Thoracic Spine Fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
=== '''Non-Operative''' === | === '''Non-Operative''' === | ||
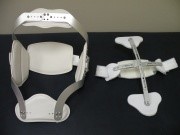
[[File:Fig. 4- Jewett & CASH Braces.JPG|thumb|Jewett (left) & CASH (right) Braces - courtesy of Orthotic & Prosthetic Technologies, Inc., San Marcos, TX]]Compression fractures, stable burst fractures and neurologically intact patients can typically be treated non-operatively:<ref name="Alpantaki 2010" /><ref name="Shaffrey 1997">Shaffrey CI, Shaffrey ME, Whitehill R, Nockels RP. Surgical treatment of thoracolumbar fractures. Neurosurg Clin N Am 1997;8(4):519-40.</ref><ref name="Wood 2003" /><ref name="Weninger 2009">Weninger P, Schultz A, Hertz H. Conservative management of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine compression and burst fractures: functional and radiographic outcomes in 136 cases treated by closed reduction and casting. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009;129:207-19.</ref><ref name="Giele 2009">Giele BM, Wiertsema SH, Beelen A, va der Schaaf M, Lucas C, Been HD, et al. No evidence for the effectiveness of bracing in patients with thoracolumbar fractures: a systematic review. Acta Orthopaedica 2009;80(2):226-32.</ref> ''(Level of evidence 1B; 3A; 4)'' | |||
Compression fractures, stable burst fractures and neurologically intact patients can typically be treated non-operatively:<ref name="Alpantaki 2010" /><ref name="Shaffrey 1997">Shaffrey CI, Shaffrey ME, Whitehill R, Nockels RP. Surgical treatment of thoracolumbar fractures. Neurosurg Clin N Am 1997;8(4):519-40.</ref><ref name="Wood 2003" /><ref name="Weninger 2009">Weninger P, Schultz A, Hertz H. Conservative management of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine compression and burst fractures: functional and radiographic outcomes in 136 cases treated by closed reduction and casting. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009;129:207-19.</ref><ref name="Giele 2009">Giele BM, Wiertsema SH, Beelen A, va der Schaaf M, Lucas C, Been HD, et al. No evidence for the effectiveness of bracing in patients with thoracolumbar fractures: a systematic review. Acta Orthopaedica 2009;80(2):226-32.</ref> ''(Level of evidence 1B; 3A; 4)'' | |||
*Bed rest/activity limitation ranging from days to weeks | *Bed rest/activity limitation ranging from days to weeks | ||
*Bracing: 8 to 12 weeks in Jewett or Cruciform Anterior Spinal Hyperextension (CASH) | *Bracing: 8 to 12 weeks in Jewett or Cruciform Anterior Spinal Hyperextension (CASH) | ||
*Casting: 8 to 12 weeks | *Casting: 8 to 12 weeks | ||
*Closed reduction | *Closed reduction | ||
*Pain medication | *Pain medication | ||
*Physical therapy | *Physical therapy | ||
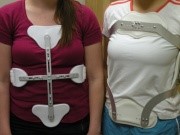
There is no consensus on the exact duration of treatment. ''(Level of evidence 3A)'' | There is no consensus on the exact duration of treatment. ''(Level of evidence 3A)''[[File:Fig. 5- CASH & Jewett Braces on Patients.JPG|thumb|CASH (left) & Jewett (right) Braces - courtesy of Orthotic & Prosthetic Technologies, Inc., San Marcos, TX]]Preventative treatment for fractures related to [[Osteoporosis|osteoporosis]] include bisophosphonates, calcium, vitamin D and exercise.<ref name="Demir 2007">Demir S, Akin C, Aras M, Koseoglu F. Spinal cord injury associated with thoracic osteoporotic fracture. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2007;86(3):242-6.</ref><br> ''(Level of evidence 3B)'' | ||
Preventative treatment for fractures related to [[Osteoporosis|osteoporosis]] include bisophosphonates, calcium, vitamin D and exercise.<ref name="Demir 2007">Demir S, Akin C, Aras M, Koseoglu F. Spinal cord injury associated with thoracic osteoporotic fracture. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2007;86(3):242-6.</ref><br> ''(Level of evidence 3B)'' | |||
