Uterine Prolapse: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Uterine prolapse is the herniation of the uterus into the vaginal canal due to the weakening of its support structures. This is a common condition that is not life-threatening; however, it causes significant morbidity among women.<ref name=":0">Chen CJ, Thompson H. [https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/30897 Uterine Prolapse]. StatPearls [Internet]. 2020 Nov 19.Available from:https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/30897 (accessed 4.4.2021)</ref> | Uterine prolapse is the herniation of the uterus into the vaginal canal due to the weakening of its support structures. This is a common condition that is not life-threatening; however, it causes significant morbidity among women.<ref name=":0">Chen CJ, Thompson H. [https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/30897 Uterine Prolapse]. StatPearls [Internet]. 2020 Nov 19.Available from:https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/30897 (accessed 4.4.2021)</ref> | ||
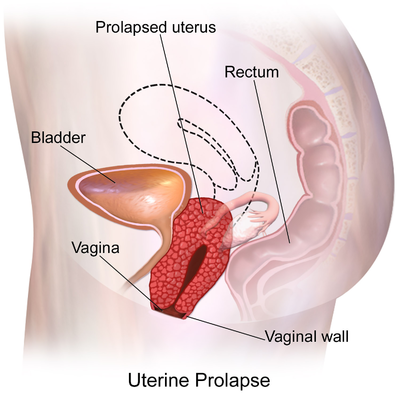
Uterine prolapse is the herniation of the uterus from its natural anatomical location into the vaginal canal, through the hymen, or through the introitus of the vagina. This is due to the weakening of its surrounding support structures. Uterine prolapse is one of the multiple conditions that are classified under the broader term of pelvic organ prolapse. | Uterine prolapse is the herniation of the uterus from its natural anatomical location into the vaginal canal, through the hymen, or through the introitus of the vagina. This is due to the weakening of its surrounding support structures. Uterine prolapse is one of the multiple conditions that are classified under the broader term of [[Pelvic Organ Prolapse|pelvic organ prolapse]]. | ||
In its usual state, the uterus rests in the apical compartment of pelvic organs. The [[Female Genital Tract|uterus and vagina]] are suspended from the [[sacrum]] and lateral pelvic sidewall via the uterosacral and cardinal ligament complexes. The weakening of these ligaments allows for the prolapse of the uterus into the vaginal vault. | In its usual state, the uterus rests in the apical compartment of pelvic organs. The [[Female Genital Tract|uterus and vagina]] are suspended from the [[sacrum]] and lateral pelvic sidewall via the uterosacral and cardinal ligament complexes. The weakening of these ligaments allows for the prolapse of the uterus into the vaginal vault. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
* Approximately 50% of women in the US can be expected to have some degree of pelvic organ prolapse in advanced age ( affects 9.7% of women between ages 20-39 and 49.7% of women >80 years old). | * Approximately 50% of women in the US can be expected to have some degree of pelvic organ prolapse in advanced age ( affects 9.7% of women between ages 20-39 and 49.7% of women >80 years old). | ||
* In less developed countries such as Nepal, greater than 1 million women out of approximately 15 million women have been found to have uterine prolapse, equating to approximately 7% of the Nepalese female population<ref name=":0" /> | * In less developed countries such as Nepal, greater than 1 million women out of approximately 15 million women have been found to have uterine prolapse, equating to approximately 7% of the Nepalese female population<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Treatment/Management == | |||
Treatment of uterine prolapse is largely dependent on the extent to which a patient is experiencing symptoms. Conservative treatments include pelvic floor muscle training and vaginal pessaries. There are many surgical options for treatment, as well<ref name=":0" />. | |||
Proper diagnosis and management of uterine prolapse can majorly impact a patient’s quality of life and can have long-term physical and mental health effects. Healthcare practitioners should thoroughly counsel patients with uterine prolapse so they can make informed decisions and choose the treatment that is right for them. | |||
Pelvic floor muscle training is typically taught to patients in association with a physiotherapist. They have been shown to result in subjective improvement in symptoms by patients as well as objective improvement in the POP-Q score by examiners.[9] | |||
Vaginal pessaries are objects often made of silicone that are inserted into the vagina to provide support for the prolapsed pelvic organs. It has been found that vaginal pessary has been a successful solution in 84% of cases of advanced pelvic organ prolapse with mild adverse events in 31% of cases.[10] While pessaries do not reverse the herniation of pelvic organs, they can decrease symptoms and prevent the progression of prolapse. Patients must be fitted for a pessary and commonly try several pessaries before finding the appropriate one. Patients should have empty bowels and bladder when being fitted for a pessary. The examiner should be able to sweep a single finger between the pessary and vaginal walls. The patient should be able to walk, bend, and urinate comfortably without shifting the pessary. Complications of pessary placement include vaginal irritation/ulceration, discharge, pain, bleeding, and odor.[11] | |||
