Leprosy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
When cell mediated immunity (CMI) is effective in controlling infection, lesions are healed spontaneously or produce paucibacillary type of leprosy. Person with good CMI may have granuloma formation in cutaneous nerve causing swelling of nerve and hence destroyed. It causes inflammation in epineurium causes compression and destruction of unmyelinated sensory and autonomic fiber. Myelinated motor fibers are the last to get affected causing motor impairments. Good CMI limits disease to schwann cells-pure neural leprosy. | When cell mediated immunity (CMI) is effective in controlling infection, lesions are healed spontaneously or produce paucibacillary type of leprosy. Person with good CMI may have granuloma formation in cutaneous nerve causing swelling of nerve and hence destroyed. It causes inflammation in epineurium causes compression and destruction of unmyelinated sensory and autonomic fiber. Myelinated motor fibers are the last to get affected causing motor impairments. Good CMI limits disease to schwann cells-pure neural leprosy. | ||
If CMI is deficient, produce multibacilary leprosy with multi system involvement. Bacilli which escapes from nerve to adjacent skin caused classical skin lesions. Bacilli liberated by schwann cells engulfed by histiocytes-wandering macrophages-travel to other tissue through blood and lymph. Phagocytosis of ''M. leprae'' by monocyte-derived macrophages can be mediated by complement receptors CR1 (CD35), CR3 (CD11b/CD18), and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) and is regulated by protein kinase. | If CMI is deficient, produce multibacilary leprosy with multi system involvement. Bacilli which escapes from nerve to adjacent skin caused classical skin lesions. Bacilli liberated by schwann cells engulfed by histiocytes-wandering macrophages-travel to other tissue through blood and lymph. Phagocytosis of ''M. leprae'' by monocyte-derived macrophages can be mediated by complement receptors CR1 (CD35), CR3 (CD11b/CD18), and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) and is regulated by protein kinase. | ||
== Immunological reactions == | |||
Lepra reaction is the immune- mediated complication is associated up to 50% of patients, can cause rapid nerve damage resulting in anaesthesia and weakness, which in turn increases risk of injury and deformity. They can occur at presentation, during treatment for leprosy with multi-drug therapy (MDT) and occasionally following completion of MDT. | |||
Two types of reactions are recognized: | |||
* Type 1 (T1R, also known as reversal or downgrading) | |||
** Occurs BT, BB, or BL disease | |||
** Caused by an increase in cell-mediated immunity, result in skin or nerve inflammation at sites of ''Mycobacterium leprae'' infection. | |||
** Clinical manifestations: | |||
*** A red swollen patch in preexisting skin lesion or overlying a major nerve trunk. | |||
*** Erythema and induration of pre-existing skin lesion | |||
*** Inflammation associated with reactions can lead to severe nerve injury with subsequent paralysis and deformity | |||
*** Ulcerated skin lesions | |||
*** Pain or tenderness in one or more nerves | |||
*** Loss of nerve function with muscle weakness or loss of sensation. | |||
** Observed recovery rate is 60-70% in those who are identified and treated within six months of onset. | |||
* Type 2 reactions (erythema nodosum leprosum, ENL) | |||
** Caused by immune complex-mediated. | |||
** Symptoms are diverse with characteristic painful, erythematous subcutaneous nodules occurring with systemic features including fever, lymphadenitis, arthritis, neuritis, iridocyclitis or orchitis. | |||
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
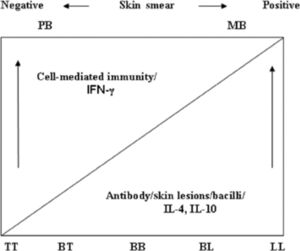
[[File:Classification of leprosy.jpeg|thumb|Relationship of various forms of leprosy, immune response, bacterial load and skin lesions.]] | |||
Leprosy can be broadly classified via two classification system. | Leprosy can be broadly classified via two classification system. | ||
| Line 155: | Line 177: | ||
* Perforated nasal septum | * Perforated nasal septum | ||
* Trophic ulcers | * Trophic ulcers | ||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 25 January 2022
Top Contributors - Manisha Shrestha, Kim Jackson, Nikhil Benhur Abburi and Nupur Smit Shah
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (25/01/2022)
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Leprosy is a chronic infectious bacterial disease affecting the nerves, skin, eyes, and muscosa of upper respiratory tract. Leprosy was renamed Hansen’s disease after Norwegian scientist Gerhard Henrik Armauer Hansen, who in 1873 discovered the slow-growing bacterium now known as Mycobacterium leprae as the cause of the illness.
