Lumbar Facet Joint Injections: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[Mckenzie Method" to "[[McKenzie Method") |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
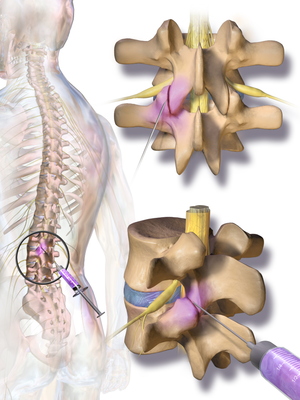
[[File:Facet joint injection.png|right|frameless]]Facet (zygapophyseal) joint injections are performed primarily for the diagnosis and differentiation of facet syndrome and radicular pain syndrome, and are one of the spinal interventional procedures. | [[File:Facet joint injection.png|right|frameless]]Facet (zygapophyseal) joint injections are performed primarily for the diagnosis and differentiation of facet syndrome and [[Lumbar Radiculopathy|radicular pain syndrome]], and are one of the spinal interventional procedures. | ||
* They can be performed under fluoroscopic, or CT image guidance | * They can be performed under fluoroscopic, or [[CT Scans|CT]] image guidance (cervical, thoracic or most commonly lumbosacral facet joints can be injected) | ||
* One or multiple joints can be injected during one procedure<ref name=":1">Radiopedia [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/facet-joint-injection Facet joint injections] Available from:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/facet-joint-injection (last accessed 10.9.2020)</ref>. | |||
* Spinal injections are one of the many varieties of treatments considered when an individual presents with chronic LBP <ref name="Hospital Episode Statistics, 2011">NHS Hospital Episode Statistics, 2011. main Procedures and Interventions: Outpatient Statistics[excel]Available at: http://www.hesonline.nhs.uk [Accessed 20 November 2012]</ref>. | * Spinal injections are one of the many varieties of treatments considered when an individual presents with chronic LBP <ref name="Hospital Episode Statistics, 2011">NHS Hospital Episode Statistics, 2011. main Procedures and Interventions: Outpatient Statistics[excel]Available at: http://www.hesonline.nhs.uk [Accessed 20 November 2012]</ref>. | ||
The effectiveness of facet joint injections is largely unknown but despite this, the procedure is still commonly performed by clinicians <ref name="Eckel. T, 2004">Eckel. T, 2004, Facet Joint Injections, Department of radiology, Lewis-Gale medical centre, 1900 Electric road, Salem, Virginia, USA, Journal of spinal pain, Volume 21, Edition 1, Pages 123-129</ref>. | The effectiveness of facet joint injections is largely unknown but despite this, the procedure is still commonly performed by clinicians <ref name="Eckel. T, 2004">Eckel. T, 2004, Facet Joint Injections, Department of radiology, Lewis-Gale medical centre, 1900 Electric road, Salem, Virginia, USA, Journal of spinal pain, Volume 21, Edition 1, Pages 123-129</ref>. | ||
* Although early studies reported reasonable long term relief of symptoms (20-54%), more recent studies have suggested that steroid injection "is of little value". However, short term relief is common (59-94%) and therefore it remains a useful procedure, especially to confirm the diagnosis<ref name=":1" />. | * Although early studies reported reasonable long term relief of symptoms (20-54%), more recent studies have suggested that steroid injection "is of little value". However, short term relief is common (59-94%) and therefore it remains a useful procedure, especially to confirm the diagnosis<ref name=":1" />. | ||
== Lumbar Facet Joints == | |||
== Lumbar Facet | |||
[[File:Lumbar vertebra.png|right|frameless]] | [[File:Lumbar vertebra.png|right|frameless]] | ||
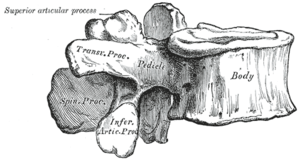
Lumbar Facet (zygapophysial) joints are formed of the superior and inferior articulating processes of adjacent vertebra <ref name="Strayer,A. 2005">Strayer,A., 2005. Lumbar Spine: Common Pathology and Interventions. The Journal of Neuroscience Nursing. 37(4) pp 181-193.</ref>. | Lumbar Facet (zygapophysial) joints are formed of the superior and inferior articulating processes of adjacent vertebra <ref name="Strayer,A. 2005">Strayer,A., 2005. Lumbar Spine: Common Pathology and Interventions. The Journal of Neuroscience Nursing. 37(4) pp 181-193.</ref>. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 18: | ||
== Facet Joint Injection == | == Facet Joint Injection == | ||
