Work-Related Musculoskeletal Injuries and Prevention: Difference between revisions
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "</big>" to "") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
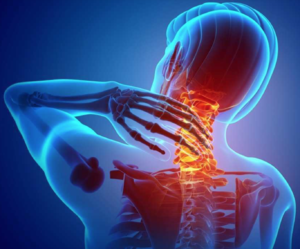
[[File:Neck Pain Diagram.png|right|frameless]] | Adverse ergonomic factors is considered risky. Especially, bad postures, high loads, fast movements, reduced recovery time is proved to be harmful to the upper extremity. [[File:Neck Pain Diagram.png|right|frameless]] | ||
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMDs) refer to the musculoskeletal disorders that are caused by one's work | Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMDs) refer to the musculoskeletal disorders that are caused by one's work | ||
Revision as of 09:33, 7 July 2023
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Adverse ergonomic factors is considered risky. Especially, bad postures, high loads, fast movements, reduced recovery time is proved to be harmful to the upper extremity.
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMDs) refer to the musculoskeletal disorders that are caused by one's work
- Common in occupations such as manufacturing, industrial technicians, office workers, etc.
- Primary cause of work-related disability and loss of productivity[3]
- High workload and sustained stress may result in anxiety and mental health issue[1]
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
As we targeting the musculoskeletal disorders at neck and upper limb, these anatomy structure may be included in WRMDs:
- Neck
- Cervical and thoracic spine
- Shoulder joint
- Elbow
- Forearm
- Wrist
- Fingers
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
- Musculoskeletal pain and myalgias[1]
- Muscle stiffness
- Redness
- Weakness[4]
- Numbness
- Tendon inflammations and related conditions, such as bursitis, tenosynovitis, etc.[4]
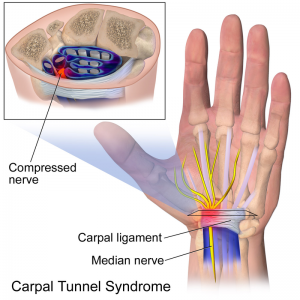
- Nerve compression disorders, such as carpal tunnel syndrome[4]
- Osteoarthritis[4]
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Inability to work or execute daily function
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
Interventions:
Resistance training[1]
- According to the research, individualized resistance training specific to the pain affected area has positive effect to the pain intensity
- Elastic resistance exercises
- Progressive training with variable resistance and/or contraction type and speed
Motor control training[1]
- Isolated dynamic joint mobility movements
- Slow speed (15-30 seconds/repetitive)
- Target the site of pain
Posture modification
Manual therapy
- Should be conducted by physiotherapists based on individual's condition
Management
Job modifications
Pain relief by using prescribed medication
Search for professionals such as physiotherapists for advice
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Jay K, Brandt M, Sundstrup E, Schraefel M, Jakobsen MD, Sjøgaard G, et al.. Effect of individually tailored biopsychosocial workplace interventions on chronic musculoskeletal pain, stress and work ability among laboratory technicians: randomized controlled trial protocol. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders [Internet]. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders; 2014;15(1):444. Available from: https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-15-444
- ↑ Zebis MK, Andersen LL, Pedersen MT, Mortensen P, Andersen CH, Pedersen MM, et al.. Implementation of neck/shoulder exercises for pain relief among industrial workers: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders [Internet]. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders; 2011;12(1):205. Available from: https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-12-205
- ↑ Rasotto C, Bergamin M, Simonetti A, Maso S, Bartolucci GB, Ermolao A, et al. Tailored exercise program reduces symptoms of upper limb work-related musculoskeletal disorders in a group of metalworkers: A randomized controlled trial. Manual Therapy. 2015;20(1):56–62.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Etana G, Ayele M, Abdissa D, Gerbi A. Prevalence of Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders and Associated Factors Among Bank Staff in Jimma City, Southwest Ethiopia, 2019: An Institution-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Pain Research. Journal of Pain Research; 2021;Volume 14:2071–82.