Sciatic Nerve Injury: Difference between revisions
(physiosection funny fact) |
Rachael Lowe (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Definition/Description == | == Definition/Description == | ||
[[File:Sciatic nerve.png|right|frameless|581x581px]] | [[File:Sciatic nerve.png|right|frameless|581x581px]] | ||
The causes can be spinal or non spinal causes<ref name=":10" /> or iatrogenic | [[Sciatic Nerve]] Injury can occur due to trauma (pressure, stretching or cutting) to the nerve. This type of injury injury can cause degrees of muscle power loss and altered sensation.<ref>Orthoinfo. [https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/nerve-injuries/ Nerve injuries]. Available from: https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/nerve-injuries/ (last accessed 15.3.2019)</ref> The causes can be spinal or non spinal causes<ref name=":10" /> or iatrogenic: | ||
Spinal causes | Spinal causes | ||
* [[Spinal Stenosis|Spinal stenosis]] (due to degenerative bone disorders, trauma, inflammatory | * [[Spinal Stenosis|Spinal stenosis]] (due to degenerative bone disorders, trauma, inflammatory disease | ||
* [[Spondylolisthesis]] | * [[Spondylolisthesis]] | ||
* Growth in spinal canal (eg.abscess) | * Growth in spinal canal (eg.abscess) | ||
Non Spinal causes which compress or damage the nerve | Non Spinal causes which compress or damage the nerve | ||
* [[Piriformis Syndrome| | * [[Piriformis Syndrome|Piriformis]] syndrome | ||
* [[Pregnancy Related Pelvic Pain| | * [[Pregnancy Related Pelvic Pain|Pregnancy]] | ||
* Trauma to leg | * Trauma to leg | ||
* Pelvic tumours | * Pelvic tumours | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
== Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | == Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | ||
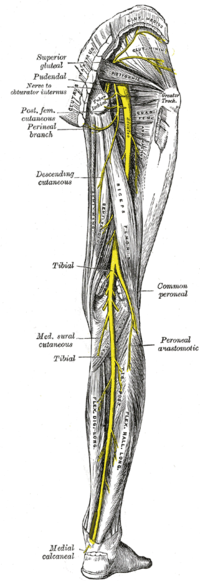
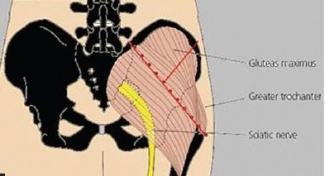
Sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body (with nerve root L4,L5,S1,S2,S3) and the continuation of the sacral plexus. The sciatic nerve is the most lateral structure emerging through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis. Medial to it are the inferior gluteal nerve and vessels, the internal pudendal vessels, and the pudendal nerve. It crosses the posterior surface of the ischium, crosses obturator internus, with its gemelli, quadratus femoris and descends on adductor magnus.The sciatic divides into its terminal branches, the tibial and common peroneal nerves, usually just below the mid-thigh, although a higher division is not uncommon.<ref>Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th Edition. 2006 Pg 621</ref><ref>Ellis H. Clinical Anatomy: A revision and applied anatomy for clinical students. 11<sup>th</sup> Edition. 2006 Pg 253-254</ref><br> | Sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body (with nerve root L4,L5,S1,S2,S3) and the continuation of the sacral plexus. The sciatic nerve is the most lateral structure emerging through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis. Medial to it are the inferior gluteal nerve and vessels, the internal pudendal vessels, and the pudendal nerve. It crosses the posterior surface of the ischium, crosses obturator internus, with its gemelli, quadratus femoris and descends on adductor magnus. The sciatic divides into its terminal branches, the tibial and common peroneal nerves, usually just below the mid-thigh, although a higher division is not uncommon.<ref>Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th Edition. 2006 Pg 621</ref><ref>Ellis H. Clinical Anatomy: A revision and applied anatomy for clinical students. 11<sup>th</sup> Edition. 2006 Pg 253-254</ref><br> | ||
[[File:Ca.jpg|center|thumb|325x325px|<ref>Dayananda L, Belaval V V, Raina A, Chandana R. Intended intramuscular gluteal injections: Are they truly intramuscular?. J Postgrad Med [serial online] 2014 [cited 2017 Aug 16];60:175-8. Available from: <nowiki>http://www.jpgmonline.com/text.asp?2014/60/2/175/132334</nowiki></ref>Figure 1]] | [[File:Ca.jpg|center|thumb|325x325px|<ref>Dayananda L, Belaval V V, Raina A, Chandana R. Intended intramuscular gluteal injections: Are they truly intramuscular?. J Postgrad Med [serial online] 2014 [cited 2017 Aug 16];60:175-8. Available from: <nowiki>http://www.jpgmonline.com/text.asp?2014/60/2/175/132334</nowiki></ref>Figure 1]] | ||
== Epidemiology/ | == Epidemiology/Aetiology == | ||