Wood et al. found no significant long-term difference in pain, disability and return to work for non-neurologically involved patients who received surgery compared to those who received bracing or casting.<ref name="Wood 2003">Wood K, Butterman G, Mehbod A, Garvey T, Jhanjee R, Sechriest V. Operative compared to nonoperative treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture without neurological deficit: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85-A(5):773-81.(LoE:1B)</ref> ''(Level of evidence 1B)'' This indicates that the higher risk and cost of surgery may not be justified and that bracing/casting would be the preferred treatment in this patient population. Braces are a common component of both post-operative and non-operative thoracic fracture treatment protocols.<ref name="Giele 2009" /> ''(Level of evidence 1B)'' | Wood et al. found no significant long-term difference in pain, disability and return to work for non-neurologically involved patients who received surgery compared to those who received bracing or casting.<ref name="Wood 2003">Wood K, Butterman G, Mehbod A, Garvey T, Jhanjee R, Sechriest V. Operative compared to nonoperative treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture without neurological deficit: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85-A(5):773-81.(LoE:1B)</ref> ''(Level of evidence 1B)'' This indicates that the higher risk and cost of surgery may not be justified and that bracing/casting would be the preferred treatment in this patient population. Braces are a common component of both post-operative and non-operative thoracic fracture treatment protocols.<ref name="Giele 2009" /> ''(Level of evidence 1B)'' | ||
Revision as of 09:44, 30 June 2019
Original Editors - Tre Hinojosa, Heather Hughes, Erin Locati, and Melissa Osti as part of the Texas State University Evidence-based Practice Project
Top Contributors - Erin Locati, Melissa Osti, Lucy Aird, Heather Hughes, Jin Yoo, Kim Jackson, Abbey Wright, Tre Hinojosa, Hannah Willocx, Admin, Joshua Samuel, Liesbeth Vanden Brande, Evan Thomas, Nick Van Doorsselaer, WikiSysop, Lucinda hampton, Karen Wilson, 127.0.0.1, Claire Knott, Eric Robertson and Jeremy Brady
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
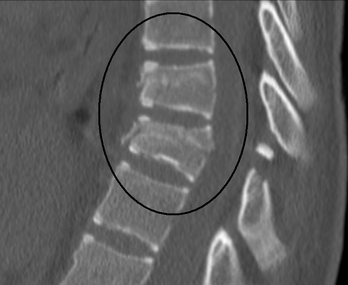
Most thoracic spine fractures occur in the lower thoracic spine, with 60% to 70% of thoraco-lumbar fractures occurring in the T11 to L2 region, which is the bio-mechanically weak for stress. The majority of these fractures occur without spinal cord injury. 20 to 40% of the fractures are associated with neurological injuries.
Major (high-energy) trauma, is the most common cause of thoracic fractures such as falls from height or road traffic accidents.[1] Minor trauma can also cause a thoracic spine fracture in individuals who have a condition associated with loss of bone mass such as osteoporosis.
There are two current classification systems that radiographers use for thoracic spine fractures: Magerl[2] and Denis[3]
There are four major types (based on the mechanism of injury):
- Compression (wedge fractures)
- Burst
- Flexion-distraction (seat belt injury/ Chance fracture)
- Fracture-dislocation
Epidemiology /Etiology[edit | edit source]
1. Compression[edit | edit source]
Caused by axial compression alone or flexion forces, when the spine is bent forward or in side flexion at the moment of trauma. It is a stable fracture and patients rarely accompanied neurological deficits.
Failure of the anterior column of the spine due to compression forces, mainly into flexion. The most common causes in younger patients are falls and motor vehicle accidents. The most common causes in older patients are minor incidents during normal activities of daily living secondary to osteoporosis or metabolic bone diseases.[4] Associated neurological complications are rare[5].
2. Burst[edit | edit source]
Similar to compression fractures except that the entire vertebra is evenly crushed. It is a very severe fracture, accompanied with retropulsed bone fragments into spinal canal. Neurological injury and posterior column injury can occur more frequently
Fracture of the anterior and middle columns of the spine due to axial loading[6] such as from a fall landing on the buttocks or lower extremities. The concentration of axial forces is to the thoracolumbar junction. [7][5]
3. Flexion-distraction[edit | edit source]
Involves the separation (distraction) of the fractured vertebra. It occurs by primary distraction forces on the spine. The axis of rotation is located within or in front of anterior vertebral body.