[[Facet Joints|Facet joints]] have been recognised as a possible source of chronic LBP since the early 1900's <ref name="Peh,2009" /><ref name="Manchikanti et al, 2004" />. | * [[Facet Joints|Facet joints]] have been recognised as a possible source of chronic LBP since the early 1900's <ref name="Peh,2009" /><ref name="Manchikanti et al, 2004" />. | ||
* Facet joint injections have two main purposes; one to relieve pain both short and long term and the other to be used conjunctively with the physical examination as a diagnostic tool to determine whether the facet joint is the source of pain <ref name="Peh,2009" /><ref name="Manchikanti et al, 2004" /><ref name="Sehgal et al, 2007" />. <br> | |||
Facet joint injections have two main purposes; one to relieve pain both short and long term and the other to be used conjunctively with the physical examination as a diagnostic tool to determine whether the facet joint is the source of pain <ref name="Peh,2009" /><ref name="Manchikanti et al, 2004" /><ref name="Sehgal et al, 2007" />. <br> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FJq68eIx4KM|width}}<ref>Facet injections Facet Injections - Pain Management Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FJq68eIx4KM Last accessed 14.11.2019)</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FJq68eIx4KM|width}}<ref>Facet injections Facet Injections - Pain Management Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FJq68eIx4KM Last accessed 14.11.2019)</ref> | ||
# '''Diagnostic Facet Joint Injection''' | # '''Diagnostic Facet Joint Injection''' | ||
| Line 43: | Line 37: | ||
== Procedures == | == Procedures == | ||
Facet joint injections | Facet joint injections: Minimally-invasive - outpatient procedure can be performed in just a couple hours. The procedure itself usually takes less than 15 minutes. | ||
Minimally-invasive - outpatient | |||
The procedure itself usually takes less than 15 minutes. | |||
* To start, patients usually only receive a local anesthetic, but in some cases they may opt for general sedation. | * To start, patients usually only receive a local anesthetic, but in some cases they may opt for general sedation. | ||
* To begin the procedure, patients will lie face down on the examining table. The area to be injected will be cleaned and numbed with a topical numbing agent before a local anesthetic is administered. | * To begin the procedure, patients will lie face down on the examining table. The area to be injected will be cleaned and numbed with a topical numbing agent before a local anesthetic is administered. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 53: | ||
== Implications for Treatment == | == Implications for Treatment == | ||
Facet injections are generally offered | Facet injections are generally offered following failure to improve from a period of conservative treatments eg physiotherapy, drug therapy, bed rest, and [[Back Education Program|exercise]]. | ||
* Studies have shown the interval of 6 weeks post-injection, when pain is ideally 80-100% elimintated<ref name=":0" /> physiotherapy treatments (eg land-based lower back mobility exercise, [[Manual Therapy Techniques For The Lumbar Spine|Manual Therapy Techniques]] For The Lumbar Spine, [[McKenzie Method]]) may be of benefit to improve the longer-term outcomes of patients with [[Chronic Low Back Pain|chronic low back pain]].<ref name="Staal, 2008" /> | |||
The following are examples of when injections may be used | |||
#[[Lumbar Facet Syndrome|Lumbar Facet Syndrome]]: both diagnostic (i.e. relief of pain after injection of local anaesthetic) and therapeutic chronic low back pain. | #[[Lumbar Facet Syndrome|Lumbar Facet Syndrome]]: both diagnostic (i.e. relief of pain after injection of local anaesthetic) and therapeutic chronic low back pain. | ||
#[[Spondylolisthesis|Spondylolisthesis]] | #[[Spondylolisthesis|Spondylolisthesis]] | ||
#[[Spondylolysis|Spondylolysis]] | #[[Spondylolysis|Spondylolysis]] | ||
#[[Ankylosing Spondylitis|Ankylosing Spondylitis]] | #[[Ankylosing Spondylitis (Axial Spondyloarthritis)|Ankylosing Spondylitis]] | ||
#[[Spinal Stenosis|Spinal Stenosis]] | #[[Spinal Stenosis|Spinal Stenosis]] | ||