Injection palsy can begin suddenly or hours following damage to the sciatic nerve. Misplaced intramuscular injection at the gluteal region is the most common cause of injury and it is attributed to either frequent injections or poor techniques as a result of inadequately trained staff or unqualified staff. <ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /><br>It affects more males than females with a ratio of 2.7:1.<ref name=":8">Geyik S, Geyik M, Yigiter R, Kuzudisli S, Saglam S, Elci MA, Yilmaz M. Preventing Sciatic Nerve Injury due to Intramuscular Injection: Ten-Year Single-Center Experience and Literature Review. Turk Neurosurg 27(4):636-640, 2017</ref> Within a period of two years, Pakistan recorded annual incidence of six (6) million | Injection palsy can begin suddenly or hours following damage to the sciatic nerve. Misplaced intramuscular injection at the gluteal region is the most common cause of injury and it is attributed to either frequent injections or poor techniques as a result of inadequately trained staff or unqualified staff. <ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /><br>It affects more males than females with a ratio of 2.7:1.<ref name=":8">Geyik S, Geyik M, Yigiter R, Kuzudisli S, Saglam S, Elci MA, Yilmaz M. Preventing Sciatic Nerve Injury due to Intramuscular Injection: Ten-Year Single-Center Experience and Literature Review. Turk Neurosurg 27(4):636-640, 2017</ref> Within a period of two years, Pakistan recorded annual incidence of six (6) million children.<ref name=":0" /> For overview of nerve [[Axillary Nerve Injury|injury]] | ||
== Clinical Presentation/Characteristics == | == Clinical Presentation/Characteristics == | ||
The persistent and most reported symptoms are pain and abnormal gait pattern.<ref name=":2" /> However, pain intensity is difficult to quantity or rate particularly in the | The persistent and most reported symptoms are pain and abnormal gait pattern.<ref name=":2" /> However, pain intensity is difficult to quantity or rate particularly in the Paediatric population but facial expression is quite helpful. Others include; | ||
* Foot drop<ref name=":3">Napiontek M, Ruszkowski K. Paralytic drop foot and Gluteal fibrosis after intramuscular injection. ''J Bone Joint Surg'' ''[Br]'' 1993; 75-B: 83-5</ref><ref name=":4">Brown BA: Sciatic injection neuropathy. Calif Med 116: 13-15, May 1972</ref> | * Foot drop<ref name=":3">Napiontek M, Ruszkowski K. Paralytic drop foot and Gluteal fibrosis after intramuscular injection. ''J Bone Joint Surg'' ''[Br]'' 1993; 75-B: 83-5</ref><ref name=":4">Brown BA: Sciatic injection neuropathy. Calif Med 116: 13-15, May 1972</ref> | ||
* External rotation and abduction contracture of the hip<ref name=":3" /> | * External rotation and abduction contracture of the hip<ref name=":3" /> | ||
* Equinovarus or Equinus deformity<ref name=":3" /> | * Equinovarus or Equinus deformity<ref name=":3" /> | ||
* Muscular weakness/atrophy<ref name=":4" /> | * Muscular weakness/atrophy<ref name=":4" /> | ||
* Motor and sensory deficit such as | * Motor and sensory deficit such as paraesthesia and numbness<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":1" /> | ||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
Sciatic neuropathy is more of a clinical diagnosis. Well detailed subjective and objective examination is the golden rule. In recent times, debate on the use of imaging modalities is on the fast pace. Electro-diagnostic studies are; | Sciatic neuropathy is more of a clinical diagnosis. Well detailed subjective and objective examination is the golden rule. In recent times, debate on the use of imaging modalities is on the fast pace. Electro-diagnostic studies are; | ||
* Electromyography<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":5" /> | * Electromyography<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":5" /> | ||
* Magnetic Resonance Imaging<ref name=":7">Ong MJF, Lim GHT, Kei PL. Clinics in diagnostic imaging (140). ''Singapore Med J 2012; 53(8): 551–555''</ref><ref name=":5" /> | * Magnetic Resonance Imaging<ref name=":7">Ong MJF, Lim GHT, Kei PL. Clinics in diagnostic imaging (140). ''Singapore Med J 2012; 53(8): 551–555''</ref><ref name=":5" /> | ||
== Medical Management == | == Medical Management == | ||
In most cases, symptoms of sciatic nerve injury does not respond to the use of non | In most cases, symptoms of sciatic nerve injury does not respond to the use of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), opioids and myorelaxants.<ref name=":6" /> However, the use of methyl prednisolone via transscaral block was effective to manage the neuropathic pain, motor and sensory deficits.<ref name=":6" /> In addition, a recent study showed beneficial use of methyprednisolone via both intravenous and oral routes.<ref name=":5" /> | ||
