Rectus Femoris: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka|Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | |||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User:Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka]] | |||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | |||
</div> | |||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
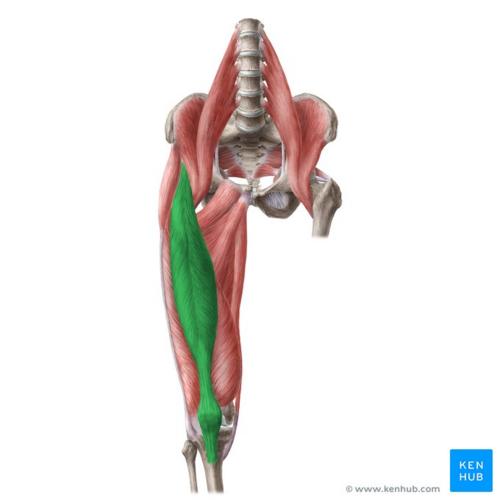
Rectus femoris is a bulk of muscle located in the middle | [[File:Rectus femoris muscle - Kenhub.png|alt=Rectus femoris muscle (highlighted in green) - anterior view|right|frameless|500x500px|Rectus femoris muscle (highlighted in green) - anterior view]] | ||
Rectus femoris is part of the [[Quadriceps Muscle|quadriceps]] group. It is a bulk of [[muscle]] located in the superior, anterior middle compartment of the thigh and is the only muscle in the quadriceps group that crosses the hip<ref name=":0">Drake, RL, Vogl, W, Mitchell, AW, Gray, H. Gray's anatomy for Students 2nd ed. Philadelphia : Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, 2010</ref>. | |||
It is superior and overlying of the [[Vastus Intermedius|vastus intermedius]] muscle and superior-medial part of [[Vastus Lateralis|Vastus lateralis]] and [[Vastus Medialis|Vastus medialis]]. | |||
The word rectus is a latin word connoting “straight”. Thus the rectus femoris received its name because it runs straight down the thigh<ref name=":1">Moore, KL, Dalley, AF, Agur, AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 7<sup>th</sup> ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2014</ref>. | |||
It is a two way acting muscle as it crosses over the hip and knee joint; therefore, it functions to extend the knee and also assists [[Iliacus|iliopsoas]] in hip flexion<ref name=":2">Page, P, Frank, CC, Lardner, R. Assessment And Treatment Of Muscle Imbalance: The Janda Approach. Sheridan Books, USA; 2010. </ref><ref name=":0" />. It is thus also a [[Hip Flexors|hip flexor]]. | |||
A short rectus femoris may contribute to a higher positioned patella in relation to the contralateral side. A markedly shortened rectus femoris is suggested by knee flexion of less than 80°or by marked prominence of superior patellar groove<ref name=":3">Miller, A, Heckert, KD, Davis, BA.The 3-Minute Musculoskeletal & Peripheral Nerve Exam. New York: Demos Medical Publishing. 2009; p.116-117</ref> | |||
Image: Rectus femoris muscle (highlighted in green) - anterior view<ref >Rectus femoris muscle (highlighted in green) - anterior view image - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/lower-extremity-anatomy</ref> | |||
== | == Anatomy == | ||
===Origin=== | |||
originates from anterior inferior iliac spine(AIIS) and the part of alar of ilium superior to the acetabulum<ref name=":0" /> | |||
It has a proximal tendinous complex (PTC) which is constituted by a direct tendon (DT), an indirect tendon (IT), and a variable third head. Direct and indirect tendons finally converge into a common tendon (CT). | |||
There is a membrane connecting the CT with the anterior superior iliac spine.<ref>Mechó S, Iriarte I, Pruna R, Pérez-Andrés R, Rodríguez-Baeza A. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35536396/ A newly discovered membrane at the origin of the proximal tendinous complex of the rectus femoris.] Surg Radiol Anat [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Jul 31];44(6):835–43. </ref> | |||
===Insertion=== | |||
Rectus Femoris together with vastus medialis, vastus lateralis and vastus intermedius joins the quadriceps tendon to insert at the patella and tibial tuberosity (via patellar ligament)<ref name=":3" />. | |||
=== Nerve supply === | |||
Rectus Femoris is innervated by the femoral nerve, originating from lumbar nerve 2, 3, and 4 nerve roots | |||
=== Bloody supply === | |||
Blood is supplied to the Rectus Femoris via descending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral (LCF) artery. | |||
==Function== | |||
==== Hip flexion ==== | |||
* Rectus Femoris acts with [[Iliopsoas Bursitis|iliopsoas]] to produce [[Hip|hip flexion]] especially if the knee is flexed<ref name=":1" />. | |||
