Sacroiliac Joint
Original Editors - Kathleen Nestor and Katie Sheidler
Editors
Description[edit | edit source]
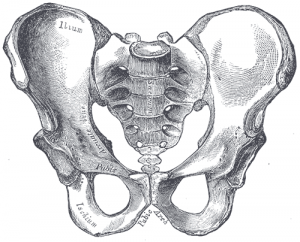
The sacroiliac joint (simply called the SI joint) is the joint connection between the spine and the pelvis. It is a large diathrodial joint made up of the sacrum and the two innominates of the pelvis. Each innominate is formed by the fusion of the three bones of the pelvis: the ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. [1]
Motions Available [edit | edit source]
The main function of the SI joint is to provide stability and attenuate forces to the lower extremies. The strong ligamentous system of the joint makes it better designed for stability and limits the amount of motion available. [2]
Nutation - occurs as the sacrum moves anteriorly and inferiorly while the coccyx moves posteriorly relative to the ilium. [3] This motion is opposed by the wedge shape of the sacrum, the ridges and depression of the articular surfaces, the friction coefficient of the joint surface, and the integrity of the posterior, interosseous, and sacrotuberous ligaments that are also supported by muscles that insert into the ligaments.[1]
Counternutation - occurs as the sacrum moves posteriorly and superiorly while the coccyx moves anteriorly relative to the ilium. [4] This motion is opposed by the posterior sacroiliac ligament that is supported by the multifidus. [5]
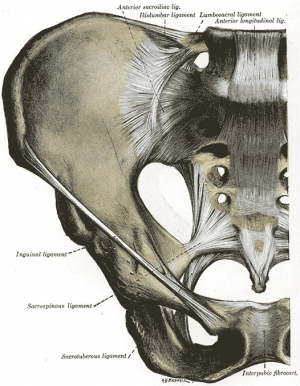
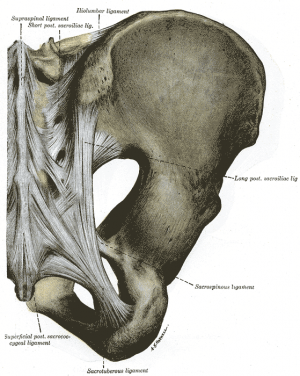
Ligaments & Joint Capsule[6][7]
[edit | edit source]
Joint Capsule
The sacroiliac joint capsule articular surfaces are made up of two strong layers which are C-shaped. The capsular portion on the ilium consists of a fibrocartilage while the capsular portion on the sacrum is made up of a hyaline cartilage. The capsule attaches to both articular margins of the joint and becomes thicker as it moves inferiorly (sacral cartilage thicker than iliac cartilage).
Ligaments:
The ligaments stabilizing the SI joint are the strongest ligaments in the body. They consist of:
- Anterior Sacroiliac - an anteroinferior thickening of the fibrous capsule and is weak and thin when compared to the other ligaments of the joint. It connects the third sacral ligament to the lateral side of the preauricular sulcus and is better developed closer to the arcuate line and the PSIS. This ligament is injured most often and is a common source of pain because its thinness.
- Interosseus Sacroiliac - forms the major connection between the sacrum and the innominate and is a strong, short ligament deep to the posterior sacroiliac ligament. It resists anterior and inferior movement of the sacrum.
- Posterior (Dorsal) Sacroiliac - connects the PSIS with the lateral crest of the third and fourth segments of the sacrum and is very stong and tough. Nutation, which is anterior motion of the sacrum, slackens the ligament, and counternutation, which is posterior motion will make the ligament taut. It can be palpated directly below the PSIS and can often be a source of pain.
- Sacrotuberous - consists of three large fibrous bands and is blended with the posterior (dorsal) sacroiliac ligament. It stabilitzes against nutation of the sacrum and counteracts against posterior and superior migration of the sacrum during weight bearing.
- Sacrospinous - triangular shaped and thinner than the sacrotuberous ligament and goes from the ischial spine to the lateral parts of the sacrum and coccyx and then to the ischial spine laterally. Along with the sacrotuberous ligament, it opposes forward tilting of the sacrum on the innominates during weight bearing.
Muscles[edit | edit source]
There are 35 muscles that attach to the sacrum or innominates which mainly provide stability to the joint rather than producing movements.
Muscles that attach to the sacrum or innominates:
- Adductor brevis
- Adductor longus
- Adductor magnus
- Biceps femoris - long head
- Coccygeus
- Erector spinae
- External oblique
- Gluteus maxiumus
- Gluteus medius
- Gluteus minimus
- Gracilis
- Iliacus
- Inferior gemellus
- Internal oblique
- Latissimus dorsi
- Levator ani
- Multifidus
- Obturator internus
- Obturator externus
- Pectineus
- Piriformis
- Psoas minor
- Pyramidalis
- Quadratus femoris
- Quadratus lumborum
- Rectus abdominis
- Rectus femoris
- Sartorius
- Semimembranosus
- Semitendonosus
- Sphincter urethrae
- Superficial transverse perineal ischiocavernous
- Superior gemellus
- Tensor fascia lata
- Transversus abdominus
Specific Pathologies[edit | edit source]
There are many pathologies that could present at the site of the sacroiliac joint including: [8]
- Sacroiliac tuberculosis
- Spondyloarthropathy
- Crystal and pyogenic arthropathies
- Groin pain
- Osteitis pubis
- Pubic symphysis dysfunction
- Osteoarthritis
- Stress fracture
Special Tests[edit | edit source]
SI Joint stress tests
- Anterior Gapping test
- Posterior Distraction test
- Pubic Stress test
- Sacrotuberous Ligament Stress test
- Sacral Compression test
- Rotational Stress test
Leg Length tests
- Prone test
- Standing leg length test
- Functional leg length test
Other Special Tests
- Seated Flexion test (Piedallu's Sign)
- Long Sit test
- Sign of the Buttock
- Posterior Pelvic Pain Provocation test
- Gaenslen's test
- Yeoman's test
- FABER (Figure-Four) test
Other Important Information[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dutton M. Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw Hill, 2008.
- ↑ Cohen SP. Sacroiliac Joint Pain: A Comprehensive Review of Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Anesth Analg 2005; 101:1440-1453.
- ↑ Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function: A Comprehensive Analysis. 4th ed. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis, 2005.
- ↑ Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function: A Comprehensive Analysis. 4th ed. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis, 2005.
- ↑ Dutton M. Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw Hill, 2008.
- ↑ Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function: A Comprehensive Analysis. 4th ed. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis, 2005.
- ↑ Dutton M. Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw Hill, 2008.
- ↑ Dutton M. Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw Hill, 2008.