#Trauma (e.g. road traffic accidents or sports/work with repetitive forceful hyperextensions)<ref name="Peh,2009" /><ref name="Harvey, 1991">Harvey,J., Tanner, S., 1991. Low Back Pain in Young Athletes. Journal of Sports Medicine. 12(6) pp.394-406.</ref> | #Trauma (e.g. road traffic accidents or sports/work with repetitive forceful hyperextensions)<ref name="Peh,2009" /><ref name="Harvey, 1991">Harvey,J., Tanner, S., 1991. Low Back Pain in Young Athletes. Journal of Sports Medicine. 12(6) pp.394-406.</ref> | ||
#Low back pain (+/- sciatica) with normal imaging findings | #Low back pain (+/- [[sciatica]]) with normal imaging findings | ||
#Post-laminectomy syndrome<ref name=":1" /> | #Post-laminectomy syndrome<ref name=":1" /> | ||
== Complications | == Complications == | ||
Rare: | |||
* Infection, including [[Septic (Infectious) Arthritis|septic arthritis]] and discitis-[[osteomyelitis]] | |||
* Allergic/anaphylactic reaction | |||
* Local reaction to [[Therapeutic Corticosteroid Injection|steroid injection]] (usually >48 hours) | |||
* Bleeding<ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Contraindications == | == Contraindications == | ||
| Line 117: | Line 83: | ||
#Progressive neurological disorders that may be masked by the procedure | #Progressive neurological disorders that may be masked by the procedure | ||
#Pregnancy (due to exposure to radioactive material, eg x-ray) | #Pregnancy (due to exposure to radioactive material, eg x-ray) | ||
#Uncontrolled diabetes and heart disease | #Uncontrolled [[diabetes]] and [[Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)|heart disease]]<ref name="Peh,2009" /><ref name="MedCentral Health System, 2012">MedCentral Health System, 2012. Facet Injections. [online] Available athttp://www.medcentral.org/Main/FacetInjections.aspx[Accessed 30 December 2012].</ref> | ||
<ref name="Peh,2009" /><ref name="MedCentral Health System, 2012">MedCentral Health System, 2012. Facet Injections. [online] Available athttp://www.medcentral.org/Main/FacetInjections.aspx[Accessed 30 December 2012].</ref> | |||
== Effectiveness of Facet Joint Injections == | == Effectiveness of Facet Joint Injections == | ||
On conclusion, the evidence on the effectiveness of facet joint injections is inconclusive due to wide variation between studies that limits the number of comparable studies. | |||
A recent Cochrane review <ref name="Staal, 2008">Staal. B, Bie. R, De Vet. H, Hildebrandt. J, Nelemans. P, 2008, Injection therapy for subacute and chronic low back pain, Department of Epidemiology and Caphri Research Institute, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands, The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, Volume 16, Edition 3</ref> evaluated lumbar facet injections random controlled trials used in sub-acute (< 6 weeks) and chronic (> 3 months) | A recent Cochrane review <ref name="Staal, 2008">Staal. B, Bie. R, De Vet. H, Hildebrandt. J, Nelemans. P, 2008, Injection therapy for subacute and chronic low back pain, Department of Epidemiology and Caphri Research Institute, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands, The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, Volume 16, Edition 3</ref> evaluated lumbar facet injections random controlled trials used in sub-acute (< 6 weeks) and chronic (> 3 months) | ||
* They stated due to a lack of inconsistency between studies in terms of area, drugs, dosage and outcome measures statistical pooling was not possible and as such performed a best-evidence synthesis. | |||
NICE guidelines (2009) for LBP recommends | |||
* Further comparable research is required into this area before reliable conclusions can be made (including research into which demographic groups respond more favourably).<ref name="NICE 2009">NICE clinical guidelines, CG88, Low Back Pain, 2009</ref> | |||
== Conclusions == | == Conclusions == | ||
Facet joint injections are becoming increasingly more popular in current practice <ref name="Mayer, 2004">Mayer. T, Gatchel. R, Keeley. J, McGeary. D, Dersh. J, Anagnostis. C, 2004, A randomised clinical trial of treatment for lumbar segmental rigidity, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, TX, USA, Spine, Volume 29, Edition 20, Pages 2199-2205</ref> | Facet joint injections are becoming increasingly more popular in current practice <ref name="Mayer, 2004">Mayer. T, Gatchel. R, Keeley. J, McGeary. D, Dersh. J, Anagnostis. C, 2004, A randomised clinical trial of treatment for lumbar segmental rigidity, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, TX, USA, Spine, Volume 29, Edition 20, Pages 2199-2205</ref> | ||
