Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Difference between revisions
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Added to Queens Neuromotor Function Category) |
(Added link to AD page) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User: | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Angelique Travlos|Angelique Travlos]] as part of the [[Queen's University Neuromotor Function Project]]<br> | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | |||
== Definition/Description == | == Definition/Description == | ||
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) is a form of [[Parkinsonism]]. It is an uncommon neurological disorder that can affect movement, gait, balance, speech, swallowing, vision, eye movements, mood, behavior, and cognition. | |||
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) is a | |||
The disorder's name refers to the disease worsening (progressive) and causing weakness (palsy) by damaging the brain above nerve cell clusters called nuclei (supranuclear). These nuclei predominantly control eye movement<ref name="7 Canada">Parkinson Canada. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. http://www.parkinson.ca/site/c.kgLNIWODKpF/b.8647261/k.4815/Progressive_Supranuclear_Palsy.htm (accessed 3 May 2017).</ref>. | The disorder's name refers to the disease worsening (progressive) and causing weakness (palsy) by damaging the brain above nerve cell clusters called nuclei (supranuclear). These nuclei predominantly control eye movement<ref name="7 Canada">Parkinson Canada. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. http://www.parkinson.ca/site/c.kgLNIWODKpF/b.8647261/k.4815/Progressive_Supranuclear_Palsy.htm (accessed 3 May 2017).</ref>. | ||
The 5 minute video below is good for an overview of symptoms and diagnosis. | The 5-minute video below is good for an overview of symptoms and diagnosis. | ||
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qn4VrJRiBOk|width}}<ref>CurePSP Symptoms and Diagnosis; PSP, CBD and MSA Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qn4VrJRiBOk (last accessed 18.1.2020)</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qn4VrJRiBOk|width}}<ref>CurePSP Symptoms and Diagnosis; PSP, CBD and MSA Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qn4VrJRiBOk (last accessed 18.1.2020)</ref> | ||
== Etiology == | == Etiology == | ||
The cause of progressive supranuclear palsy is unknown. | |||
* Advanced age and environmental factors eg exposure to toxins and heavy metals may be causes. | |||
* Tau protein aggregates may be due: an unconventional infectious agent; random genetic mutations; or some unknown chemical in the food, air, or water.<ref name=":2">Agarwal S, Gilbert R. Progressive supranuclear palsy. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Apr 11.Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526098/<nowiki/>(accessed 17.3.20220</ref><br> | |||
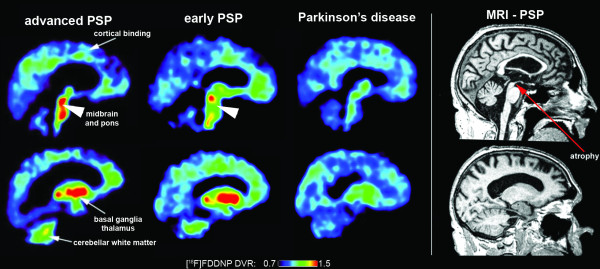
[[Image:Ligand.png]]<br> | [[Image:Ligand.png]]<br> | ||
'''Tau ligand binding patterns in | '''Tau ligand binding patterns in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy''' | ||
== Epidemiology == | == Epidemiology == | ||
Recent studies have reported the prevalence of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy to be 5.8 to 6.5 per 100,000<ref name=":2" />. PSP typically becomes clinically apparent in the 6th decade of life and progresses to death usually within a decade (2-17 years from diagnosis)<ref>Radiopedia PSP Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/progressive-supranuclear-palsy-1<nowiki/>(accessed 17.3.2022)</ref>. | |||
=== Pathophysiology === | === Pathophysiology === | ||
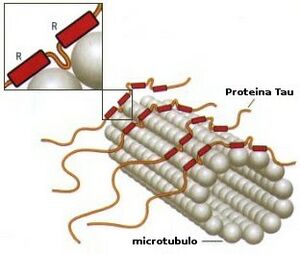
[[File:Tau.jpeg|thumb|Tau in the cohesion of microtubules]] | |||
PSP belongs to the family of [[Tauopathy|tauopathies.]] PSP is a four-repeat tau proteinopathy. Abnormal tau deposition found in other pathological states and is the basic pathologic finding in some other neurodegenerative disorders such as [[Alzheimer's Disease|Alzheimer's disease]] (AD). | |||
Abnormalities in the protein tau lead to damage in both cortical and subcortical areas of the brain. Histopathologic features of progressive supranuclear palsy are an intracerebral aggregation of the microtubule-associated protein tau with preferential involvement of the subthalamic nucleus, pallidum, striatum, red nucleus, [[Substantia Nigra|substantia nigr]]<nowiki/>a, pontine tegmentum, oculomotor nucleus, [[Brainstem|medulla]], and dentate nucleus. | |||
