Posterior atlanto-occipital ligament: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[Image:Atlanto-occipital joint posterior.png|thumb|right|Posterior atlanto-occipital ligament and membrane]] | [[Image:Atlanto-occipital joint posterior.png|thumb|right|Posterior atlanto-occipital ligament and membrane]] | ||
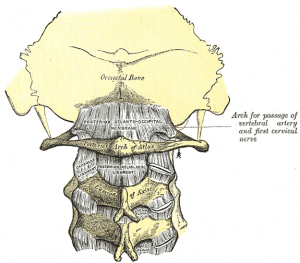
The posterior atlantooccipital membrane (posterior atlantooccipital ligament) is a broad but thin membrane. It is connected above to the posterior margin of the foramen magnum and below to the upper border of the posterior arch of the atlas. | The posterior atlantooccipital membrane (posterior atlantooccipital ligament) is a broad but thin membrane. It is connected above to the posterior margin of the foramen magnum and below to the upper border of the posterior arch of the atlas. It is a continuation from the Ligamentum Flavum. | ||
On each side of this membrane there is defect above the groove for the vertebral artery which serves as an opening for the entrance of the artery. The suboccipital nerve also passes through this defect. | On each side of this membrane there is defect above the groove for the vertebral artery which serves as an opening for the entrance of the artery. The suboccipital nerve also passes through this defect. | ||
Revision as of 16:39, 18 January 2014
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Admin, Kim Jackson, Evan Thomas and WikiSysop
Description[edit | edit source]
The posterior atlantooccipital membrane (posterior atlantooccipital ligament) is a broad but thin membrane. It is connected above to the posterior margin of the foramen magnum and below to the upper border of the posterior arch of the atlas. It is a continuation from the Ligamentum Flavum.
On each side of this membrane there is defect above the groove for the vertebral artery which serves as an opening for the entrance of the artery. The suboccipital nerve also passes through this defect.
The free border of the membrane arches over the artery and nerve and is sometimes ossified.
The membrane is deep to the Rectus capitis posterior minor and Obliqus capitis superior and is superficial to the dura mater of the vertebral canal to which it is closely associated.
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.