* The increasing popularity of this treatment may be due to it being passive compared to the alternatives (exercise programs and postural care) which require the patient to make active changes to their lifestyle. | |||
* The small amount of literature on whether a facet joint injection is as effective as its alternatives have contrasting conclusions. | |||
* It is clear that the literature base is simply not large enough yet to effectively inform practice. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 10:28, 13 April 2022
Top Contributors - Tommy Pearson, Joe Wakefield, Michelle harvey, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, Laura Ritchie, Admin, Rachael Lowe and George Baker
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Facet (zygapophyseal) joint injections are performed primarily for the diagnosis and differentiation of facet syndrome and radicular pain syndrome, and are one of the spinal interventional procedures.
- They can be performed under fluoroscopic, or CT image guidance (cervical, thoracic or most commonly lumbosacral facet joints can be injected)
- One or multiple joints can be injected during one procedure[1].
- Spinal injections are one of the many varieties of treatments considered when an individual presents with chronic LBP [2].
The effectiveness of facet joint injections is largely unknown but despite this, the procedure is still commonly performed by clinicians [3].
- Although early studies reported reasonable long term relief of symptoms (20-54%), more recent studies have suggested that steroid injection "is of little value". However, short term relief is common (59-94%) and therefore it remains a useful procedure, especially to confirm the diagnosis[1].
Lumbar Facet Joints[edit | edit source]
Lumbar Facet (zygapophysial) joints are formed of the superior and inferior articulating processes of adjacent vertebra [4].
- Classed as plane synovial joints [5].
- Orientated in a vertical projection [5].
- Articular surfaces are covered by hyaline cartilage, surrounded by a thin fibrous joint capsule that contains a synovial membrane that secretes synovial fluid into the joint space [6] [5].
- Free and encapsulated nerve endings supplied by the medial branches of the dorsi rami, innervate the facet joints [7][8].
Facet Joint Injection[edit | edit source]
- Facet joints have been recognised as a possible source of chronic LBP since the early 1900's [6][8].
- Facet joint injections have two main purposes; one to relieve pain both short and long term and the other to be used conjunctively with the physical examination as a diagnostic tool to determine whether the facet joint is the source of pain [6][8][7].
- Diagnostic Facet Joint Injection
The following two-step response pattern is the current gold standard which is used to diagnose facet joint syndrome, which may indicate a need for a therapeutic facet joint injection[10]
1. Saline is injected causing distension of the problematic facet joint - this should reproduce/increase the patients’ pain.
2. Injection of local anaesthetic into the facet joint - this should reduce/relieve the patients’ pain[11].
Diagnostic positive facet joint block can indicate facet joints as the source of chronic spinal pain.
- These patients may benefit from specific interventions to eliminate facet joint pain such as Therapeutic Facet Joint Injection or neurolysis (by radiofrequency or cryoablation)[12]
- Neurolysis is the application of a chemical or physical destructive agent to a nerve to create a long-lasting or permanent interruption of neural transmission.[13]
2. Therapeutic Facet Joint Injection
A local anaesthetic is initially given to decrease the nociceptive signals in and around the facet joint. This is followed by the therapeutic injection which typically contains a mixture of a long-acting steroid (e.g. Triamcinolone) and local anaesthesia (e.g. Bupivacaine).
- Early studies reported reasonable long term relief of symptoms (20-54%)
- More recent studies have suggested that steroid injection "is of little value".