Failures of the posterior and middle columns of the spine under tension usually from a trauma involving sudden upper body forward flexion while the lower body remains stationary (seat belt injury). Often associated with abdominal trauma due to compression of abdominal cavity during injury. The anterior column may be mildly affected, but the annulus fibrosis and anterior longitudinal ligament are intact, preventing dislocation or subluxation. A gap between the spinous processes is often present upon palpation.[5]
4. Fracture-dislocation[edit | edit source]
Found in combination with displacement of adjacent vertebrae. It is caused by various combinations of forces. It is very unstable and can cause complete neurological deficit
Failure of all three spinal columns under compression, flexion, rotation, or shear forces. The most unstable of all thoracolumbar spine injuries, they are highly associated with neurological deficits. They can be caused by a severe flexion force similar to that of a seat belt injury, or an object falling across the back.[5]
5. Clay-Shoveler's Fracture[edit | edit source]
Rare, fatigue fracture of the upper thoracic spinous process. Seen in powerlifters or in patients that are involved in hard labour causing shear forces on the vertebra, hyperflexed spine, or direct trauma.[8]
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Over 65% of vertebral fractures are asymptomatic [9]. They are sometimes detected via radiograph when a patient is being screened for another injury.
Presentation of symptomatic fractures includes: [9][4][10][11][12][13]
- Chronic back pain in thoracic and/or lumbar region
- Slower gait
- Decreased range of motion
- Impaired pulmonary function
- Increased kyphosis especially in osteoporotic patients with compression fractures
- Neurological deficits due to narrowing of spinal canal - can present as long as 1.5 years post injury
Prolonging of these symptoms leads to decreased physical function and performance of activities of daily living, and increased risk of disability. Vertebral deformities are also associated with significantly increased risk of future fractures, including hip fractures[9].
Patients with non-compression fractures are usually involved in a multi-trauma, and will have various injuries and sources of pain. Clinicians must use their best judgment and employ clinical screening criteria to determine if the thoracic spine is involved.[4]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Plain radiographs are historically the "gold standard" for detecting thoracolumbar fractures, although due to the organs and soft tissue in the thoracic region, fractures can be missed on radiographs. A CT scan is recommended to visualize thoracic fractures and an MRI to assess soft tissue damage. [14][10][11]
Multiple Myeloma and other cancers can present as thoracic pain, but will have additional signs such as unexplained weight loss and fever.[15]
Scheuermann Disease presents as exaggerated kyphosis, anterior body extension and schmorl’s nodes; can be distinguished by vetebral body height parameters on radiograph. [16]
Examination[edit | edit source]
Screening for Fracture[edit | edit source]
Algorithms for screening patients for thoracic fractures and the need for imaging have been developed but not fully validated.
O'Connor and Walsham (2009) [4][edit | edit source]
Presence of one or more of the following 5 criteria in a patient with blunt multi-trauma is an indication for thoracolumbar imaging (Sn=0.99):
- High Risk Mechanism of Injury (MOI):
- motor vehicle accident at speed >70 kph
- fall from height >3 m
- ejection from motor vehicle or motorcycle
- plus any injury outside of these criteria that could cause a thoracolumbar fracture
- Painful Distracting Injury: painful torso/long-bone injury sufficient to distract the patient from noticing the pain of the thoracolumbar injury
- New Neurological Signs or Back Pain/Tenderness with Clinical Findings Suspicious of a New Fracture:
- back pain
- back tenderness
- palpable step in vertebral palpation
- midline bruising
- neurological signs consistent with a spinal cord injury
- Cognitive Impairment:
- Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) < 15
- abnormal mentation
- clinical intoxication
- Known Cervical Spine Fracture: evidence of a new traumatic cervical spine fracture
However, as these results were derived from low-level evidence, the authors recommend future controlled trials to standardize these definitions and validate the algorithm.[4]
Other criteria for screening include:[edit | edit source]
- Holmes et al. (2003)[12]: screening criteria for radiograph of blunt trauma patients with thoracolumbar injuries (Sn=1.00, Sp=0.039)
- Complaints of thoracolumbar spine pain
- Thoracolumbar spine tenderness
- Decreased level of consciousness
- Intoxication with alcohol or drugs
- Neurologic deficit
- Painful distracting injury
- Singh et al. (2011)[11]: 3hree predictive variables for thoracic spine fracture based on a case control study (Sp=0.93):
- Fall > 2m
- Thoracic pain
- Intoxication
Physical Therapy Exam[edit | edit source]
- Thorough history including MOI and previous spine fractures
- Neurological screen
