Elbow: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Aanal Bhuva (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Rachael Lowe|Rachael Lowe]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | |||
== Anatomy == | == Anatomy == | ||
* Elbow complex is designed to serve hand. | |||
* They provide MOBILITY for Hand in space by apparent shortening and Lengthening of upper extremity. | |||
* They provide Stability for skillful and forceful movements <ref name=":0">Chaurasia BD. [https://www.pdfdrive.com/bd-chaurasia-books.html Human Anatomy Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical]. Vol 1. CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd, 2010</ref> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|I1XEPBTjYVY}}<ref>Kenhub-Learn Human Anatomy. Elbow Joint: Bones, Muscles & Movement-Human Anatomy | Kenhub.Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I1XEPBTjYVY[accessed 26/03/20]</ref> | |||
== HumeroUlnar Joint == | |||
==== Articulations of HumeroUlnar Joint ==== | |||
* The articulating surface on the Humerus is Hour glass shaped TROCHLEA | |||
* The articulating surface on Ulna is a semicircular shaped concave surface called TROCHLEAR NOTCH<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== HumeroRadial Joint == | |||
==== Articulations of HumeroRadial Joint ==== | |||
* The articulating surface on the Humerus is spherical – shaped CAPITULUM | |||
* The articulating surface on the RADIUS is the cup shaped Radial head surrounded by a rim<ref name=":0" /> | |||
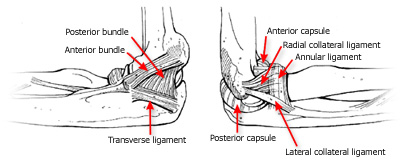
== Ligaments of Elbow joint == | |||
* MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT - Extends from Medial epicondyle of Humerus to Coronoid and Olecranon process of Ulna | |||
* LATERAL COLATERAL LIGAMENT - Extends from Lateral Epicondyle of Humerus to Annular Ligament and Olecranon process. | |||
* ANNULAR LIGAMENT - It encircles the head of Radius<ref name=":0" /> | |||
[[Image:Elbow Anatomy.jpg|400px|center]] | |||
== Movements of Elbow joint == | |||
Flexion and Extension <ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Muscles of Elbow joint == | |||
==== Flexors of Elbow ==== | |||
* Biceps Brachi---Powerful flexor when elbow is in 90 degree Flexion. | |||
* Brachialis----Flexor of elbow in all position | |||
* Brachioradialis---Flexor of elbow in midprone position<ref name=":0" /> | |||
==== Extensors of Elbow ==== | |||
* TRICEPS is the powerful extensor of the Shoulder | |||
* All three Heads of Triceps are active when heavy resistance is given to Extension.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Superior RadioUlnar Joint == | |||
==== Articulation ==== | |||
* The Radial notch on Ulna articulate with Head of Radius along with Annular Ligament & Capitulum.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
==== Ligaments ==== | |||
* Annular Ligament-----circle the head of Radius and keeps the Ulna together. | |||
* Quadrate Ligament----extends from the Inferior edge of radial notch to Neck of Radius | |||
* Oblique cord------attached to inferior part of Radial notch on Ulna to just below Radial Tuberosity<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Inferior RadioUlnar Joint == | |||
==== Articulation ==== | |||
* The Ulnar notch of Radius articulates with head of Ulna along with Articular Disc.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
==== Ligaments ==== | |||
* Anterior Radio Ulnar Ligament----attached to anterior aspect just above the Ulnar head to above Ulnar notch. | |||
* Posterior Radio Ulnar Ligament---attached to posterior part of Ulnar head to above Ulnar notch. | |||
* Interosseous Membrane---binds the shaft of Radius and Ulna together.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