Surgery is opted for patients that did not improve beyond 3 months of sustaining injection palsy<ref name=":9">Arindhom Kakati, Dhananjaya Bhat, Bhagavathula Indira Devi, Dhaval Shukla J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013 Jan-Mar; 4(1): 13–18. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.105603</ref>. Common procedures include neurolysis<ref name=":9" /><ref name=":4" /> and grafting<ref name=":7" /> with serial clinical and electrophysiological monitoring. Patients with foot deformity can opt for elongation of the tendon Achilles, osteotomy and capsulotomy.<ref name=":3" /> Although, there are conflicting findings comparing conservative and surgical interventions. | Surgery is opted for patients that did not improve beyond 3 months of sustaining injection palsy<ref name=":9">Arindhom Kakati, Dhananjaya Bhat, Bhagavathula Indira Devi, Dhaval Shukla J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013 Jan-Mar; 4(1): 13–18. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.105603</ref>. Common procedures include neurolysis<ref name=":9" /><ref name=":4" /> and grafting<ref name=":7" /> with serial clinical and electrophysiological monitoring. Patients with foot deformity can opt for elongation of the tendon Achilles, osteotomy and capsulotomy.<ref name=":3" /> Although, there are conflicting findings comparing conservative and surgical interventions. | ||
== Physical Therapy Management == | == Physical Therapy Management == | ||
Conservative means is the first line approach for the management of patients with sciatic nerve injury | [[File:Rehab equipment.png|right|frameless]]Conservative means is the first line approach for the management of patients with sciatic nerve injury<ref name=":9" /><ref name=":4" /><ref name=":7" /><ref name=":3" /><ref name=":8" /> | ||
* Exercise prescription | |||
Exercise prescription | * Electrical muscle stimulation | ||
* Bio-laser stimulation<ref name=":11">Suszyński K, Marcol W, Górka D. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4705788/ Physiotherapeutic techniques used in the management of patients with peripheral nerve injuries.] Neural regeneration research. 2015 Nov;10(11):1770. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4705788/ (last accessed 15.3.2019)</ref> | |||
Electrical muscle stimulation | * Magnetotherapy<ref name=":11" /> | ||
* Massage therapy | |||
Bio-laser stimulation<ref name=":11">Suszyński K, Marcol W, Górka D. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4705788/ Physiotherapeutic techniques used in the management of patients with peripheral nerve injuries.] Neural regeneration research. 2015 Nov;10(11):1770. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4705788/ (last accessed 15.3.2019)</ref> | * Use of physical agents | ||
* Splinting | |||
Magnetotherapy<ref name=":11" /> | Physiotherapists should ensure thorough evaluation through out the course of the treatment. Good clinical judgement, decision making skills and experience are quite important for effective rehabilitation. | ||
Massage therapy | |||
Use of physical agents | |||
Splinting | |||
Physiotherapists | |||
A 2015 paper reported that Physiotherapeutic techniques used in peripheral nerve injures lack good randomised data. It went on to outline that many physiotherapists, physicians and clinicians understand fully treatment and intervention therapy, often not comprehending the time that nerves need to regenerate.<ref name=":11" /> | A 2015 paper reported that Physiotherapeutic techniques used in peripheral nerve injures lack good randomised data. It went on to outline that many physiotherapists, physicians and clinicians understand fully treatment and intervention therapy, often not comprehending the time that nerves need to regenerate.<ref name=":11" /> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 67: | ||
== Differential Diagnosis == | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
* [[Sciatica]] | * [[Sciatica]] | ||
* [[Piriformis Syndrome| | * [[Piriformis Syndrome|Piriformis Syndrome]]<ref name=":5" /> | ||
* [[Lumbar Radiculopathy]]<ref name=":4" /> | * [[Lumbar Radiculopathy]]<ref name=":4" /> | ||
* Sciatic nerve | * Sciatic nerve tumour<ref name=":7" /> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references />''' | <references />'''[[Category:Primary Contact]]''' | ||
[[Category:Primary Contact]]''' | |||