- Assessment of patient's pain level and location
- Palpation of the thoracic spine
- Screen for thoracic fracture
- Identification of impairments in ROM, strength, flexibility
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
Operative[edit | edit source]
The benefits of a surgical treatment of thoracolumbar fractures compared to a non-operative approach include avoiding an orthosis in the presence of multiple injuries, skin injuries, and obesity, immediate mobilization and earlier rehabilitation and better restoration of sagittal alignment. On the other hand, these benefits should be weighed against the possible surgical morbidity. Conventional open surgical techniques may be accompanied by approach-related muscle injury, increased infection rates and higher blood loss. There is no difference between operative and non-operative treatment regarding neurological recovery and long-term functional outcomes. (Level of evidence 3A)
Indications for surgery include neurological involvement and/or progressive neurological deterioration, >50% spinal canal compromise, >50% anterior vertebral body height loss, >25° to 35° angle of kyphotic deformity, and posterior ligament complex (PLC) compromise. Surgical approaches can be anterior, posterior or a combination.[7] (Level of evidence 3A) Recently, minimally invasive techniques have been described in thoracolumbar fractures. (Level of evidence 3A)
For more information on spinal surgery refer to:
- Harding IJ. Anterior spinal surgery. Available from: https://www.ianjharding.com/uploads/anterior_spinal_approaches.pdf (accessed 20 Sep 2011). [17] (Level of evidence 5)
- Cervical Spinal Surgery
Non-Operative[edit | edit source]
Compression fractures, stable burst fractures and neurologically intact patients can typically be treated non-operatively:[7][18][19][20][21] (Level of evidence 1B; 3A; 4)
- Bed rest/activity limitation ranging from days to weeks
- Bracing: 8 to 12 weeks in Jewett or Cruciform Anterior Spinal Hyperextension (CASH)
- Casting: 8 to 12 weeks
- Closed reduction
- Pain medication
- Physical therapy
There is no consensus on the exact duration of treatment. (Level of evidence 3A)
Preventative treatment for fractures related to osteoporosis include bisophosphonates, calcium, vitamin D and exercise.[8]
(Level of evidence 3B)
Wood et al. found no significant long-term difference in pain, disability and return to work for non-neurologically involved patients who received surgery compared to those who received bracing or casting.[19] (Level of evidence 1B) This indicates that the higher risk and cost of surgery may not be justified and that bracing/casting would be the preferred treatment in this patient population. Braces are a common component of both post-operative and non-operative thoracic fracture treatment protocols.[21] (Level of evidence 1B)
Physical Therapy Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
Management of vertebral fractures remains controversial [7] ,[22],[23](level of evidence:3A,2A,2B) and research is limited on identifying physical therapy intervention. Until recently, conservative management of fractures consisted of pain medications, rest and bracing to reduce spinal movements [24],[22],[25],[19].(level of evidence: 1B,2A,3A,1B)
Rehabilitation programs must be designed specifically for the individual based on their physical abilities and impairments.
With conservative treatment, the majority of fractures heal with a significant decrease in pain in 8-12 weeks. Significant declines in pain (5.9cm on VAS) are experienced 12-24 hours post-surgery [24](LoE:1B). Therefore, interventions depend largely on whether the patient chose surgery or conservative treatment. Interventions should always be prescribed and progressed based on patient tolerance.
Physical Therapy Goals[edit | edit source]
- Reduce pain
- Improve posture
- Improve thoracic mobility
- Strengthen trunk extensors
- Improve trunk control
- Provide education
- Lower extremity strengthening
Bennell et al. found that a multimodal treatment approach over a 10-week period was successful in reducing pain and improving function in patients who suffered from osteoporotic vertebral fractures [26](LoE:2B). However, because it was a multimodal approach the effectiveness of each treatment is unclear.
APTA Preferred Practice Patterns[27](LoE:5)[edit | edit source]
4B: Impaired Posture
4G: Impaired Joint Mobility, Muscle Performance, and Range of Motion Associated with Fracture
4I: Impaired Joint Mobility, Muscle Performance, and Range of Motion Associated with Bony or Soft Tissue Surgery
General Exercise Recommendations [26],[27] (level of evidence: 2B,5)[edit | edit source]
A major concern is refracture within a year of the initial injury. Researchers agree that strengthening back-extensor muscles can help decrease the rate of refracture or prolong occurance of refracture [25](LoE:3A),[26](LoE:2B) Studies show significant improvement in reported pain levels and increased function in patients with back-extensor exercises as part of their exercise regimen [25],[28],[29],[26]. (level of evidence: 3A,1B,2B,2B)Therefore, patient should begin strengthening back-extensor muscles as soon as they are physically able.