Definite diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy currently requires neuropathological examination.<ref name=":1">Agarwal S, Gilbert R. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526098/ Progressive supranuclear palsy. InStatPearls] [Internet] 2019 Mar 27. StatPearls Publishing.available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526098/ (last accessed 18.1.2020)</ref> | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Clinical features of PSP include early [[Posture|postural]] instability with recurrent [[falls]] (mostly backwards), speech problems, swallowing difficulties, visual dysfunctions (vertical supranuclear gaze palsy), pseudobulbar palsy, bradykinesia, axial rigidity and neuropsychological deficits.Falls represent the main cause of reduced independence, morbidity and mortality in this disorder | Clinical features of PSP include early [[Posture|postural]] instability with recurrent [[falls]] (mostly backwards), speech problems, swallowing difficulties, visual dysfunctions (vertical supranuclear gaze palsy), pseudobulbar palsy, bradykinesia, axial rigidity, and neuropsychological deficits. Falls represent the main cause of reduced independence, morbidity, and mortality in this disorder | ||
* Bradykinesia, | '''Movement disorders''' <ref name=":1" /> | ||
* Rigidity in patients | * [[Bradykinesia]], marked micrographia | ||
* | * Rigidity in patients is more apparent in axial than limb muscles, especially the neck and upper trunk. | ||
* | * Resistance to passive movement of the neck, possible [[dystonia]] of the neck, typically retrocollis. | ||
* | * Face stiff, immobile, and deeply furrowed (the look of surprise) also due to dystonia. | ||
* May develop [[Extrapyramidal and Pyramidal Tracts|pyramidal signs]], including [[Reflexes|hyperreflexia]] and [[Babinski Sign|Babinski signs]]. | |||
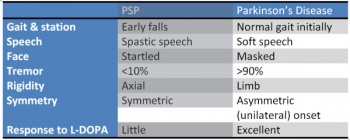
[[Image:PSPvsPD.jpg|thumb|right|350px|Comparison of PSP and Parkinson's]]'''Postural Instability and Falls'''<ref name=":1" /> | |||
[[Image:PSPvsPD.jpg|thumb|right|350px|Comparison of PSP and Parkinson's]] | * Stiff and broad-based gait, with an inclination to have their knees and trunk extended (as opposed to the flexed posture of idiopathic Parkinson Disease), and arms slightly abducted. | ||
* Stiff and broad-based gait, with an inclination to have their knees and trunk extended (as opposed to the flexed posture of idiopathic Parkinson | * Pivot quickly when turning, increases the risk of falls, referred to as the "drunken sailor gait." When they fall, it is usually backward due to a lack of postural reflexes. | ||
* | * As the disease continues to progress people have increased difficulty with movement (many movements become slow and clumsy)<ref name="7 Canada" />. | ||
* As the disease continues to progress people have increased difficulty with movement (many movements become slow and clumsy) | * Eventually, most PSP patients require [[Wheelchair Biomechanics|wheelchair]] assistance due to balance issues<ref name="10 Library">US National Library of Medicine. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/progressive-supranuclear-palsy (accessed 3 May 2017).</ref>.<br> | ||
'''Visual problems'''<ref name="10 Library" />, can lead to blurry vision, double vision, light sensitivity, and staring gaze<ref name="7 Canada" />. | |||
* Eventually, most PSP patients require wheelchair assistance due to balance issues<ref name="10 Library">US National Library of Medicine. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/progressive-supranuclear-palsy (accessed 3 May 2017).</ref>.<br> | |||
* Abnormal eye movements develop several years after other movement dysfunctions and often present as an inability to move the eyes up and down. | * Abnormal eye movements develop several years after other movement dysfunctions and often present as an inability to move the eyes up and down. | ||
* Difficulty opening and closing the eyelids, infrequent blinking, and retraction of the eyelids. | * Difficulty opening and closing the eyelids, infrequent blinking, and retraction of the eyelids. | ||
* In very advanced stages the eyes may not move at all<ref name="7 Canada" />. | * In very advanced stages the eyes may not move at all<ref name="7 Canada" />. | ||
'''Swallowing''' ([[dysphagia]]) | |||
'''Speech''' ([[dysarthria]])<ref name="7 Canada" />. | |||
