Occipital Bone: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
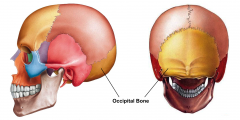
The Occipital bone is a trapezoidal-shaped bone forming the base of the [[Bones of the skull|skull]]. It is situated at the the lower and back part of the cranium. The large oval opening in the bone is called the foramen magnum through which the [[Spinal cord anatomy|spinal cord]] exits the cranial vault. | [[File:Occipital_bone.png|alt=|right|240x240px]] | ||
The Occipital bone is a trapezoidal-shaped [[bone]] forming the base of the [[Bones of the skull|skull]]. It is situated at the the lower and back part of the cranium. The large oval opening in the bone is called the foramen magnum through which the [[Spinal cord anatomy|spinal cord]] exits the cranial vault. | |||
=== Articulations === | === Articulations === | ||
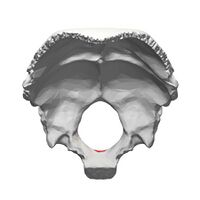
[[File:Fullsizeoutput_c1.jpeg| | [[File:Fullsizeoutput_c1.jpeg|200x200px|alt=|thumb|Occiput bone from above]]The occipital bone articulate with six bones: | ||
* Two temporal bones | * Two temporal bones | ||
* Two parietal bones | * Two parietal bones | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
=== Muscle attachments === | === Muscle attachments === | ||
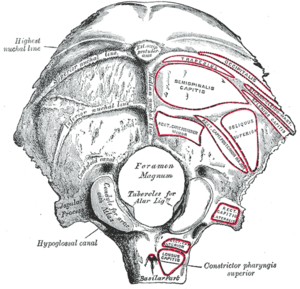
[[File:Occiput attachments.png|thumb|Muscle attachments]] | |||
Space between the curved lines: Complexus; Splenius capitis; Obliquus superior | # Superior curved line: Occipito frontalis; [[Trapezius]]; [[Sternocleidomastoid]] | ||
# Space between the curved lines: Complexus; [[Splenius Capitis|Splenius capitis]]; Obliquus superior | |||
Inferior curved line and space between it and the foramen magnum: Rectus posticus major and minor | # Inferior curved line and space between it and the foramen magnum: Rectus posticus major and minor | ||
# Transverse process: Rectus lateralis | |||
Transverse process: Rectus lateralis | # Basilar process: Rectus antics major and minor; Superior constrictor of pharynx<ref>Gray H, Anatomy, descriptive and surgical, 8th edition, Philadelphia, Collins, June, 1878</ref> | ||
Basilar process: Rectus antics major and minor; Superior constrictor of pharynx<ref>Gray H, Anatomy, descriptive and surgical, 8th edition, Philadelphia, Collins, June, 1878</ref> | |||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
Revision as of 06:12, 3 February 2022
Original Editor- Hannah Hassel Top Contributors - Mande Jooste, Hannah Hassell, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton and Tony Lowe
Description[edit | edit source]
The Occipital bone is a trapezoidal-shaped bone forming the base of the skull. It is situated at the the lower and back part of the cranium. The large oval opening in the bone is called the foramen magnum through which the spinal cord exits the cranial vault.
Articulations[edit | edit source]
The occipital bone articulate with six bones:
- Two temporal bones
- Two parietal bones
- Sphenoid bone
- Atlas
Muscle attachments[edit | edit source]
- Superior curved line: Occipito frontalis; Trapezius; Sternocleidomastoid
- Space between the curved lines: Complexus; Splenius capitis; Obliquus superior
- Inferior curved line and space between it and the foramen magnum: Rectus posticus major and minor
- Transverse process: Rectus lateralis
- Basilar process: Rectus antics major and minor; Superior constrictor of pharynx[1]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Basilar skull fracture
Resources[edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Occipital neuralgia[2]