Neuropathies: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | == Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | ||
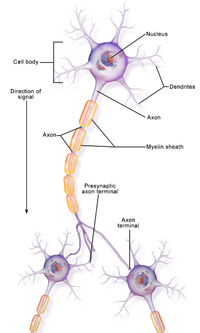
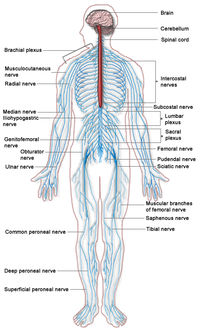
Neuropathy is a dysfunction of one or more peripheral nerves or peripheral nervous system. Neuropathy can involve damage o: only one nerve (called mononeuropathy); two or more nerves in different areas, called mononeuropathy multiplex; or most commonly, many nerves are affected (called polyneuropathy). | |||
The short video below illustrates the types of neuropathies and their treatment. | The short video below illustrates the types of neuropathies and their treatment. | ||
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hYVtd3hB2_w|width}}<ref>Manipal hospitals. Types of neuropathies. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hYVtd3hB2_w (last accessed 18.4.2019)</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hYVtd3hB2_w|width}}<ref>Manipal hospitals. Types of neuropathies. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hYVtd3hB2_w (last accessed 18.4.2019)</ref> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
* Autoimmune diseases that attack nerves eg Guillain-Barre syndrome, Multifocal motor neuropathy. | * Autoimmune diseases that attack nerves eg Guillain-Barre syndrome, Multifocal motor neuropathy. | ||
* Toxins eg from toxic amounts of substances in the blood associated with kidney and liver disorders, alcoholism, chemotherapy drugs | * Toxins eg from toxic amounts of substances in the blood associated with kidney and liver disorders, alcoholism, chemotherapy drugs | ||
* Infections eg Varicella zoster virus (shingles), White Nile virus, AIDS, Lyme disease ( carried by ticks)<ref name=":0">NIH [https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Peripheral-Neuropathy-Fact-Sheet Peripheral neuropathy fact sheet.] Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Peripheral-Neuropathy-Fact-Sheet (last accessed 18 | * Infections eg Varicella zoster virus (shingles), White Nile virus, AIDS, Lyme disease ( carried by ticks)<ref name=":0">NIH [https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Peripheral-Neuropathy-Fact-Sheet Peripheral neuropathy fact sheet.] Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Peripheral-Neuropathy-Fact-Sheet (last accessed 18 April 2019)</ref> | ||
[[File:Nervous system diagram.png|thumb|330x330px]] | [[File:Nervous system diagram.png|thumb|330x330px]] | ||
Neuropathies may primarily affect sensory nerves, motor nerves, autonomic nerves, or multiple types. Anything that damages nerves can interfere with their ability to transmit accurate signals, which can lead to a number of signs and symptoms.<br> | Neuropathies may primarily affect sensory nerves, motor nerves, autonomic nerves, or multiple types. Anything that damages nerves can interfere with their ability to transmit accurate signals, which can lead to a number of signs and symptoms.<br> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
* Motor nerve damage will cause muscle weakness, painful cramps, fasciculations (uncontrolled muscle twitching visible under the skin) and muscle shrinking. | * Motor nerve damage will cause muscle weakness, painful cramps, fasciculations (uncontrolled muscle twitching visible under the skin) and muscle shrinking. | ||
* Sensory nerve damage causes various symptoms because sensory nerves have a broad range of functions. Damage to large sensory fibers affects the ability to feel vibrations and touch. The client may feel as if you are wearing gloves and stockings. This damage may contribute to the loss of reflexes (along with | * Sensory nerve damage causes various symptoms because sensory nerves have a broad range of functions. Damage to large sensory fibers affects the ability to feel vibrations and touch. The client may feel as if you are wearing gloves and stockings. This damage may contribute to the loss of reflexes (along with motor nerve damage). Loss of position sense presenting with eg balance problems. The “small fibers”( without myelin sheaths ) damage affects the transmission of pain and temperature sensations which interferes with the ability to feel pain or changes in temperature. This causes [[Neuropathic pain|neuropathic pain,]] which can erode a person's [[Quality-Adjusted Life Year|quality of life.]] | ||