[[Category:Neuropathy]] | [[Category:Neuropathy]] | ||
Revision as of 10:37, 15 March 2019
Original Editor - User: Fasuba Ayobami Top Contributors - Fasuba Ayobami, Lucinda hampton, Rosie Swift, Olajumoke Ogunleye, Amanda Ager, Aminat Abolade, Rachael Lowe, Shaimaa Eldib and Claire Knott
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Sciatic Nerve Injury can occur due to trauma (pressure, stretching or cutting) to the nerve. This type of injury injury can cause degrees of muscle power loss and altered sensation.[1] The causes can be spinal or non spinal causes[2] or iatrogenic:
Spinal causes
- Spinal stenosis (due to degenerative bone disorders, trauma, inflammatory disease
- Spondylolisthesis
- Growth in spinal canal (eg.abscess)
Non Spinal causes which compress or damage the nerve
- Piriformis syndrome
- Pregnancy
- Trauma to leg
- Pelvic tumours
Iatrogenic causes ( caused by medical examination or treatment ) After viewing this video this page goes on to describe these iatrogenic causes.
Iatrogenic causes of Sciatic Nerve Injury.[edit | edit source]
Trauma to the sciatic nerve through
- Injection injuries ( Also referred to as injection palsy.[3][4] via intramuscular injection at gluteal region (dorsogluteal site),It describes a situation where there is a loss of movement and or lack of sensation at the affected lower extremity with or without pain.)
- Total Hip Replacement (nerve compression and stretch during surgery.[6][7][8] causing damage to the sciatic nerve that serves the majority of muscle groups in the lower limb, resulting in dysfunction. Reported at a level of 1%)[9]
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body (with nerve root L4,L5,S1,S2,S3) and the continuation of the sacral plexus. The sciatic nerve is the most lateral structure emerging through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis. Medial to it are the inferior gluteal nerve and vessels, the internal pudendal vessels, and the pudendal nerve. It crosses the posterior surface of the ischium, crosses obturator internus, with its gemelli, quadratus femoris and descends on adductor magnus. The sciatic divides into its terminal branches, the tibial and common peroneal nerves, usually just below the mid-thigh, although a higher division is not uncommon.[10][11]
Epidemiology/Aetiology[edit | edit source]
Injection palsy can begin suddenly or hours following damage to the sciatic nerve. Misplaced intramuscular injection at the gluteal region is the most common cause of injury and it is attributed to either frequent injections or poor techniques as a result of inadequately trained staff or unqualified staff. [6][7][3]
It affects more males than females with a ratio of 2.7:1.[13] Within a period of two years, Pakistan recorded annual incidence of six (6) million children.[6] For overview of nerve injury
Clinical Presentation/Characteristics[edit | edit source]
The persistent and most reported symptoms are pain and abnormal gait pattern.[3] However, pain intensity is difficult to quantity or rate particularly in the Paediatric population but facial expression is quite helpful. Others include;
- Foot drop[14][15]
- External rotation and abduction contracture of the hip[14]
- Equinovarus or Equinus deformity[14]
- Muscular weakness/atrophy[15]
- Motor and sensory deficit such as paraesthesia and numbness[3][7]
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
Sciatic neuropathy is more of a clinical diagnosis. Well detailed subjective and objective examination is the golden rule. In recent times, debate on the use of imaging modalities is on the fast pace. Electro-diagnostic studies are;
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
In most cases, symptoms of sciatic nerve injury does not respond to the use of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), opioids and myorelaxants.[4] However, the use of methyl prednisolone via transscaral block was effective to manage the neuropathic pain, motor and sensory deficits.[4] In addition, a recent study showed beneficial use of methyprednisolone via both intravenous and oral routes.[8]
Surgery is opted for patients that did not improve beyond 3 months of sustaining injection palsy[17]. Common procedures include neurolysis[17][15] and grafting[16] with serial clinical and electrophysiological monitoring. Patients with foot deformity can opt for elongation of the tendon Achilles, osteotomy and capsulotomy.[14] Although, there are conflicting findings comparing conservative and surgical interventions.