'''Sleep Disturbances'''.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
'''Personality, behaviour and [[Rancho Los Amigos Level of Cognitive Functioning Scale|cognitive]] changes'''<ref name="10 Library" />. Personality changes are often presented as apathy (loss of interest and enthusiasm). Cognitive changes present as difficulties with cognition, attention, planning, and problem solving<ref name="Webmd">Webmd. Parkinson's and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. http://www.webmd.com/parkinsons-disease/progressive-supranuclear-palsy-psp#1 (accessed 2 May 2017).</ref>. | |||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
# There are no known laboratory tests or imaging techniques that can specifically diagnose PSP at this time<ref name="Fact Sheet">National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Fact Sheet. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Progressive-Supranuclear-Palsy-Fact-Sheet&lt;%22&gt; (accessed 2 May 2017).</ref>. A diagnosis is generally made using the patient history in combination with both physical and neurological scans. | # There are no known laboratory tests or imaging techniques that can specifically diagnose PSP at this time<ref name="Fact Sheet">National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Fact Sheet. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Progressive-Supranuclear-Palsy-Fact-Sheet&lt;%22&gt; (accessed 2 May 2017).</ref>. A diagnosis is generally made using the patient history in combination with both physical and neurological scans. | ||
=== | === Differential Diagnosis === | ||
Clinically it can be challenging to distinguish PSP from other entities especially when features are not typical. | |||
* [[Parkinson's|Parkinson disease]] | |||
* [[Multiple System Atrophy|Multiple system atrophy]] (MSA) | |||
* Corticobasal degeneration (CBD) | |||
* Cortical atrophy prominent | |||
== | === Management and Interventions === | ||
The management of the cognitive, motor, and gait aspects of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy is challenging, and the treatment for individuals suspected to have progressive supranuclear palsy remains symptomatic and supportive, with ongoing clinical trials striving to identify disease-modifying therapies often targeting the underlying tau pathology.<ref name=":1" /> There are no effective medical or surgical treatments for PSP.<ref name=":0">Clerici I, Ferrazzoli D, Maestri R, Bossio F, Zivi I, Canesi M, Pezzoli G, Frazzitta G. [https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0170927 Rehabilitation in progressive supranuclear palsy: Effectiveness of two multidisciplinary treatments.] PloS one. 2017 Feb 3;12(2):e0170927.Available from:https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0170927 (last accessed 18.1.2020)</ref> | |||
* There is little known long term benefit to drug agents in this disease, despite its parkinsonian presentation<ref name="Fact Sheet" />. Occasionally, bradykinesia and stiffness of gait can be altered transiently with levodopa, and botulinum toxin often can decrease involuntary eye closing and results in no long term effects. | |||
* Non-drug treatments for PSP can include assistive walking devices for the prevention of falls (often include counterweights for extensor postures). Often people are prescribed prism glasses that treat the patient’s decreased ability to look down, allowing better visual input for balance and walking<ref name="Fact Sheet" />. There is evidence of exercise through physiotherapy for the maintenance of strength, coordination, and balance in these patients<ref name="Clerici et al" /> <sup></sup> | |||
* | |||
== Outcome Measures == | == Outcome Measures == | ||
*[https://pspblogdotorg.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/psprs-form-4-2014.pdf Progressive | *[https://pspblogdotorg.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/psprs-form-4-2014.pdf Progressive Supranuclear Palsy rating scale (PSPRS)]<ref name="Hall et al">Hall DA, Forjaz MJ, Golbe LI, Litvan I, Payan CA, Goetz CG, Leentjens AF, Martinez‐Martin P, Traon AP, Sampaio C, Post B. Scales to Assess Clinical Features of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: MDS Task Force Report. Movement Disorders Clinical Practice. 2015 Jun 1;2(2):127-34.</ref> | ||
*Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Quality of Life scale (PSP-QoL)<ref name="Hall et al" /> | *Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Quality of Life scale (PSP-QoL)<ref name="Hall et al" /> | ||
