Becker Muscular Dystrophy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [https://www.physio-pedia.com/User:Shreya_Pavaskar Shreya Pavaskar]<br> | |||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [https://www.physio-pedia.com/User:Shreya_Pavaskar Shreya Pavaskar]<br> | |||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)—one of a spectrum of X-linked muscular dystrophies shows the same pattern of muscle involvement as seen in [[Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - A Case Study|Duchenne muscular dystrophy]] (DMD), but with a more slowly progressive clinical course.<ref>Bushby KM, Thambyayah M, Gardner-Medwin D. Prevalence and incidence of Becker muscular dystrophy. The Lancet. 1991 Apr 27;337(8748):1022-4.</ref> | Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)—one of a spectrum of X-linked muscular dystrophies shows the same pattern of muscle involvement as seen in [[Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - A Case Study|Duchenne muscular dystrophy]] (DMD), but with a more slowly progressive clinical course.<ref>Bushby KM, Thambyayah M, Gardner-Medwin D. Prevalence and incidence of Becker muscular dystrophy. The Lancet. 1991 Apr 27;337(8748):1022-4.</ref> | ||
[[File:Muscular dystrophy gait.jpg|thumb]] | |||
== Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | == Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | ||
| Line 32: | Line 29: | ||
* Contractures | * Contractures | ||
* Weakness may be limited to specific proximal muscles | * Weakness may be limited to specific proximal muscles | ||
* Preservation of neck flexor muscle strength may be present<br> | * Preservation of neck flexor muscle strength may be present | ||
* Waddling gait in severe cases<br> | |||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
| Line 42: | Line 40: | ||
* Nerve conduction studies - expected to be normal | * Nerve conduction studies - expected to be normal | ||
* Electrocardiogram/Echocardiogram | * Electrocardiogram/Echocardiogram | ||
* Pulmonary function test | * [[Pulmonary function test]] | ||
* X-rays to detect any bone abnormalities due to contractures and wasting of muscles | * X-rays to detect any bone abnormalities due to contractures and wasting of muscles | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 60: | ||
Medications are administered to treat symptoms that are commonly are associated with BMD (such as cardiac medications for heart disease). | Medications are administered to treat symptoms that are commonly are associated with BMD (such as cardiac medications for heart disease). | ||
Corticosteroid medications to help individuals remain able to walk for as long as possible by delaying the inflammatory process.<br> | Corticosteroid medications to help individuals remain able to walk for as long as possible by delaying the inflammatory process. | ||
== Physiotherapy Management == | |||
Passive and Active stretching to improve joint flexibility (range of motion) and prevent or delay the development of contractures. | |||
Activities such as bicycle riding and swimming can be used to improve cardiovascular fitness and strength training. However, care should be taken that these activities are not strenuous or fatiguing as it can cause more harm to the muscles. | |||
Respiratory training - In the early stages of the condition, the physiotherapist will be involved in helping '''keep the child active'''. During later stages of the condition, the physiotherapist will help more with respiratory issues as well by using [[spirometry]], positioning, huffing and coughing in an efficient way. | |||
Improving the child's motor developmental skills and helping him reach the milestones by using [[Proprioceptive neuromuscular functioning|PNF]] techniques, various approaches like [[Roods approach|Roods]], [[Brunnstorm Approach|Brunnstorm]] and [[Bobath Approach|Bobath]] | |||
Progressive [[Strength Training|resistance exercises]] with minimal weights without fatiguing the muscles. | |||
Massage can be done over the muscles to reduce pain and contractures. | |||
== Occupational Therapy == | |||
Activities of Daily Living (ADL) can be modified based on the level of impairment. Adaptations using tools can be can be done using aids like dressing sticks, grab bars, modified dinner set, handles., raised toilet seats, etc. Items can be placed at lower levels for wheelchair bound patients. | |||
== Orthosis == | |||
Mobility concerns are addressed, including the need for devices to assist with mobility, such as a scooter or a fully adapted wheelchair with a custom seat and back, custom supports, and electric power. | |||
== Speech Therapy == | |||
[[Dysphagia]] concerns may be evaluated by a speech therapist. Clinical evaluation may result in the recommendation to avoid specific food textures and liquid viscosities, as well as to avoid certain positions during feeding. | |||
== Recreational Therapy == | |||
Avocational needs, desires and hobbies can be motivated to promote well-being and overall physical health of the individual. These activities should be evaluated based on the child's interest and capabilities. Various musical instruments, dances, crafts, art along with yoga can be learned or motivated in the child. | |||
<br> | |||
== Differential Diagnosis == | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
| Line 81: | Line 106: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Muscular Dystrophy]] | |||
[[Category:Neurological - Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Paediatrics]] | |||
[[Category:Paediatrics - Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Non Communicable Diseases]] | |||
[[Category:Genetic Disorders]] | |||
Revision as of 18:37, 16 April 2021
Top Contributors - Shreya Pavaskar, Rucha Gadgil, Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka, Laura Ritchie, Kim Jackson and Kirenga Bamurange Liliane
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)—one of a spectrum of X-linked muscular dystrophies shows the same pattern of muscle involvement as seen in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), but with a more slowly progressive clinical course.[1]
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Dystrophin is responsible for connecting the cytoskeleton of each muscle fiber to the underlying basal lamina. The absence of dystrophin stops calcium entering the cell membrane affecting the signaling of the cell, water enters the mitochondria causing the cell the burst. In a complex cascading process that involves several pathways, increased oxidative stress within the cell damages the sarcolemma resulting in the death of the cell, and muscle fibers undergo necrosis and are replaced with connective tissue.
Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
BMD is a type of recessive, X-linked dystrophinopathy. Clinical variations in patients with BMD are due to differences in dystrophin mutations from exon deletions[2].
Dystrophin levels in BMD are generally 30-80% of normal, while in DMD, the levels are less than 5%[3].
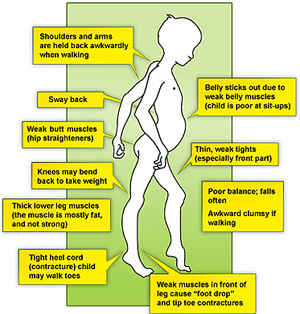
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
- Delayed developmental motor milestones might be the first observation from parents.
- Clumsy
- Frequent falls
- Difficulty rising from floor, may show Gowers's sign (non-specific)
- Subclinical cases may manifest later in life; dilated cardiomyopathy can be the first sign of BMD.
- Contractures
- Weakness may be limited to specific proximal muscles
- Preservation of neck flexor muscle strength may be present
- Waddling gait in severe cases
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
- Serum creatine kinase - moderate to severe elevation
- Dystrophin gene deletion analysis by gene analysis
- Muscle biopsy with dystrophin antibody staining
- Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Electromyography
- Nerve conduction studies - expected to be normal
- Electrocardiogram/Echocardiogram
- Pulmonary function test
- X-rays to detect any bone abnormalities due to contractures and wasting of muscles
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Outcome measures to quantify disease progression, including:
- 6‐minute walking test
- North Star ambulatory assessment scale,
- Time taken to climb four steps
- Time taken to rise from the floor
- Performance of upper limb.
One of the limitations of these measures is the fact they target either ambulant or non‐ambulant patients[5]. However, as the disease progresses, the outcome measures change making it difficult to use a single outcome measure to analyze the patient. Studies are being carried out to create a uniform measure for the muscular dystrophies.
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
No medications are provided to patients for the specific treatment of BMD.
Medications are administered to treat symptoms that are commonly are associated with BMD (such as cardiac medications for heart disease).
Corticosteroid medications to help individuals remain able to walk for as long as possible by delaying the inflammatory process.
Physiotherapy Management[edit | edit source]
Passive and Active stretching to improve joint flexibility (range of motion) and prevent or delay the development of contractures.
Activities such as bicycle riding and swimming can be used to improve cardiovascular fitness and strength training. However, care should be taken that these activities are not strenuous or fatiguing as it can cause more harm to the muscles.
Respiratory training - In the early stages of the condition, the physiotherapist will be involved in helping keep the child active. During later stages of the condition, the physiotherapist will help more with respiratory issues as well by using spirometry, positioning, huffing and coughing in an efficient way.
Improving the child's motor developmental skills and helping him reach the milestones by using PNF techniques, various approaches like Roods, Brunnstorm and Bobath
Progressive resistance exercises with minimal weights without fatiguing the muscles.
Massage can be done over the muscles to reduce pain and contractures.
Occupational Therapy[edit | edit source]
Activities of Daily Living (ADL) can be modified based on the level of impairment. Adaptations using tools can be can be done using aids like dressing sticks, grab bars, modified dinner set, handles., raised toilet seats, etc. Items can be placed at lower levels for wheelchair bound patients.
Orthosis[edit | edit source]
Mobility concerns are addressed, including the need for devices to assist with mobility, such as a scooter or a fully adapted wheelchair with a custom seat and back, custom supports, and electric power.
Speech Therapy[edit | edit source]
Dysphagia concerns may be evaluated by a speech therapist. Clinical evaluation may result in the recommendation to avoid specific food textures and liquid viscosities, as well as to avoid certain positions during feeding.
Recreational Therapy[edit | edit source]
Avocational needs, desires and hobbies can be motivated to promote well-being and overall physical health of the individual. These activities should be evaluated based on the child's interest and capabilities. Various musical instruments, dances, crafts, art along with yoga can be learned or motivated in the child.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Distal muscular dystrophy
- Scapulo-humeral dystrophy
- Spinal muscular atrophy
- Inflammatory myopathy
Resources[edit | edit source]
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - A Case Study
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Bushby KM, Thambyayah M, Gardner-Medwin D. Prevalence and incidence of Becker muscular dystrophy. The Lancet. 1991 Apr 27;337(8748):1022-4.
- ↑ Nicolas A, Raguénès-Nicol C, Ben Yaou R, Ameziane-Le Hir S, Chéron A, Vié V, Claustres M, Leturcq F, Delalande O, Hubert JF, Tuffery-Giraud S. Becker muscular dystrophy severity is linked to the structure of dystrophin. Human molecular genetics. 2015 Mar 1;24(5):1267-79.
- ↑ Angelini C, Fanin M, Pegoraro E, et al. Clinical-molecular correlation in 104 mild X-linked muscular dystrophy patients: characterization of sub-clinical phenotypes. Neuromuscul Disord. 1994 Jul. 4(4):349-58.
- ↑ Medicosis Perfectionalis. Becker Muscular Dystrophy. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Ult-apDFB8 [last accessed 16/4/2021]
- ↑ Outcome measures in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: sensitivity to change, clinical meaningfulness, and implications for clinical trials Joana Domingos Francesco Muntoni https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13634