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
Conservative means is the first line approach for the management of patients with sciatic nerve injury[17][15][16][14][13]
- Exercise prescription
- Electrical muscle stimulation
- Bio-laser stimulation[18]
- Magnetotherapy[18]
- Massage therapy
- Use of physical agents
- Splinting
Physiotherapists should ensure thorough evaluation through out the course of the treatment. Good clinical judgement, decision making skills and experience are quite important for effective rehabilitation.
A 2015 paper reported that Physiotherapeutic techniques used in peripheral nerve injures lack good randomised data. It went on to outline that many physiotherapists, physicians and clinicians understand fully treatment and intervention therapy, often not comprehending the time that nerves need to regenerate.[18]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Sciatica
- Piriformis Syndrome[8]
- Lumbar Radiculopathy[15]
- Sciatic nerve tumour[16]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Orthoinfo. Nerve injuries. Available from: https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/nerve-injuries/ (last accessed 15.3.2019)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Osmosis. Sciatica. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VYj-JfX0wT0 (last accessed 15.3.2019)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Toopchizadeh V, Barzegar M, Habibzadeh A. Sciatic Nerve Injection Palsy in Children, Electrophysiologic Pattern and Outcome: A Case Series Study. Iran J Child Neurol. Summer 2015;9(3):69-72.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Evren Eker H, Yalcin Cok O, Aribogan A. A Treatment Option for Post-Injection Sciatic Neuropathy: Transsacral Block with Methylprednisolone. A Case Report. Pain Physician 2010; 13:451-456
- ↑ Nabil Ebraheim. Glut injections. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c68pLxbqs_M (last accessed 15.3.2019)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Cornwall, J. Are nursing students safe when choosing gluteal intramuscular injection locations? AMJ 2011, 4, 6, 315-‐321
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Mishra P, Stringer MD. Sciatic nerve injury from intramuscular injection: a persistent and global problem. Int J Clin Pract, October 2010, 64, 11, 1573–1579
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Altıntaş A, Gündüz A, Kantarcı F, Gözübatık Çelik G, Koçer N, Kızıltan ME. Sciatic neuropathy developed after injection during curettage. A Case Report. Agri 2016;28(1):46–48
- ↑ Schmalzried TP, Noordin S, Amstutz HC. Update on nerve palsy associated with total hip replacement. Clinical orthopaedics and related research. 1997 Nov(344):188-206. (last accessed 15.3.2019)
- ↑ Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th Edition. 2006 Pg 621
- ↑ Ellis H. Clinical Anatomy: A revision and applied anatomy for clinical students. 11th Edition. 2006 Pg 253-254
- ↑ Dayananda L, Belaval V V, Raina A, Chandana R. Intended intramuscular gluteal injections: Are they truly intramuscular?. J Postgrad Med [serial online] 2014 [cited 2017 Aug 16];60:175-8. Available from: http://www.jpgmonline.com/text.asp?2014/60/2/175/132334
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Geyik S, Geyik M, Yigiter R, Kuzudisli S, Saglam S, Elci MA, Yilmaz M. Preventing Sciatic Nerve Injury due to Intramuscular Injection: Ten-Year Single-Center Experience and Literature Review. Turk Neurosurg 27(4):636-640, 2017
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 Napiontek M, Ruszkowski K. Paralytic drop foot and Gluteal fibrosis after intramuscular injection. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1993; 75-B: 83-5
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 Brown BA: Sciatic injection neuropathy. Calif Med 116: 13-15, May 1972
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 Ong MJF, Lim GHT, Kei PL. Clinics in diagnostic imaging (140). Singapore Med J 2012; 53(8): 551–555
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Arindhom Kakati, Dhananjaya Bhat, Bhagavathula Indira Devi, Dhaval Shukla J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013 Jan-Mar; 4(1): 13–18. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.105603
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Suszyński K, Marcol W, Górka D. Physiotherapeutic techniques used in the management of patients with peripheral nerve injuries. Neural regeneration research. 2015 Nov;10(11):1770. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4705788/ (last accessed 15.3.2019)
'