When developing a plan of care, the therapist should consider the individual characteristics of a vertebral fracture and possible secondary limitations.
Physiotherapy and Home Exercise Program[edit | edit source]
Adapted from: Bennell et al (2010). [26](LoE:2B)
Within a pain-free range, progressed as tolerated:
| Technique/Exercise | Dosage | Weeks | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Postural taping* - From anterior aspect of each shoulder, posteriorly and obliquely to opposite rib cage |
Worn full time | 1 | |
|
Soft tissue massage* - In prone, to erector spinae, rhomboids, upper traps - stroking, circular frictions, petrissage |
5 mins | 1-10 | |
|
Passive accessory postero-anterior vertebral moblisation* - In prone from T1 down to 2 levels below most painful vertebral region (Grd 2-3) |
5 mobilising movements at each central level x2 reps |
1-10 | |
|
Supine lying over rolled up towel - Towel placed lengthways along the back to facilitate thoracic extension |
5-10 mins | 1 daily | |
|
Erect sitting with transversus abdominus stabilising - Sit forward on chair (no back rest), chin retraction, scapular retraction and TA contraction |
10 sec hold x 5 reps |
1-10 daily | |
|
Elbows back in sitting - Hands befind head, elbows pointing out to side. Press elbows back by scapular retraction |
5 sec hold x5 reps |
1-10 daily | |
|
Trunk mobility in sitting - Hands on shoulders, gentle rotation in both directions and lateral flexion to each side |
5 reps in each direction |
1-10 daily | |
|
Head to wall in standing - Back and heels agaist wall with rolled up towel behind head. Chin retraction |
10 sec hold x 5 reps |
1-10 daily | |
|
Standing corner stretch - Face corner, both hands chest height on wall and moving in closer to stretch anterior chest |
10-30 sec hold x 3 reps |
2-10 daily | |
|
Walking hands up wall in standing - Facing wall, walking hands up wall until arms upstretched then holding hands off wall |
5 sec hold x5 reps |
3-10 daily | |
|
Shoulder flexion in supine - Arms outstretched holding onto cane/towel and taking arms over head to hold at end of range |
10- sec hold x5 reps |
3-10 daily | |
|
Standing wall push ups - Face wall, arms in front, shoulder height. Keep body straight, bend and straighten elbows |
8-10 reps x2 |
1-10 3x/week | |
|
Seated row with dumbbells - Upright sitting and pull hands up towards chest by bending elbows and then lowering |
8-10 reps x2 |
1-10 3x/week | |
|
Seated overhead dumbbell press - With elbows bent and out to side, press dumbbells straight up until arms extended overhead |
8-10 reps x2 |
3-10 3x/week | |
|
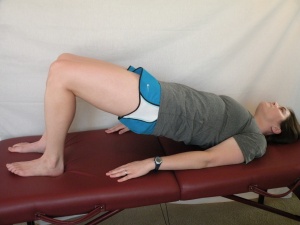
Bridging in supine - Knee bent and feet flat on ground. Pushing through feet to lift back and pelvis off ground |
5-10 sec hold x5 |
1-2 3x/week | |
|
Hip extension in prone - Raising one leg off the ground and then the other |
8-10 reps x2 |
3-10 3x/week | |
|
Half squats - progress to holding dumbbells - Standing in front of chair and squatting down to touch chair with buttocks then standing up |
8-10 reps x2 |
1-2 3x/week | |
|
Step ups - progress to holding dumbells - Stepping up and down a 10 cm step. Alternate legs |
8-10 reps x2 |
3-10 3x/week | |
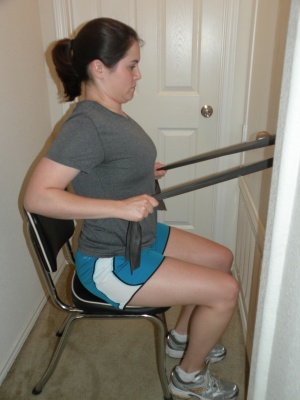
|
Scapular retraction with theraband in sitting - Holding theraband in both hands with elbows tucked into sides and performing wrist extension, supination and shoulder external rotation then scapular retraction |
8-10 reps x2 |
1-10 3x/week | |
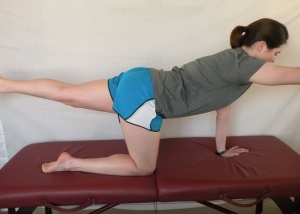
|
Four-point kneeling with transversus abdominus - Push into floor with hands, knees and feet then draw navel up and in, hold 5 secs |
8-10 reps x2 |
2 3x/week | |
|
Four point kneeling with one arm and leg lift - As above; lift one arm off ground. Progress to also lifting extended leg off ground at same time |
8-10 reps x2 |
3-10 3x/week | |
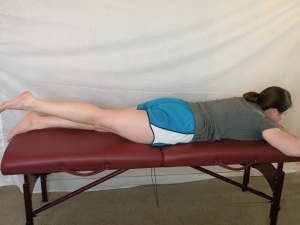
|
Prone lying with arm elevation - Arms at shoulder height and bent at elbows. Scapular retraction then lift arms off floor |
