Bone: Difference between revisions
Joao Costa (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Candace Goh (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div>Bones are connected to each other to form skeleton, which forms the framework of the body. | </div>Bones are connected to each other to form skeleton, which forms the framework of the body. Bone tissue is formed by collagen matrix hardened by deposited calcium. | ||
== Functions == | == Functions == | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
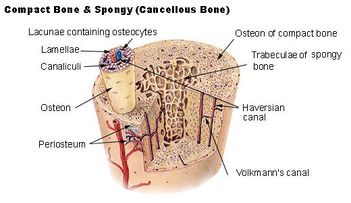
==== Individual bone structure ==== | ==== Individual bone structure ==== | ||
[[File:Bone 2.jpg|none|thumb|351x351px]] | [[File:Bone 2.jpg|none|thumb|351x351px]] | ||
*'''Compact/cortical bone''' | *'''Compact/cortical bone''' - makes up outer part of bone, rigid | ||
*'''Cancellous/spongy bone''' | *'''Cancellous/spongy bone''' - makes up inner part of bone, more porous, storage of bone marrow | ||
== Cellular structure == | == Cellular structure == | ||
Osteoblasts | * Osteoblasts - produce matrix (osteoid), build up bone tissue | ||
* Osteoclasts - secretes acids and enzymes to breakdown bone tissue | |||
Osteoclasts | * Osteocytes - maintain bone tissue by mineralising osteoid | ||
Osteocytes | |||
== Molecular structure == | == Molecular structure == | ||
Revision as of 18:12, 22 November 2018
This article is currently under review and may not be up to date. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (22/11/2018)
Original Editors -
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Candace Goh, Admin, Shaimaa Eldib, Kim Jackson, Jess Bell, Wataru Okuyama, Khloud Shreif, Robin Tacchetti, George Prudden, Claire Knott, Manisha Shrestha, Sai Kripa, Tony Lowe, Stephanie Geeurickx, WikiSysop and Joao Costa
Bones are connected to each other to form skeleton, which forms the framework of the body. Bone tissue is formed by collagen matrix hardened by deposited calcium.
Functions[edit | edit source]
Mechanical[edit | edit source]
- Protect internal organs
- Give shape and support to the body
- Movement
Synthetic[edit | edit source]
- Manufactures blood cells from the bone marrow (hematopoiesis)
Metabolic[edit | edit source]
- Mineral storage
- Fat storage
- Role in acid-base balance
Structure[edit | edit source]
Gross anatomy[edit | edit source]
Individual bone structure[edit | edit source]
- Compact/cortical bone - makes up outer part of bone, rigid
- Cancellous/spongy bone - makes up inner part of bone, more porous, storage of bone marrow
Cellular structure[edit | edit source]
- Osteoblasts - produce matrix (osteoid), build up bone tissue
- Osteoclasts - secretes acids and enzymes to breakdown bone tissue
- Osteocytes - maintain bone tissue by mineralising osteoid
Molecular structure[edit | edit source]
Matrix[edit | edit source]
- Inorganic
- Organic
Woven or lamellar[edit | edit source]
Types[edit | edit source]
Formation[edit | edit source]
Intramembranous ossification[edit | edit source]
Endochondral ossification[edit | edit source]
Bone marrow[edit | edit source]
Remodeling[edit | edit source]
Purpose[edit | edit source]
Calcium homeostasis/balance must exist between osteoclasts and osteoblasts activity[edit | edit source]
- If too much new tissue is formed, the bones become abnormally large and thick (acromegaly)
- Excessive loss of calcium weakens the bones, as occurs in osteoporosis
Repair[edit | edit source]
Paracrine cell signalling[edit | edit source]
Osteoblast stimulation[edit | edit source]
Osteoclast inhibition[edit | edit source]
Disorders[edit | edit source]
- Osteoporosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteomalacia
- Rickets
- Epiphyseal plate disorders
References[edit | edit source]
see adding references tutorial.