Leprosy is curable and treatment in the early stages can prevent disability. It can be cured with multidrug treatment regime, if early diagnosis is made.
Leprosy is a polymorphic infectious disease, the manifestation of which is determined by the immune system of the host.[1]
World Leprosy Day is observed on the last Sunday of January each year. Established in 1954 by French philanthropist Raoul Follereau, it aims to raise awareness about leprosy (now called Hansen’s disease) and teach people about this ancient disease that is easily curable today.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Around the world:
- The number of new cases reported globally to World Health Organization (WHO)external icon in 2019 was more than 200,000.
- Close to 15,000 children were diagnosed with Hansen’s disease in 2019, more than 40 a day.
- An estimated 2 to 3 million people are living with Hansen’s disease-related disabilities globally.
- In 2019, the countries with the highest number of new diagnoses were India, Brazil, and Indonesia.
- Over half of all new cases of Hansen’s disease are diagnosed in India, which remains home to a third of the world’s poor, a group disproportionately affected by the disease.[1]
- Among the new cases, 10 816 new cases were detected with grade- 2 disabilities (G2D) and the G2D rate was recorded at 1.4 per million population.[2]
Mycobacterium leprae[edit | edit source]
Mycobacterium leprae is
- an intracellular, pleomorphic, acid-fast, pathogenic bacterium
- an aerobic bacillus (rod-shaped bacterium)
- in size and shape, it closely resembles Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- The difficulty in culturing the organism appears to be because it is an obligate intracellular parasite that lacks many necessary genes for independent survival.
- grown in mouse foot pads and more recently in nine-banded armadillos
- It multiplies slowly. On average, the disease incubation period is 5 years but symptoms may occur within 1 year. It can also take as long as 20 years or even more to occur.
- They can be grown in the laboratory by injection into the footpads of mice.
Mode of transmission[edit | edit source]
- Two exit routes of M. leprae from the human body often described are the skin and the nasal mucosa.
- The entry route of M. leprae into the human body is also not definitively known. The skin and the upper respiratory tract are most likely; however, recent research increasingly favours the respiratory route.[2]
- The bacillus is likely transmitted via droplets, from the nose and mouth, during close and frequent contact with untreated cases.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
[edit | edit source]
Pheripheral nervous system
Pheripheral nerve and adjacent cells( schwann cell)
Layers of Skin
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
Lepra bacilli enters into the body through respiratory route. Then those bacilli migrates towards the neural tissues and binds to schwann cells ( which is the major target of the bacilli). Afterward, it invades schwann cells by specific laminin binding protein and phenolic glycolipid-1(PGL-1). Binding of M. leprae to SCs induces demyelination and loss of axonal conductance. Bacteria are also found in macrophages, muscle cells and endothelial cells of blood vessels. Bacilli start multiplying slowly within the cells and gets liberated from destroyed cells and then enter unaffected cells. As bacilli multiply ,bacterial load increases in body and thus infection is recognized by body immune system. Specific and effective cell mediated immunity provides protection to a person against leprosy.
When cell mediated immunity (CMI) is effective in controlling infection, lesions are healed spontaneously or produce paucibacillary type of leprosy. Person with good CMI may have granuloma formation in cutaneous nerve causing swelling of nerve and hence destroyed. It causes inflammation in epineurium causes compression and destruction of unmyelinated sensory and autonomic fiber. Myelinated motor fibers are the last to get affected causing motor impairments. Good CMI limits disease to schwann cells-pure neural leprosy.
If CMI is deficient, produce multibacilary leprosy with multi system involvement. Bacilli which escapes from nerve to adjacent skin caused classical skin lesions. Bacilli liberated by schwann cells engulfed by histiocytes-wandering macrophages-travel to other tissue through blood and lymph. Phagocytosis of M. leprae by monocyte-derived macrophages can be mediated by complement receptors CR1 (CD35), CR3 (CD11b/CD18), and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) and is regulated by protein kinase.
