Occipital Bone: Difference between revisions
Mande Jooste (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mande Jooste (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor''' | '''Original Editor'''- [[User:Hannah Hassel|Hannah Hassel]] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | |||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{}}}} | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
[[File:Fullsizeoutput_c1.jpeg|480x480px]] | [[File:Fullsizeoutput_c1.jpeg|480x480px]] | ||
Revision as of 13:19, 25 March 2019
Original Editor- Hannah Hassel Top Contributors - Mande Jooste, Hannah Hassell, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton and Tony Lowe
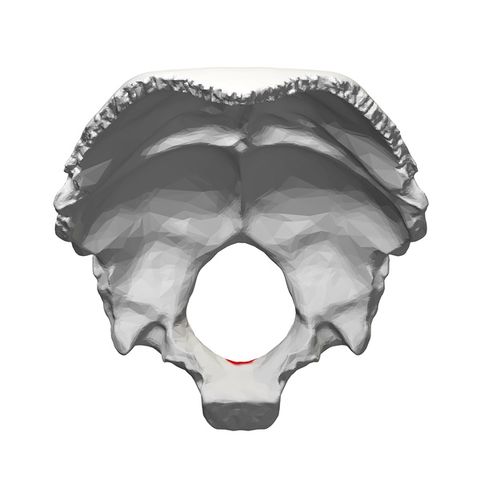
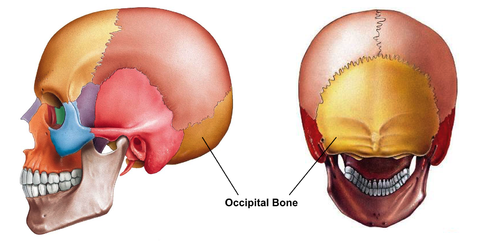
Description[edit | edit source]
Structure[edit | edit source]
Function[edit | edit source]
Articulations[edit | edit source]
The occipital bone articulate with six bones:
- Two temporal bones
- Two parietal bones
- Sphenoid bone
- Atlas
Muscle attachments[edit | edit source]
Superior curved line: Occipito frontalis; Trapezius; Sternocleidomastoid
Space between the curved lines: Complexus; Splenius capitis; Obliquus superior
Inferior curved line and space between it and the foramen magnum: Rectus posticus major and minor
Transverse process: Rectus lateralis
Basilar process: Rectus antics major and minor; Superior constrictor of pharynx[1]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Gray H, Anatomy, descriptive and surgical, 8th edition, Philadelphia, Collins, June, 1878