* During [[Gait Cycle|gait]], as a hip flexor, it acts with the [[Psoas Major|iliopsoas]] in "Toe off" phase,. | |||
==== Knee extension ==== | |||
*Together with other muscles that are part of the Quadriceps femoris, it facilitates knee extension. | |||
*In terminal swing phase rectus femoris acts as an extensor of the knee, as a muscle in the quadriceps group, it generate force needed for loading(foot flat phase) in stance phase<ref>Rectus femoris muscle [Internet]. En.wikipedia.org. 2018 [cited 15 October 2018]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rectus_femoris_muscle</ref>. | |||
*Rectus femoris is more efficient in movement combining hip hyper-extension and knee flexion or from a position of knee extension and hip flexion. For example kicking a soccer ball<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /> | |||
== Assessment == | |||
=== Palpation === | |||
Rectus femoris can be palpated as it is the most superior of the quadriceps muscles. Start palpation at AIIS, rectus femoris can be felt until its insertion into the quadriceps tendon. Asking the patient to isometrically contract quadriceps will help to identify the muscle belly. | |||
==== | === Strength<ref>Hislop, HJ, Montgomery,J. Daniels and Worthingham's Muscle Testing: Techniques of Manual Examination. 8<sup>th</sup> ed. Missouri: Saunders Elsevier, 2007; p201-204</ref> === | ||
To assess [[Muscle Strength Testing|muscle strength]] for the Rectus Femoris (including rest of the quadriceps group) position the patient in sitting with the hip and knee flexed to 90° for grade 5, 4 and 3 while grade 2, is assessed in side-lying with test limb uppermost and knee flexed to 90° position. | |||
====Other Tests<ref>Reider, B. The orthopaedic physical exam/Bruce Reider.-2nd ed. Elsevier Saunders, USA; 2005</ref> ==== | |||
In Rectus femoris [[Quadriceps Muscle Strain|injury]] : | In Rectus femoris [[Quadriceps Muscle Strain|injury]] : | ||
* FABER (Patrick's test) | * [[FABER Test|FABER]] (Patrick's test) - illicit no pain | ||
* Pain is felt in resisted hip flexion | * Pain is felt in resisted hip flexion<ref>Mendiguchia J, Alentorn-Geli E, Idoate F, Myer GD. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22864009 Rectus femoris muscle injuries in football: a clinically relevant review of mechanisms of injury, risk factors and preventive strategies]. Br J Sports Med. 2013 Apr 1;47(6):359-66.</ref> | ||
* Ely’ test illicit pain on [[Quadricpes Muscle Contusion|tightness]] | * [[Ely's test|Ely’ test]] - illicit pain on [[Quadricpes Muscle Contusion|tightness]] | ||
* Knee ROM is reduced below 80° in shortness of Rectus femoris or prominence of [[Knee|patella grove]] is noted. | * Knee ROM is reduced below 80° in shortness of Rectus femoris or prominence of [[Knee|patella grove]] is noted.<ref>Huri G, Dubin JM, Ozgonen K, Kaya D, Doral MN. [https://europepmc.org/abstract/med/29252783 A Unique Rectus Femoris Injury in an Adolescent Professional Soccer Player: A Case Report.] JBJS case connector. 2014 Oct 1;4(4):e115.</ref> | ||
= | {| width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | ||
> https://www. | |- | ||
|{{#ev:youtube|v=1Av_KKvCcVI&t=8s}}<ref>Quadriceps femoris muscle video - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-quadriceps-femoris-muscle</ref> | |||
= References = | = References = | ||
Latest revision as of 18:23, 25 September 2023
Description[edit | edit source]
Rectus femoris is part of the quadriceps group. It is a bulk of muscle located in the superior, anterior middle compartment of the thigh and is the only muscle in the quadriceps group that crosses the hip[1].
It is superior and overlying of the vastus intermedius muscle and superior-medial part of Vastus lateralis and Vastus medialis.
The word rectus is a latin word connoting “straight”. Thus the rectus femoris received its name because it runs straight down the thigh[2].
It is a two way acting muscle as it crosses over the hip and knee joint; therefore, it functions to extend the knee and also assists iliopsoas in hip flexion[3][1]. It is thus also a hip flexor.