* Autonomic nerve damage affects the axons in small-fiber neuropathies. Common symptoms include excess sweating, heat intolerance, inability to expand and contract the small blood vessels that regulate blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms.<ref name=":0" /> | * Autonomic nerve damage affects the axons in small-fiber neuropathies. Common symptoms include excess sweating, heat intolerance, inability to expand and contract the small blood vessels that regulate blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
* Nerve function tests, checking nerve conduction. | * Nerve function tests, checking nerve conduction. | ||
* Nerve biopsy, looking for abnormalities | * Nerve biopsy, looking for abnormalities | ||
* Skin biopsy, looking for reduction in nerve endings<ref name=":1">Mayo clinic. [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352067 Peripheral neuropathy.] Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352067 (last accessed 18 | * Skin biopsy, looking for reduction in nerve endings<ref name=":1">Mayo clinic. [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352067 Peripheral neuropathy.] Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352067 (last accessed 18 April 2019)</ref><br> | ||
== Outcome Measures == | == Outcome Measures == | ||
The many different presentations of neuropathies lead to a need to client | The many different presentations of neuropathies lead to a need to client -pecific outcome measure.s Usually related to muscle strength, pain, QOL, and activity limitations. They include | ||
The SF-36 is a measure of health status and an abbreviated variant of it, the SF-6D, is commonly used in health economics as a variable in the quality-adjusted life year calculation to determine the cost-effectiveness of a health treatment.<ref>Wikipedia. SF-36 Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SF-36 (last accessed 19 | The SF-36 is a measure of health status and an abbreviated variant of it, the SF-6D, is commonly used in health economics as a variable in the quality-adjusted life year calculation to determine the cost-effectiveness of a health treatment.<ref>Wikipedia. SF-36 Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SF-36 (last accessed 19 April 2019)</ref> | ||
INCAT (inflammatory cause and treatment) score is a measure of activity limitation | INCAT (inflammatory cause and treatment) score is a measure of activity limitation | ||
[[Timed Up and Go Test (TUG)|TUG]]; | [[Timed Up and Go Test (TUG)|TUG]]; 10 metre walk test; grip strength; [[Fatigue Severity Scale|FSS;]] PSFS; oxford muscle strength scale; [[Romberg Test|Romberg]] test. | ||
[[File:Pill banner.png|right|frameless]] | [[File:Pill banner.png|right|frameless]] | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
Restore, or maintain muscle strength, and prevent muscle shortening and deformity | Restore, or maintain muscle strength, and prevent muscle shortening and deformity | ||
Balance, co-ordination and functional training. | [[Balance]], co-ordination and functional training. | ||
Pain relief eg provision of TENS, massage | Pain relief eg provision of [[Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)|TENS]], [[massage]] | ||
Splints as needed, prevent deformity and contractures | Splints as needed, prevent deformity and contractures | ||
Education re managing | Education re managing conditions, preventing damage and emotional support. | ||
For a comprehensive guide see individual neuropathies below | For a comprehensive guide see individual neuropathies below | ||
Revision as of 17:17, 22 October 2019
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Lead Editors
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Neuropathy is a dysfunction of one or more peripheral nerves or peripheral nervous system. Neuropathy can involve damage o: only one nerve (called mononeuropathy); two or more nerves in different areas, called mononeuropathy multiplex; or most commonly, many nerves are affected (called polyneuropathy). The short video below illustrates the types of neuropathies and their treatment.
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
The causes of neuropathies are manyfold and include:
- Physical injury eg pressure from disc herniation , pressure from a cast, trauma, arthritis.
- Systemic autoimmune diseases eg diabetes, Sjogren's syndrome, RA
- Autoimmune diseases that attack nerves eg Guillain-Barre syndrome, Multifocal motor neuropathy.