- Short term relief is common (59-94%) [1].
Procedures[edit | edit source]
Facet joint injections: Minimally-invasive - outpatient procedure can be performed in just a couple hours. The procedure itself usually takes less than 15 minutes.
- To start, patients usually only receive a local anesthetic, but in some cases they may opt for general sedation.
- To begin the procedure, patients will lie face down on the examining table. The area to be injected will be cleaned and numbed with a topical numbing agent before a local anesthetic is administered.
- The doctor inserts a needle using fluoroscopy to ensure proper placement.
- Once the needle is in place, guided also by a fluoroscopic dye, an anesthetic and a steroid will be injected into the facet joint.
- The steroid reduces inflammation and irritation and the anesthetic numbs the pain.
- The combination medicine then spreads to other levels and portions of the spine, reducing inflammation and irritation.[14]
- The needle will then be removed and a dressing applied to the injection area.
- Post-procedure care
- pain score assessed immediately and 15-20 minutes post-procedure
- observe for 20 minutes for any immediate complications
- advise to complete pain diary for the next two weeks[1]
- In normal circumstances, the patient is able to return home via escort two hours post-procedure. Under no circumstances is the patient allowed to drive home 2 hours post-treatment.[15]
Implications for Treatment[edit | edit source]
Facet injections are generally offered following failure to improve from a period of conservative treatments eg physiotherapy, drug therapy, bed rest, and exercise.
- Studies have shown the interval of 6 weeks post-injection, when pain is ideally 80-100% elimintated[12] physiotherapy treatments (eg land-based lower back mobility exercise, Manual Therapy Techniques For The Lumbar Spine, McKenzie Method) may be of benefit to improve the longer-term outcomes of patients with chronic low back pain.[16]
The following are examples of when injections may be used
- Lumbar Facet Syndrome: both diagnostic (i.e. relief of pain after injection of local anaesthetic) and therapeutic chronic low back pain.
- Spondylolisthesis
- Spondylolysis
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Spinal Stenosis
- Trauma (e.g. road traffic accidents or sports/work with repetitive forceful hyperextensions)[6][17]
- Low back pain (+/- sciatica) with normal imaging findings
- Post-laminectomy syndrome[1]
Complications[edit | edit source]
Rare:
- Infection, including septic arthritis and discitis-osteomyelitis
- Allergic/anaphylactic reaction
- Local reaction to steroid injection (usually >48 hours)
- Bleeding[1]
Contraindications[edit | edit source]
There were no definite contraindications; however this procedure was generally avoided in patients with;
- Systematic infections
- Skin infections over the injection site
- Bleeding disorders (Coagulopathy) or patients taking blood thinning medication
- Allergies to the medication or contrast agents used during the procedure
- Progressive neurological disorders that may be masked by the procedure
- Pregnancy (due to exposure to radioactive material, eg x-ray)
- Uncontrolled diabetes and heart disease[6][18]
Effectiveness of Facet Joint Injections[edit | edit source]
On conclusion, the evidence on the effectiveness of facet joint injections is inconclusive due to wide variation between studies that limits the number of comparable studies.
A recent Cochrane review [16] evaluated lumbar facet injections random controlled trials used in sub-acute (< 6 weeks) and chronic (> 3 months)
- They stated due to a lack of inconsistency between studies in terms of area, drugs, dosage and outcome measures statistical pooling was not possible and as such performed a best-evidence synthesis.
NICE guidelines (2009) for LBP recommends
- Further comparable research is required into this area before reliable conclusions can be made (including research into which demographic groups respond more favourably).[19]
Conclusions[edit | edit source]
Facet joint injections are becoming increasingly more popular in current practice [20]
- The increasing popularity of this treatment may be due to it being passive compared to the alternatives (exercise programs and postural care) which require the patient to make active changes to their lifestyle.
- The small amount of literature on whether a facet joint injection is as effective as its alternatives have contrasting conclusions.