A short rectus femoris may contribute to a higher positioned patella in relation to the contralateral side. A markedly shortened rectus femoris is suggested by knee flexion of less than 80°or by marked prominence of superior patellar groove[4]
Image: Rectus femoris muscle (highlighted in green) - anterior view[5]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
originates from anterior inferior iliac spine(AIIS) and the part of alar of ilium superior to the acetabulum[1]
It has a proximal tendinous complex (PTC) which is constituted by a direct tendon (DT), an indirect tendon (IT), and a variable third head. Direct and indirect tendons finally converge into a common tendon (CT).
There is a membrane connecting the CT with the anterior superior iliac spine.[6]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Rectus Femoris together with vastus medialis, vastus lateralis and vastus intermedius joins the quadriceps tendon to insert at the patella and tibial tuberosity (via patellar ligament)[4].
Nerve supply[edit | edit source]
Rectus Femoris is innervated by the femoral nerve, originating from lumbar nerve 2, 3, and 4 nerve roots
Bloody supply[edit | edit source]
Blood is supplied to the Rectus Femoris via descending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral (LCF) artery.
Function[edit | edit source]
Hip flexion[edit | edit source]
- Rectus Femoris acts with iliopsoas to produce hip flexion especially if the knee is flexed[2].
- During gait, as a hip flexor, it acts with the iliopsoas in "Toe off" phase,.
Knee extension[edit | edit source]
- Together with other muscles that are part of the Quadriceps femoris, it facilitates knee extension.
- In terminal swing phase rectus femoris acts as an extensor of the knee, as a muscle in the quadriceps group, it generate force needed for loading(foot flat phase) in stance phase[7].
- Rectus femoris is more efficient in movement combining hip hyper-extension and knee flexion or from a position of knee extension and hip flexion. For example kicking a soccer ball[2][3]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Rectus femoris can be palpated as it is the most superior of the quadriceps muscles. Start palpation at AIIS, rectus femoris can be felt until its insertion into the quadriceps tendon. Asking the patient to isometrically contract quadriceps will help to identify the muscle belly.
Strength[8][edit | edit source]
To assess muscle strength for the Rectus Femoris (including rest of the quadriceps group) position the patient in sitting with the hip and knee flexed to 90° for grade 5, 4 and 3 while grade 2, is assessed in side-lying with test limb uppermost and knee flexed to 90° position.
Other Tests[9][edit | edit source]
In Rectus femoris injury :
- FABER (Patrick's test) - illicit no pain
- Pain is felt in resisted hip flexion[10]
- Ely’ test - illicit pain on tightness
- Knee ROM is reduced below 80° in shortness of Rectus femoris or prominence of patella grove is noted.[11]
[12]
References[edit | edit source] |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Drake, RL, Vogl, W, Mitchell, AW, Gray, H. Gray's anatomy for Students 2nd ed. Philadelphia : Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, 2010
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Moore, KL, Dalley, AF, Agur, AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 7th ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2014
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Page, P, Frank, CC, Lardner, R. Assessment And Treatment Of Muscle Imbalance: The Janda Approach. Sheridan Books, USA; 2010.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Miller, A, Heckert, KD, Davis, BA.The 3-Minute Musculoskeletal & Peripheral Nerve Exam. New York: Demos Medical Publishing. 2009; p.116-117
- ↑ Rectus femoris muscle (highlighted in green) - anterior view image - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/lower-extremity-anatomy
- ↑ Mechó S, Iriarte I, Pruna R, Pérez-Andrés R, Rodríguez-Baeza A. A newly discovered membrane at the origin of the proximal tendinous complex of the rectus femoris. Surg Radiol Anat [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Jul 31];44(6):835–43.
- ↑ Rectus femoris muscle [Internet]. En.wikipedia.org. 2018 [cited 15 October 2018]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rectus_femoris_muscle
- ↑ Hislop, HJ, Montgomery,J. Daniels and Worthingham's Muscle Testing: Techniques of Manual Examination. 8th ed. Missouri: Saunders Elsevier, 2007; p201-204
- ↑ Reider, B. The orthopaedic physical exam/Bruce Reider.-2nd ed. Elsevier Saunders, USA; 2005
- ↑ Mendiguchia J, Alentorn-Geli E, Idoate F, Myer GD. Rectus femoris muscle injuries in football: a clinically relevant review of mechanisms of injury, risk factors and preventive strategies. Br J Sports Med. 2013 Apr 1;47(6):359-66.
- ↑ Huri G, Dubin JM, Ozgonen K, Kaya D, Doral MN. A Unique Rectus Femoris Injury in an Adolescent Professional Soccer Player: A Case Report. JBJS case connector. 2014 Oct 1;4(4):e115.
- ↑ Quadriceps femoris muscle video - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-quadriceps-femoris-muscle