Rectus Capitis Anterior: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Category:Cervical_Anatomy" to "Category:Cervical Spine - Anatomy") |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User:Venus Pagare|Venus Pagare]] | '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Venus Pagare|Venus Pagare]] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description<br> == | == Description<br> == | ||
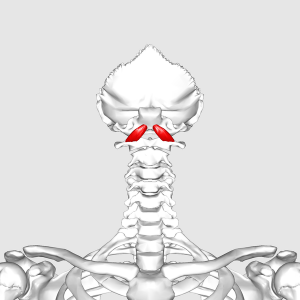
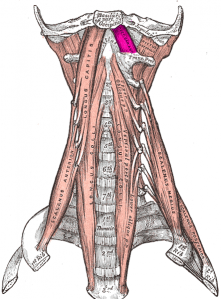
The Rectus capitis anterior is a short, flat muscle, situated immediately behind the upper part of the [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Longus_Capitis Longus capitis]. It is also known as Obliquus Capitis Superior. | |||
<br> | |||
{| width="100%" border="0" align="center" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | {| width="100%" border="0" align="center" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 11: | Line 15: | ||
| [[Image:RECTUS CAP ANT2.PNG|center|300x300px]] | | [[Image:RECTUS CAP ANT2.PNG|center|300x300px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Origin | == Origin == | ||
Anterior surface of the lateral mass of the atlas (C1 vertebra) and the root of its transverse process | Anterior surface of the lateral mass of the atlas (C1 vertebra) and the root of its transverse process<ref name="wheelessonline"/> | ||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
The inferior surface of the occipital bone anterior to the foreamen magnum<ref name="wheelessonline">http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/rectus_capitis_anterior</ref> | |||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
| Line 24: | Line 29: | ||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
The muscle receives blood from the ascending cervical artery, which is a small branch of the inferior thyroid artery from the thyrocervical trunk of the subclavian artery.<ref>http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5273/</ref> | |||
== Action == | == Action == | ||
Aids in flexion of the head and the neck | Aids in flexion of the head and the neck | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /><br> | <references /><br> | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Cervical Spine - Anatomy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:37, 16 August 2019
Original Editor - Venus Pagare
Top Contributors - Venus Pagare, Evan Thomas, Admin, 127.0.0.1, Tarina van der Stockt, WikiSysop and Kim Jackson
Description
[edit | edit source]
The Rectus capitis anterior is a short, flat muscle, situated immediately behind the upper part of the Longus capitis. It is also known as Obliquus Capitis Superior.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Anterior surface of the lateral mass of the atlas (C1 vertebra) and the root of its transverse process[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
The inferior surface of the occipital bone anterior to the foreamen magnum[1]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
C1, C2
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The muscle receives blood from the ascending cervical artery, which is a small branch of the inferior thyroid artery from the thyrocervical trunk of the subclavian artery.[2]
Action[edit | edit source]
Aids in flexion of the head and the neck