis.<br>It is a continuation of the [[Ligamentum flavum]], and is in relation, behind, with the obliqus capitis inferior muscle. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
<references /><br> | <references /><br> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Cervical]] [[Category:Ligaments]] [[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Cervical Spine]] [[Category:Ligaments]] [[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 13 October 2016
Original Editor - Rachael Lowe
Top Contributors - Kim Jackson, Evan Thomas, Daniele Barilla, Admin, Rachael Lowe and WikiSysop
Description[edit | edit source]
The posterior atlantoaxial ligament is a broad, thin membrane attached, above, to the lower border of the posterior arch of the atlas; below, to the upper edges of the lamina of the axis.
It is a continuation of the Ligamentum flavum, and is in relation, behind, with the obliqus capitis inferior muscle.
References[edit | edit source]