==== Muscles ==== | |||
* PRONATOR TERES----- helps in Pronation,it acts in all position of Elbow, helps in Stabilization of Superio Radio Ulnar Joint. Active during rapid and resisted Pronation. | |||
* PRONATOR QUADRATUS---- helps in Pronation in all position of Elbow | |||
* SUPINATOR---------helps in Supination in all position of Elbow | |||
* BICEPS BRACHI-------- helps in Supination when Elbow is flexed to 90 degree<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Movements of RadioUlnar Joint == | |||
* Pronation & Supination | |||
* Pronation and Supination movement is good when Elbow is Flexed to 90 degree | |||
* In Elbow extended position Pronation is limited due to passive tension in Biceps Brachi. Supination is limited due to passive tension in Interosseous Membrane.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Clinical Examination == | == Clinical Examination == | ||
*[[Elbow Examination|Elbow Examination]] | *[[Elbow Examination|Elbow Examination]] | ||
*Special Tests | *Special Tests | ||
**[[Cozen’s Test|Cozen’s Test]] | **[[Cozen’s Test|Cozen’s Test]] | ||
**[[ | **[[Elbow Flexion Test]] | ||
**[[Elbow Quadrant Tests|Elbow Quadrant Tests]] | |||
**[[ | |||
**[[Elbow Valgus Stress|Elbow Valgus Stress]] | **[[Elbow Valgus Stress|Elbow Valgus Stress]] | ||
**[[Moving Valgus Stress Test|Moving Valgus Stress Test]] | **[[Moving Valgus Stress Test|Moving Valgus Stress Test]] | ||
**[[Elbow Varus Stress|Elbow Varus Stress]] | **[[Elbow Varus Stress|Elbow Varus Stress]] | ||
**[[Elbow | **[[Golfer’s Elbow Test|Golfer’s Elbow Test]] | ||
**[[Mill’s Test|Mill’s Test]] | |||
**[[Polk's Test]] | |||
**[[Pronator Teres Syndrome Test|Pronator Teres Syndrome Test]] | **[[Pronator Teres Syndrome Test|Pronator Teres Syndrome Test]] | ||
**[[Elbow | **[[Tinel's Sign at Elbow|Tinel’s Sign at Elbow]] | ||
**[[Wartenberg’s Sign|Wartenbergs Sign]] | **[[Wartenberg’s Sign|Wartenbergs Sign]] | ||
*Outcome Measures | *Outcome Measures | ||
**[[DASH Outcome Measure]] | |||
**[[Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy Toolkit: Section C - Outcome Measures]] | |||
**[[Upper Extremity Functional Index]] | |||
== Conditions == | == Conditions == | ||
*[[ | *[[Cubital Tunnel Syndrome|Cubital Tunnel Syndrome]] | ||
*[[Elbow Ligamentous Injuries|Ligamentous Injuries]] | *[[Elbow Ligamentous Injuries|Ligamentous Injuries]] | ||
*[[Lateral Epicondylitis|Lateral Epicondylitis]] | *[[Lateral Epicondylitis|Lateral Epicondylitis]] | ||
*[[Medial Epicondylitis|Medial Epicondylitis]] | *[[Medial Epicondylitis|Medial Epicondylitis]] | ||
*[[Olecranon Bursitis|Olecranon Bursitis]] | *[[Olecranon Bursitis|Olecranon Bursitis]] | ||
*[[Olecranon Fracture|Olecranon Fracture]] | *[[Olecranon Fracture|Olecranon Fracture]] | ||
*[[Osteochondritis Dissecans|Osteochondritis Dissecans]] | *[[Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Elbow|Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Elbow]] | ||
*[[Radial Head Fracture|Radial Head Fracture]] | * [[Proximal Radial Head Fracture|Radial Head Fracture]] | ||
*[[Ulnar Nerve Entrapment|Ulnar Nerve Entrapment]] | *[[Ulnar Nerve Entrapment|Ulnar Nerve Entrapment]] | ||
*[[Rheumatoid Arthritis]] | |||
== Procedures == | == Procedures == | ||
| Line 42: | Line 128: | ||
*Ulnar nerve decompression<br> | *Ulnar nerve decompression<br> | ||
== | == References == | ||
[[Category: Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Elbow - Anatomy]] | |||
Latest revision as of 23:22, 30 January 2024
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
- Elbow complex is designed to serve hand.
- They provide MOBILITY for Hand in space by apparent shortening and Lengthening of upper extremity.