- Toxins eg from toxic amounts of substances in the blood associated with kidney and liver disorders, alcoholism, chemotherapy drugs
- Infections eg Varicella zoster virus (shingles), White Nile virus, AIDS, Lyme disease ( carried by ticks)[2]
Neuropathies may primarily affect sensory nerves, motor nerves, autonomic nerves, or multiple types. Anything that damages nerves can interfere with their ability to transmit accurate signals, which can lead to a number of signs and symptoms.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Neuropathies may primarily affect sensory nerves, motor nerves, autonomic nerves, or multiple types. Anything that damages nerves can interfere with their ability to transmit accurate signals, which can lead to a number of signs and symptoms.
Dependant on the type of nerves affected
- Motor nerve damage will cause muscle weakness, painful cramps, fasciculations (uncontrolled muscle twitching visible under the skin) and muscle shrinking.
- Sensory nerve damage causes various symptoms because sensory nerves have a broad range of functions. Damage to large sensory fibers affects the ability to feel vibrations and touch. The client may feel as if you are wearing gloves and stockings. This damage may contribute to the loss of reflexes (along with motor nerve damage). Loss of position sense presenting with eg balance problems. The “small fibers”( without myelin sheaths ) damage affects the transmission of pain and temperature sensations which interferes with the ability to feel pain or changes in temperature. This causes neuropathic pain, which can erode a person's quality of life.
- Autonomic nerve damage affects the axons in small-fiber neuropathies. Common symptoms include excess sweating, heat intolerance, inability to expand and contract the small blood vessels that regulate blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms.[2]
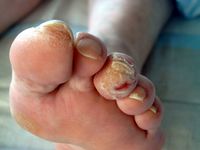 An example of foot damage due to sensory loss.
An example of foot damage due to sensory loss.
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
A full Medical History (including client symptoms, lifestyle, exposure to toxins, drinking habits and a family history of nervous system (neurological) diseases).
Neurological examination
Other tests ordered include
- Blood tests, checking for eg toxins, vitamin deficiencies, diabetes
- Imaging test eg CT MRI for eg tumours, disc herniation.
- Nerve function tests, checking nerve conduction.
- Nerve biopsy, looking for abnormalities
- Skin biopsy, looking for reduction in nerve endings[3]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
The many different presentations of neuropathies lead to a need to client -pecific outcome measure.s Usually related to muscle strength, pain, QOL, and activity limitations. They include
The SF-36 is a measure of health status and an abbreviated variant of it, the SF-6D, is commonly used in health economics as a variable in the quality-adjusted life year calculation to determine the cost-effectiveness of a health treatment.[4]
INCAT (inflammatory cause and treatment) score is a measure of activity limitation
TUG; 10 metre walk test; grip strength; FSS; PSFS; oxford muscle strength scale; Romberg test.
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
Besides medications used to treat conditions associated with peripheral neuropathy, medications used to relieve peripheral neuropathy signs and symptoms include:[3]
Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin; Pregabalin; Valproate
Antidepressants:Amitriptyline; Duloxetine; Venlafaxine
Opioids: Dextromethorphan; Morphine sustained release; Oxycodene; Tapentadol; Tramadol.
Others: Topical nitrate sprays; Capsaicin cream
Physiotherapy[edit | edit source]
The main role of physiotherapy is to
Restore, or maintain muscle strength, and prevent muscle shortening and deformity
Balance, co-ordination and functional training.
Pain relief eg provision of TENS, massage
Splints as needed, prevent deformity and contractures
Education re managing conditions, preventing damage and emotional support.
For a comprehensive guide see individual neuropathies below
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Manipal hospitals. Types of neuropathies. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hYVtd3hB2_w (last accessed 18.4.2019)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 NIH Peripheral neuropathy fact sheet. Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Peripheral-Neuropathy-Fact-Sheet (last accessed 18 April 2019)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mayo clinic. Peripheral neuropathy. Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352067 (last accessed 18 April 2019)
- ↑ Wikipedia. SF-36 Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SF-36 (last accessed 19 April 2019)