Rectus Capitis Anterior: Difference between revisions
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
== Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
<div class="researchbox"> | <div class="researchbox"> | ||
<rss>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1DC34RKGsqmJ2iUEq4gO2_KjTqbahDeCpgRXyd0FZnmoRLVgEV | <rss>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1DC34RKGsqmJ2iUEq4gO2_KjTqbahDeCpgRXyd0FZnmoRLVgEV</rss> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 11:38, 6 June 2017
Original Editor - Venus Pagare
Top Contributors - Venus Pagare, Evan Thomas, Admin, 127.0.0.1, Tarina van der Stockt, WikiSysop and Kim Jackson
Description
[edit | edit source]
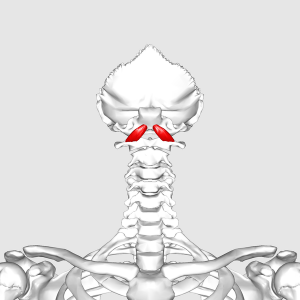
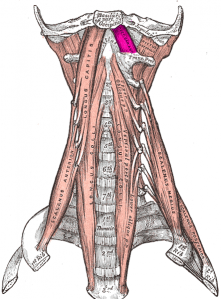
The Rectus capitis anterior is a short, flat muscle, situated immediately behind the upper part of the Longus capitis. It is also known as Obliquus Capitis Superior.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Anterior surface of the lateral mass of the atlas (C1 vertebra) and the root of its transverse process[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
The inferior surface of the occipital bone anterior to the foreamen magnum[1]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
C1, C2
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The muscle receives blood from the ascending cervical artery, which is a small branch of the inferior thyroid artery from the thyrocervical trunk of the subclavian artery.[2]
Action[edit | edit source]
Aids in flexion of the head and the neck
Function[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1DC34RKGsqmJ2iUEq4gO2_KjTqbahDeCpgRXyd0FZnmoRLVgEV: Error parsing XML for RSS