5-10 sec hold x5 |
2-3 3x/week | |
|
Prone trunk extension - Lift head and shoulders off floor while maintaining chin retraction |
5-10 sec hold x5 |
4-10 3x/week | |
| *performed by the therapist | |||
Complications to Consider [7],[23],[25] (level of evidence:3A,2B,3A)
- Cardiorespiratory compromise
- Additional Fractures
- Refractures
- Osteoporosis
- Prolonged Pain
- Limited Range of Motion
- Limited Strength
- Neurological Compromise
- Postural Dysfunction
- General Deconditioning
- Gait/Ambulation Abnormalities
- Loss of Balance
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Corenman DS. Thoraco-lumbar spine fractures. Available from: http://neckandback.com/conditions/thoraco-lumbar-spine-fractures (accessed 20 Sep 2011).
- MD Guidelines. Fracture, thoracic spine (without spinal cord injury). Available from: http://www.mdguidelines.com/fracture-thoracic-spine-without-spinal-cord-injury (accessed 20 Sep 2011).
- AO Foundation, Available from: http://www.aofoundation.org (accessed 20 Sep 2011).
- Leahy M and Gellman H. Thoracic spine fractures and dislocation. Medscape Reference. Available from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1267029-overview (accessed 20 Sep 2011).
Clinical Bottom Line[edit | edit source]
There is a lack of high-quality evidence for the management of thoracic spine fractures. Physical therapists should be familiar with screening for thoracic fractures and take an impairment-based approach when treating post-operative or non-operative patients.
Presentations[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Leucht P, Fischer K, Muhr G, Mueller EJ. Epidemiology of traumatic spine fractures. Injury. 2009 Feb 1;40(2):166-72.
- ↑ Magerl F, Aebi M, Gertzbein SD, Harms J, Nazarian S. A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. European Spine Journal. 1994 Aug 1;3(4):184-201.
- ↑ Denis F. Spinal Instability as Defined by the Three-column Spine Concept in Acute Spinal Trauma, Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research. Oct 1984; 198:65-76
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 O'Connor E, Walsham J. Indications for thoracolumbar imaging in blunt trauma patients: a review of current literature. Emerg Med Australas 2009;21(2):94-101.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Kandabarow A. Injuries of the thoracolumbar spine. Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal. 1997 Sep 1;19(3):65-80.
- ↑ Tisot R, Avanzi O. Laminar fractures as a severity marker in burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2009;17(3):261-4.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Alpantaki, K., Bano, A., Pasku, D., Mavrogenis, A. F., Papagelopoulos, P. J., Sapkas, G. S., ... & Katonis, P. (2010). Thoracolumbar burst fractures: a systematic review of management. Orthopedics, 33(6), 422-429. (LoE:3A)
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Demir S, Akin C, Aras M, Koseoglu F. Spinal cord injury associated with thoracic osteoporotic fracture. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2007;86(3):242-6.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Lentle BC, Brown JP, Khan A, Leslie WD, Levesque J, Lyons DJ, et al. Recognizing and reporting vertebral fractures: reducing the risk of future osteoporotic fractures. Can Assoc Radiol J 2007;58(1):27.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Marre B, Ballesteros V, Martinez C, Zamorano JJ, Ilabaca F, Munjin M, et al. Thoracic spine fractures: Injury profile and outcomes of a surgically treated cohort. Eur Spine J 2011;20(9):1427-33.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Singh R, Taylor DM, D’Souza D, Gorelik A, Page P, Phal P. Mechanism of injury and clinical variables in thoracic spine fracture: a case control study. Hong Kong J Emerg Med. 2011;18(1):5-12.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Holmes JF et al. Prospective evaluation of criteria for obtaining thoracolumbar radiographs in trauma patients. J Emerg Med. 2003; 24:1-7.