Regular reassessments of pessary fit should be performed to ensure that the pessary is not rubbing against the walls of the vagina, as this can lead to irritation of the vaginal mucosa and predispose patients to infection. Rare complications include movement of the pessary into the bladder or rectum, causing fistula, fecal impaction, and urosepsis [3]. Patients with dementia or poor follow up are not good candidates for pessary placement as they require frequent cleaning and regular reassessment of position to prevent complications. | |||
The decision for surgical management should be made after a detailed discussion with the patient regarding the desire for future vaginal intercourse, effects on body image, cultural views, alternative treatments, and potential complications. In-depth descriptions of surgical techniques are beyond the scope of this article. | |||
Hysterectomy can be performed via a vaginal or transabdominal approach as a treatment for uterine prolapse. It has been found that vaginal approaches are less invasive and offer the opportunity to repair pelvic floor defects. Additional procedures can be performed concomitantly to reduce the risk of prolapse of other pelvic organs. | |||
Uterine preservation strategies have also been developed to suit those patients that wish to maintain future fertility or desire to retain their uterus. Another patient-centered lifestyle advantage includes a natural transition to menopause. Patients who undergo uterine-sparing treatments require continued follow-up for surveillance of gynecological cancers; therefore uterine preservation is contraindicated in patients that have a history of uterine or cervical pathology. Hysteropexy allows for decreased intraoperative blood loss, shorter operative time, and faster recovery compared to hysterectomy with prolapse repair.[12] | |||
Colpoclesis is an obliterative, noninvasive surgical option that involves suturing the walls of the vagina together to completely occlude the vaginal canal and provide muscular support for the remainder of the pelvic organs. This procedure is ideal for those post-hysterectomy patients that do not desire to have future vaginal intercourse. | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
<u>[[Image:Pessaries.jpg|frame|center]]'''<u></u><u></u><u></u><u></u><u></u><u></u><u></u><u></u><u></u>''' | |||
== References == | |||
<u> | <u> | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 06:55, 4 April 2021
Original Editors - Amanda Mattingly from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project. Top Contributors - Amanda Mattingly, Admin, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, WikiSysop, 127.0.0.1, Elaine Lonnemann, Wendy Walker, Oyemi Sillo and Nicole Hills
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Uterine prolapse is the herniation of the uterus into the vaginal canal due to the weakening of its support structures. This is a common condition that is not life-threatening; however, it causes significant morbidity among women.[1]
Uterine prolapse is the herniation of the uterus from its natural anatomical location into the vaginal canal, through the hymen, or through the introitus of the vagina. This is due to the weakening of its surrounding support structures. Uterine prolapse is one of the multiple conditions that are classified under the broader term of pelvic organ prolapse.
In its usual state, the uterus rests in the apical compartment of pelvic organs. The uterus and vagina are suspended from the sacrum and lateral pelvic sidewall via the uterosacral and cardinal ligament complexes. The weakening of these ligaments allows for the prolapse of the uterus into the vaginal vault.
Although uterine prolapse is not inherently life-threatening, it can lead to sexual dysfunction, poor body image, and lower quality of life due to associated bowel or bladder incontinence.[1]
Uterine prolapse is classified using a four-part grading system:
- Grade 1: Descent of the uterus to above the hymen
- Grade 2: Descent of the uterus to the hymen
- Grade 3: Descent of the uterus beyond the hymen
- Grade 4: Total prolapse.[2] [3]
Etiology[edit | edit source]
The risk factors for uterine prolapse are the same as for other pelvic organ prolapses.
- The Oxford Family Planning Association study found that pelvic organ prolapse became more likely with successive births.
- Women with BMI >25 were more likely to experience uterine prolapse than women with BMI in the normal range.