Immunological reactions[edit | edit source]
Lepra reaction is the immune- mediated complication is associated up to 50% of patients, can cause rapid nerve damage resulting in anaesthesia and weakness, which in turn increases risk of injury and deformity. They can occur at presentation, during treatment for leprosy with multi-drug therapy (MDT) and occasionally following completion of MDT.
Two types of reactions are recognized:
- Type 1 (T1R, also known as reversal or downgrading)
- Occurs BT, BB, or BL disease
- Caused by an increase in cell-mediated immunity, result in skin or nerve inflammation at sites of Mycobacterium leprae infection.
- Clinical manifestations:
- A red swollen patch in preexisting skin lesion or overlying a major nerve trunk.
- Erythema and induration of pre-existing skin lesion
- Inflammation associated with reactions can lead to severe nerve injury with subsequent paralysis and deformity
- Ulcerated skin lesions
- Pain or tenderness in one or more nerves
- Loss of nerve function with muscle weakness or loss of sensation.
- Observed recovery rate is 60-70% in those who are identified and treated within six months of onset.
- Type 2 reactions (erythema nodosum leprosum, ENL)
- Caused by immune complex-mediated.
- Symptoms are diverse with characteristic painful, erythematous subcutaneous nodules occurring with systemic features including fever, lymphadenitis, arthritis, neuritis, iridocyclitis or orchitis.
Classification[edit | edit source]
Leprosy can be broadly classified via two classification system.
- Ridley and Jopling classification
In the 1960s, Ridley and Jopling proposed a histological classification scheme for leprosy that ranged in severity. Leprosy is classified within two poles of the disease with transition between the clinical forms . Clinical, histopathological, and immunological criteria identify five forms of leprosy:
- Tuberculoid leprosy (TT)
- Borderline tuberculoid (BT)
- Mid borderline (BB)
- Borderline lepromatous (BL)
- Lepromatous leprosy (LL)
2. WHO classification
Initially, patients were divided into two groups for therapeutic purposes: paucibacillary (TT, BT) and multibacillary (midborderline (BB), BL, LL) . It was recommended later that the classification is to be based on the number of skin lesions, less than or equal to five for paucibacillary (PB) and greater than five for the multibacillary (MB) form. [1]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Clinical features of Leprosy
| Characteristics | Tuberculoid | Borderline tuberculoid | Midborderline | Borderline lepromatous | Lepromatous leprosy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of lesions | Single or upto 3 | A Few (up to 10) | Several (10–30) | Numerous, asymmetrical (>30) | Innumerable, symmetrical |
| Size | Variable,
usually large |
Variable, some are large | Variable | Small, some
can be large |
Small |
| Surface changes | Hypopigmented | Dry, scaly, look bright, and infiltrated | Dull or slightly shiny | Shiny | Shiny |
| Sensations | Absent | Markedly diminished | Moderately diminished | Slightly diminished | Minimally diminished |
| Hair growth | Nil | Markedly diminished | Moderately diminished | Slightly diminished | Not affected initially |
| Skin smear | Negative | Negative or 1+ | 1–3+ | 3–5+ | Plenty, including globi (6+) |
| Lepromin test | Strongly positive | Weakly positive | Negative | Negative | Negative |
Since it mainly affects skin and nerves, these are some clinical features seen in patient with leprosy:
- Hypopigmented or reddish patch/es on skin
- Diminished sensation within skin patches
- Paresthesias (tingling or numbness in hands or feet)
- Painless wounds or burns on hands or feet
- Tender, enlarged peripheral nerves
If the diseases is left untreated, it become chronic and may lead to physical deformities. Such as:
- Weakness of hands with claw fingers
- Foot drop
- Facial paralysis
- Lagopthalmos
- Lack of eyebrows and eyelashes
- Collapsed nose
- Perforated nasal septum
- Trophic ulcers
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to diagnostic tests for the condition
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Parkash O. Classification of leprosy into multibacillary and paucibacillary groups: an analysis. FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology. 2009 Jan 1;55(1):1-5.
- ↑ Bhat RM, Prakash C. Leprosy: an overview of pathophysiology. Interdisciplinary perspectives on infectious diseases. 2012 Sep 4;2012.