- ↑ Friedrich M, Gittler G, Pieler-Bruha E. Misleading history of pain location in 51 patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Eur Spine J 2006;15(12):1797-800.
- ↑ Diaz J, Cullinane D, Vaslef S, et al. Practice management guidelines for the screening of thoracolumbar spine fracture. J Trauma 2007;63(3):709-18.
- ↑ PubMed Health: Multiple myeloma Web site. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001609/. Accessed April 29, 2001.
- ↑ Masharawi Y, Rothschild B, Peled N, Hershkovitz I. A simple radiological method for recognizing osteoporotic thoracic vertebral compression fractures and distinguishing them from Scheuermann disease. Spine 2009;34(18):1995-9.
- ↑ Harding IJ. Anterior spinal surgery. Available from: https://www.ianjharding.com/uploads/anterior_spinal_approaches.pdf (accessed 20 Sep 2011).
- ↑ Shaffrey CI, Shaffrey ME, Whitehill R, Nockels RP. Surgical treatment of thoracolumbar fractures. Neurosurg Clin N Am 1997;8(4):519-40.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Wood K, Butterman G, Mehbod A, Garvey T, Jhanjee R, Sechriest V. Operative compared to nonoperative treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture without neurological deficit: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85-A(5):773-81.(LoE:1B)
- ↑ Weninger P, Schultz A, Hertz H. Conservative management of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine compression and burst fractures: functional and radiographic outcomes in 136 cases treated by closed reduction and casting. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009;129:207-19.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Giele BM, Wiertsema SH, Beelen A, va der Schaaf M, Lucas C, Been HD, et al. No evidence for the effectiveness of bracing in patients with thoracolumbar fractures: a systematic review. Acta Orthopaedica 2009;80(2):226-32.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Van Leeuwen PJ, Bos RP, Derksen JC, de Vries J. Assessment of spinal movement reduction by thoraco-lumbar-sacral orthoses. J Rehabil Res Dev 2000;37(4):395-403.(LoE:2A)
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Dai LY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD. Posterior short-segment fixation with or without fusion for thoracolumbar burst fractures. A five to seven-year prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009;91:1033-41.(LoE:2B)
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Rousing R, Hansen KL, Andersen M, Jespersen SM, Thomsen K, Lauritsen JM. Twelve-months follow-up in forty-nine patients with acute/semiacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated conservatively or with percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine 2010;35(5):478-82.(LoE:1B)
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 Cahoj PA, Cook JL, Robinson BS. Efficacy of percutaneous vertebral augmentation and use of physical therapy intervention following vertebral compression fractures in older adults: a systematic review. J Geriatr Phys Ther 2007;30(1):31-40. (LoE:3A)
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 26.4 Bennell KL, Matthews B, Greig A, Briggs A, Kelly A, Sherburn M, et al. Effects of an exercise and manual therapy program on physical impairments, function and quality of life in people with osteoporotic vertebral fracture: a randomised, single-blind controlled pilot trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2010;11(36):1-11.(LoE:2B)
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Guide to Physical Therapist Practice. 2nd ed. Revised. Alexandria, Va: American Physical Therapy Association; 2003.(LoE:5)
- ↑ Huntoon EA, Schmidt CK, Sinaki M. Significantly fewer refractures after vertebroplasty in patients who engage in back-extensor-strengthening exercises. Mayo Clin Proc 2008;83(1):54-7.(LoE:1B)
- ↑ Sinaki M, Itoi E, Wahner HW, Wollan P, Gelzcer R, Mullan BP, et al. Stronger back muscles reduce the incidence of vertebral fractures: a prospective 10 year follow-up of postmenopausal women. Bone 2002;30(6):836-41.(LoE:2B)