Obliquus Capitis Superior: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Updated references according to Vancouver guidelines) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
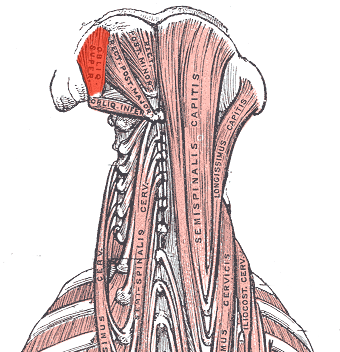
The obliquus capitis superior is a member of the suboccipital group of muscles along with [[Obliquus Capitis Inferior|obliquus capitis inferior]], [[Rectus Capitis Posterior Major|rectus capitis posterior major]] and [[Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor|rectus capitis posterior minor]]. It is narrow below, wide and expanded above, and is lateral to the [[Semispinalis Capitis|semispinalis capitis]]. It forms the superolateral border of the suboccipital triangle.<ref name="gray">Henry Gray: Anatomy of the Human Body [monograph online]. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918 [cited 2015 Mar 30]. Available from: Bartleby; New York: 2000. fckLRhttp://www.bartleby.com/107/116.html</ref> <br> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
Superior surface of the transverse process of the [[Atlas|atlas]] (C1)<ref name="wh">Wheeless III, CR. Obliquus capitis superior [Internet] 2011 Aug 16 [cited 2015 Mar 30]. Available from: http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/obliquus_capitis_superior_1</ref> | |||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
=== Nerve Supply === | === Nerve Supply === | ||
Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1)<ref name="ae">http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5212/</ref><br> | Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1)<ref name="ae">Obliquus capitis superior [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Mar 30]. Available from: http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5212/</ref><br> | ||
=== Blood Supply === | === Blood Supply === | ||
The muscle receives its blood supply from the vertebral artery and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery.<ref name="ae" /> | The muscle receives its blood supply from the [[Vertebral Artery|vertebral artery]] and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery.<ref name="ae" /> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
=== Actions === | === Actions === | ||
Bilaterally they extend the head; unilaterally they laterally flex the the head to the same side as the muscle.<ref name="wh" /> | Bilaterally, they extend the head; unilaterally, they laterally flex the the head to the same side as the muscle.<ref name="wh" /> | ||
=== Functional contributions === | === Functional contributions === | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Cervical_Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Cervical_Anatomy]] | ||
Revision as of 23:55, 30 March 2015
Top Contributors - Oyemi Sillo, Richard Benes, Kim Jackson, Daniele Barilla, WikiSysop, 127.0.0.1 and Evan Thomas
Description[edit | edit source]
The obliquus capitis superior is a member of the suboccipital group of muscles along with obliquus capitis inferior, rectus capitis posterior major and rectus capitis posterior minor. It is narrow below, wide and expanded above, and is lateral to the semispinalis capitis. It forms the superolateral border of the suboccipital triangle.[1]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Superior surface of the transverse process of the atlas (C1)[2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Between the superior and inferior nuchal lines of the occipital bone[2]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1)[3]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The muscle receives its blood supply from the vertebral artery and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery.[3]
Function[edit | edit source]
A postural muscle that monitors the position of the head.[3]
Actions[edit | edit source]
Bilaterally, they extend the head; unilaterally, they laterally flex the the head to the same side as the muscle.[2]
Functional contributions[edit | edit source]
Pathology/Injury[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapy Techniques[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1hkusKR6qehy8d6JqkZAg4USI_NTyrkd_YgboGFAHClF6RmE9A|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Henry Gray: Anatomy of the Human Body [monograph online]. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918 [cited 2015 Mar 30]. Available from: Bartleby; New York: 2000. fckLRhttp://www.bartleby.com/107/116.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Wheeless III, CR. Obliquus capitis superior [Internet] 2011 Aug 16 [cited 2015 Mar 30]. Available from: http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/obliquus_capitis_superior_1
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Obliquus capitis superior [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Mar 30]. Available from: http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5212/