- Advancing age has been shown to correlate markedly with rates of prolapse.
- Additional risk factors include connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome and Ehler’s Danlos syndrome[1]
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
It is difficult to distinguish rates of uterine prolapse from pelvic organ prolapse as most studies cohort them together.
- Approximately 50% of women in the US can be expected to have some degree of pelvic organ prolapse in advanced age ( affects 9.7% of women between ages 20-39 and 49.7% of women >80 years old).
- In less developed countries such as Nepal, greater than 1 million women out of approximately 15 million women have been found to have uterine prolapse, equating to approximately 7% of the Nepalese female population[1]
Treatment/Management[edit | edit source]
Treatment of uterine prolapse is largely dependent on the extent to which a patient is experiencing symptoms. Conservative treatments include pelvic floor muscle training and vaginal pessaries. There are many surgical options for treatment, as well[1].
Proper diagnosis and management of uterine prolapse can majorly impact a patient’s quality of life and can have long-term physical and mental health effects. Healthcare practitioners should thoroughly counsel patients with uterine prolapse so they can make informed decisions and choose the treatment that is right for them.
Pelvic floor muscle training is typically taught to patients in association with a physiotherapist. They have been shown to result in subjective improvement in symptoms by patients as well as objective improvement in the POP-Q score by examiners.[9]
Vaginal pessaries are objects often made of silicone that are inserted into the vagina to provide support for the prolapsed pelvic organs. It has been found that vaginal pessary has been a successful solution in 84% of cases of advanced pelvic organ prolapse with mild adverse events in 31% of cases.[10] While pessaries do not reverse the herniation of pelvic organs, they can decrease symptoms and prevent the progression of prolapse. Patients must be fitted for a pessary and commonly try several pessaries before finding the appropriate one. Patients should have empty bowels and bladder when being fitted for a pessary. The examiner should be able to sweep a single finger between the pessary and vaginal walls. The patient should be able to walk, bend, and urinate comfortably without shifting the pessary. Complications of pessary placement include vaginal irritation/ulceration, discharge, pain, bleeding, and odor.[11]
Regular reassessments of pessary fit should be performed to ensure that the pessary is not rubbing against the walls of the vagina, as this can lead to irritation of the vaginal mucosa and predispose patients to infection. Rare complications include movement of the pessary into the bladder or rectum, causing fistula, fecal impaction, and urosepsis [3]. Patients with dementia or poor follow up are not good candidates for pessary placement as they require frequent cleaning and regular reassessment of position to prevent complications.
The decision for surgical management should be made after a detailed discussion with the patient regarding the desire for future vaginal intercourse, effects on body image, cultural views, alternative treatments, and potential complications. In-depth descriptions of surgical techniques are beyond the scope of this article.
Hysterectomy can be performed via a vaginal or transabdominal approach as a treatment for uterine prolapse. It has been found that vaginal approaches are less invasive and offer the opportunity to repair pelvic floor defects. Additional procedures can be performed concomitantly to reduce the risk of prolapse of other pelvic organs.
Uterine preservation strategies have also been developed to suit those patients that wish to maintain future fertility or desire to retain their uterus. Another patient-centered lifestyle advantage includes a natural transition to menopause. Patients who undergo uterine-sparing treatments require continued follow-up for surveillance of gynecological cancers; therefore uterine preservation is contraindicated in patients that have a history of uterine or cervical pathology. Hysteropexy allows for decreased intraoperative blood loss, shorter operative time, and faster recovery compared to hysterectomy with prolapse repair.[12]
Colpoclesis is an obliterative, noninvasive surgical option that involves suturing the walls of the vagina together to completely occlude the vaginal canal and provide muscular support for the remainder of the pelvic organs. This procedure is ideal for those post-hysterectomy patients that do not desire to have future vaginal intercourse.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Chen CJ, Thompson H. Uterine Prolapse. StatPearls [Internet]. 2020 Nov 19.Available from:https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/30897 (accessed 4.4.2021)
- ↑ Bordman R, Telner D, Jackson B, Little D. Step-by-step approach to managing pelvic organ prolapse. Canadian Family Physician; 2007; 53: 485-487.
- ↑ Mater Mothers' Hospital. Prolapse. http://brochures.mater.org.au/Home/Brochures/Mater-Mothers--Hospitals/Prolapse (accessed 5 April 2010).