- It is clear that the literature base is simply not large enough yet to effectively inform practice.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Radiopedia Facet joint injections Available from:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/facet-joint-injection (last accessed 10.9.2020)
- ↑ NHS Hospital Episode Statistics, 2011. main Procedures and Interventions: Outpatient Statistics[excel]Available at: http://www.hesonline.nhs.uk [Accessed 20 November 2012]
- ↑ Eckel. T, 2004, Facet Joint Injections, Department of radiology, Lewis-Gale medical centre, 1900 Electric road, Salem, Virginia, USA, Journal of spinal pain, Volume 21, Edition 1, Pages 123-129
- ↑ Strayer,A., 2005. Lumbar Spine: Common Pathology and Interventions. The Journal of Neuroscience Nursing. 37(4) pp 181-193.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Palastanga,N.,Field,D.,Soames,R.,2006. Anatomy and Human Movement: Structure and Function. Butterworth Heinemann Elsevier:London
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Peh,W.C.G., 2009. Image-guided Facet Joint Injection. [online] Available at:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3107686/pdf/biij-07-e4.pdf[Accessed 27 December 2012]
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Sehgal,N., Dunbar,E.E., Shah,R.V., Colson,J., 2007. Systematic Review of Diagnostic Utility of Facet (Zygopophysial) Joint Injections In Chronic Spinal Pain: An Update. Journal of Pain Physician [online] Available at:http://www.painphysicianjournal.com/2007/january/2007%3B10%3B213-228.pdf[Accessed 29 Nov 2012].
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Manchikanti, L., Boswell,M.V., Singh,V., Pampati,V., Damron,K.S., Beyer,C.D., 2004. Prevalence of Facet Joint Pain in Chronic Spinal Pain of Cervical, Thoracic, and Lumbar Regions, [online] Available at:http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/pdf/1471-2474-5-15.pdf[Accessed 27 December 2012].
- ↑ Facet injections Facet Injections - Pain Management Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FJq68eIx4KM Last accessed 14.11.2019)
- ↑ Sehgal, N., Shah, R., McKenzie-Brown, A. and Everett, C. (2005) Diagnostic utility of facet (zygapophysial) joint injections in chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of evidence. Pain Physician 8(2): pp.211–224.
- ↑ Murtagh, F. (1988) Computed tomography and fluoroscopy guided anesthesia and steroid injection in facet syndrome. Spine 13(6): pp.686–689.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Perolat R, Kastler A, Nicot B, Pellat JM, Tahon F, Attye A, Heck O, Boubagra K, Grand S, Krainik A. Facet joint syndrome: from diagnosis to interventional management. Insights into imaging. 2018 Oct 1;9(5):773-89.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6206372/ (last accessed 14.11.2019)
- ↑ Hanania MM, Argoff CE. PERMANENT NEURAL BLOCKADE AND CHEMICAL ABLATION. Pain Management Secrets E-Book. 2009 Jul 31:296. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323040198000391 (last accessed 14.11.2019)
- ↑ Pain Dr Facet jt injections Available from:https://paindoctor.com/treatments/facet-joint-injections/ (last accessed 10.9.2020)
- ↑ NHS Evidence 2012. Lumbar facet joint injection. [online] Available at: http://www.royalberkshire.nhs.uk/pdf/Lumbar_facet_joint_injection_dec10.pdf [Accessed 04 January 2013].
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Staal. B, Bie. R, De Vet. H, Hildebrandt. J, Nelemans. P, 2008, Injection therapy for subacute and chronic low back pain, Department of Epidemiology and Caphri Research Institute, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands, The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, Volume 16, Edition 3
- ↑ Harvey,J., Tanner, S., 1991. Low Back Pain in Young Athletes. Journal of Sports Medicine. 12(6) pp.394-406.
- ↑ MedCentral Health System, 2012. Facet Injections. [online] Available athttp://www.medcentral.org/Main/FacetInjections.aspx[Accessed 30 December 2012].
- ↑ NICE clinical guidelines, CG88, Low Back Pain, 2009
- ↑ Mayer. T, Gatchel. R, Keeley. J, McGeary. D, Dersh. J, Anagnostis. C, 2004, A randomised clinical trial of treatment for lumbar segmental rigidity, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, TX, USA, Spine, Volume 29, Edition 20, Pages 2199-2205