- They provide Stability for skillful and forceful movements [1]
HumeroUlnar Joint[edit | edit source]
Articulations of HumeroUlnar Joint[edit | edit source]
- The articulating surface on the Humerus is Hour glass shaped TROCHLEA
- The articulating surface on Ulna is a semicircular shaped concave surface called TROCHLEAR NOTCH[1]
HumeroRadial Joint[edit | edit source]
Articulations of HumeroRadial Joint[edit | edit source]
- The articulating surface on the Humerus is spherical – shaped CAPITULUM
- The articulating surface on the RADIUS is the cup shaped Radial head surrounded by a rim[1]
Ligaments of Elbow joint[edit | edit source]
- MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT - Extends from Medial epicondyle of Humerus to Coronoid and Olecranon process of Ulna
- LATERAL COLATERAL LIGAMENT - Extends from Lateral Epicondyle of Humerus to Annular Ligament and Olecranon process.
- ANNULAR LIGAMENT - It encircles the head of Radius[1]
Movements of Elbow joint[edit | edit source]
Flexion and Extension [1]
Muscles of Elbow joint[edit | edit source]
Flexors of Elbow[edit | edit source]
- Biceps Brachi---Powerful flexor when elbow is in 90 degree Flexion.
- Brachialis----Flexor of elbow in all position
- Brachioradialis---Flexor of elbow in midprone position[1]
Extensors of Elbow[edit | edit source]
- TRICEPS is the powerful extensor of the Shoulder
- All three Heads of Triceps are active when heavy resistance is given to Extension.[1]
Superior RadioUlnar Joint[edit | edit source]
Articulation[edit | edit source]
- The Radial notch on Ulna articulate with Head of Radius along with Annular Ligament & Capitulum.[1]
Ligaments[edit | edit source]
- Annular Ligament-----circle the head of Radius and keeps the Ulna together.
- Quadrate Ligament----extends from the Inferior edge of radial notch to Neck of Radius
- Oblique cord------attached to inferior part of Radial notch on Ulna to just below Radial Tuberosity[1]
Inferior RadioUlnar Joint[edit | edit source]
Articulation[edit | edit source]
- The Ulnar notch of Radius articulates with head of Ulna along with Articular Disc.[1]
Ligaments[edit | edit source]
- Anterior Radio Ulnar Ligament----attached to anterior aspect just above the Ulnar head to above Ulnar notch.
- Posterior Radio Ulnar Ligament---attached to posterior part of Ulnar head to above Ulnar notch.
- Interosseous Membrane---binds the shaft of Radius and Ulna together.[1]
Muscles[edit | edit source]
- PRONATOR TERES----- helps in Pronation,it acts in all position of Elbow, helps in Stabilization of Superio Radio Ulnar Joint. Active during rapid and resisted Pronation.
- PRONATOR QUADRATUS---- helps in Pronation in all position of Elbow
- SUPINATOR---------helps in Supination in all position of Elbow
- BICEPS BRACHI-------- helps in Supination when Elbow is flexed to 90 degree[1]
Movements of RadioUlnar Joint[edit | edit source]
- Pronation & Supination
- Pronation and Supination movement is good when Elbow is Flexed to 90 degree
- In Elbow extended position Pronation is limited due to passive tension in Biceps Brachi. Supination is limited due to passive tension in Interosseous Membrane.[1]
Clinical Examination[edit | edit source]
- Elbow Examination
- Special Tests
- Outcome Measures
Conditions[edit | edit source]
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
- Ligamentous Injuries
- Lateral Epicondylitis
- Medial Epicondylitis
- Olecranon Bursitis
- Olecranon Fracture
- Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Elbow
- Radial Head Fracture
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
Procedures[edit | edit source]
- Elbow Arthrolysis
- Elbow Arthroscopy
- Open debridement or synovectomy
- Radial head excision and synovectomy
- Radial head replacement
- Reconstruction elbow replacement
- Release of lateral epicondylitis
- Total elbow replacement
- Ulnar nerve decompression
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 Chaurasia BD. Human Anatomy Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical. Vol 1. CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd, 2010
- ↑ Kenhub-Learn Human Anatomy. Elbow Joint: Bones, Muscles & Movement-Human Anatomy | Kenhub.Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I1XEPBTjYVY[accessed 26/03/20]