Splenius Cervicis: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) (references corrected. some formatting improved) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor ''' [[User:Oyemi Sillo|Oyemi Sillo]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Original Editor ''' [[User:Oyemi Sillo|Oyemi Sillo]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | |||
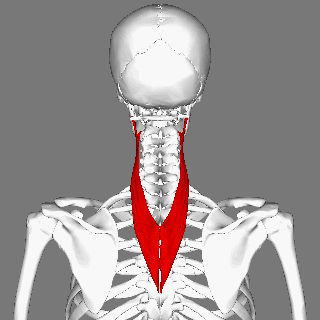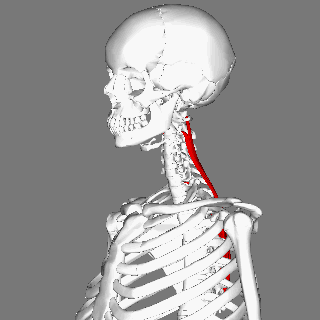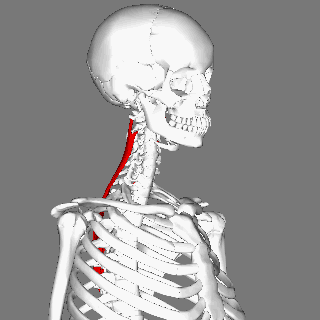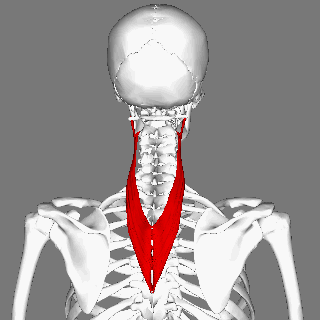
== Description == | == Description == | ||
Musculus splenius cervicis is one of the deep (or intrinsic) muscles of the | Musculus splenius cervicis is one of the deep (or intrinsic) muscles of the cervical and thoracic spine. <ref name="gray">Gray's Anatomy of Human Body, Bartleby.com edition. New York: 2000.fckLRhttp://www.bartleby.com/107/115.html</ref> Its fibres run superiorly and laterally. It assists in ipsilateral cervical side flexion and rotation, when both splenius cervicis muscles contract they extend the cervical spine. <ref name=":0">Palastanga, N., & Soames, R. (2012). Anatomy and human movement (6th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.</ref> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 12: | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
Spinous processes of T3 to T6 <ref name=" | Spinous processes of T3 to T6<ref name=":0" /> <br> | ||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 to C3.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves (C5, 6, 7, and 8)<ref name=" | Dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves (C5, 6, 7, and 8)<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
Muscular branches of the occipital artery from the external carotid artery. Dorsal branches of the posterior intercostal arteries from the thoracic aorta. <ref name=":1">Kenhub. 2021. ''Splenius cervicis muscle''. [online] Available at: <https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/splenius-cervicis-muscle> [Accessed 26 November 2021].</ref> | |||
== Action == | == Action == | ||
Bilaterally they extend the neck; unilaterally they laterally flex and rotate the head and neck to the same side. <ref name="wh" /> < | Bilaterally they extend the neck; unilaterally they laterally flex and rotate the head and neck to the ipsilateral (same) side<ref name=":1" />. <ref name="wh">Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics. 2021. ''Splenius Cervicis : Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics''. [online] Available at: <https://www.wheelessonline.com/bones/spine/splenius-cervicis/> [Accessed 26 November 2021].</ref> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Splenius cervicis also assists in supporting the head in the erect position<ref name="gray" /><br> | |||
<br> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Cervical Spine - Anatomy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:45, 26 November 2021
Original Editor Oyemi Sillo Top Contributors - Oyemi Sillo, WikiSysop, Tarina van der Stockt, Kim Jackson and Abbey Wright
Description[edit | edit source]
Musculus splenius cervicis is one of the deep (or intrinsic) muscles of the cervical and thoracic spine. [1] Its fibres run superiorly and laterally. It assists in ipsilateral cervical side flexion and rotation, when both splenius cervicis muscles contract they extend the cervical spine. [2]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Spinous processes of T3 to T6[2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 to C3.[2]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves (C5, 6, 7, and 8)[2]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Muscular branches of the occipital artery from the external carotid artery. Dorsal branches of the posterior intercostal arteries from the thoracic aorta. [3]
Action[edit | edit source]
Bilaterally they extend the neck; unilaterally they laterally flex and rotate the head and neck to the ipsilateral (same) side[3]. [4]
Function[edit | edit source]
Splenius cervicis also assists in supporting the head in the erect position[1]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gray's Anatomy of Human Body, Bartleby.com edition. New York: 2000.fckLRhttp://www.bartleby.com/107/115.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Palastanga, N., & Soames, R. (2012). Anatomy and human movement (6th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kenhub. 2021. Splenius cervicis muscle. [online] Available at: <https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/splenius-cervicis-muscle> [Accessed 26 November 2021].
- ↑ Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics. 2021. Splenius Cervicis : Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics. [online] Available at: <https://www.wheelessonline.com/bones/spine/splenius-cervicis/> [Accessed 26 November 2021].