Sternocleidomastoid: Difference between revisions
Venus Pagare (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Venus Pagare (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}   | |||
'''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}   | |||
== Description<br> == | == Description<br> == | ||
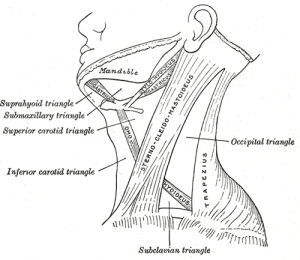
Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)is a paired superficial muscle in the anterior portion of the neck. Carotid sheath structures lie deep to it | Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)is a paired superficial muscle in the anterior portion of the neck. Carotid sheath structures lie deep to it | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 13: | ||
Mastoid process and lateral 1/2 of the superior nuchal line | Mastoid process and lateral 1/2 of the superior nuchal line | ||
<br> | |||
[[Image:STERNO2.png|center|300x300px]] | |||
[[Image:STERNO2.png|center|300x300px]] | |||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Revision as of 20:33, 26 January 2014
Lead Editors - Venus Pagare, Kim Jackson, Joao Costa, Admin, Daniele Barilla, WikiSysop, Joshua Samuel, Tarina van der Stockt, Lucinda hampton, Evan Thomas and Oyemi Sillo
Description
[edit | edit source]
Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)is a paired superficial muscle in the anterior portion of the neck. Carotid sheath structures lie deep to it
Origin[edit | edit source]
SCM origins from 2 heads as follows: Sternal head: anterior surface of the manubrium Clavicular head: medial 1/3rd of the clavicle
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Mastoid process and lateral 1/2 of the superior nuchal line
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Spinal accessory nerve (XI), with sensory supply from C2 & C3 (for proprioception)
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Sternocleidomastoid branch of the Occipital artery
Action[edit | edit source]
Draws the mastoid process down toward the same side which causes the chin to turn up toward the opposite side; acting together, the muscles of the two sides flex the neck
Function[edit | edit source]
Rotation of the head to the opposite side or obliquely rotate the head. It also flexes the neck. When acting together it flexes the neck and extends the head. When acting alone it rotates to the opposite side (contralaterally) and slightly (laterally) flexes to the same side. It also acts as an accessory muscle of inspiration.
Resources[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.