*Neuroprotection in Parkinson Plus Syndromes–Parkinson Plus Scale (NNIPPS-PPS)<ref name="Hall et al" /> | *Neuroprotection in Parkinson Plus Syndromes–Parkinson Plus Scale (NNIPPS-PPS)<ref name="Hall et al" /> | ||
*[http://www.aahf.info/pdf/Berg_Balance_Scale.pdf Berg Balance Scale] (BBS)<ref name="Clerici et al">Clerici I, Ferrazzoli D, Maestri R, Bossio F, Zivi I, Canesi M, Pezzoli G, Frazzitta G. Rehabilitation in progressive supranuclear palsy: Effectiveness of two multidisciplinary treatments. PloS one. 2017 Feb 3;12(2):e0170927.</ref> | *[http://www.aahf.info/pdf/Berg_Balance_Scale.pdf Berg Balance Scale] (BBS)<ref name="Clerici et al">Clerici I, Ferrazzoli D, Maestri R, Bossio F, Zivi I, Canesi M, Pezzoli G, Frazzitta G. Rehabilitation in progressive supranuclear palsy: Effectiveness of two multidisciplinary treatments. PloS one. 2017 Feb 3;12(2):e0170927.</ref> | ||
*[https://www.thoracic.org/statements/resources/pfet/sixminute.pdf 6 Minute Walk Test] (6MWT)<ref name="Clerici et al" /> | *[https://www.thoracic.org/statements/resources/pfet/sixminute.pdf 6 Minute Walk Test] (6MWT)<ref name="Clerici et al" /> | ||
== Prognosis == | |||
The average duration for PSP patient is about 6–8 years. The most important predictors of short survival are the PSP classical variant, early presence of falls, cognitive disorders, and dysphagia. The leading causes of death in PSP patients are pneumonia and sepsis.<ref>Shoeibi A, Olfati N, Litvan I. [https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2019.01125/full Frontrunner in translation: progressive supranuclear palsy]. Frontiers in neurology. 2019 Oct 22;10:1125.Available:https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2019.01125/full (accessed 7.10.2023)</ref> | |||
== Physiotherapy == | == Physiotherapy == | ||
Studies | Studies confirm the importance of an aerobic, multidisciplinary, motor-cognitive, goal-based, and intensive approach for the rehabilitation of patients suffering from such a complex disease as PSP<ref name=":0" />. | ||
* The potential value of physical therapy is of increasing interest, particularly given evidence of benefit for individuals with Parkinson disease, and a recent trial showed improvement in the Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Rating Scale (PSPRS)<ref name=":1" /> | * The potential value of physical therapy is of increasing interest, particularly given evidence of benefit for individuals with Parkinson disease, and a recent trial showed improvement in the Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Rating Scale (PSPRS)<ref name=":1" /> | ||
*[[File:Falls class.png|right|frameless]]Physical therapy with particular attention to balance training and “learning to fall” can minimize the potential for injury and provide patients with tools for maneuvering after a fall has occurred. | *[[File:Falls class.png|right|frameless]]Physical therapy with particular attention to balance training and “learning to fall” can minimize the potential for injury and provide patients with tools for maneuvering after a fall has occurred. | ||
| Line 120: | Line 104: | ||
=== Concluding Remarks === | === Concluding Remarks === | ||
Unlike typical Parkinson Disease, falls begin within the first year of progressive supranuclear palsy, and by year 3, they are common unless precautions are taken to prevent them.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
* Downgaze is affected before upgaze, whereas; lateral eye movements are usually preserved in progressive supranuclear palsy. | * Downgaze is affected before upgaze, whereas; lateral eye movements are usually preserved in progressive supranuclear palsy. | ||
* Apathy seems to predominate over other neurobehavioral abnormalities in progressive supranuclear palsy. | * Apathy seems to predominate over other neurobehavioral abnormalities in progressive supranuclear palsy. | ||
* Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy develop frontal cognitive impairment. | * Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy develop frontal cognitive impairment. | ||
* The pathology of progressive supranuclear palsy is characterized by widespread neurodegeneration associated with tau protein deposition in subcortical regions. | * The pathology of progressive supranuclear palsy is characterized by widespread neurodegeneration associated with tau protein deposition in subcortical regions. | ||
* Studies | * Studies confirm the importance of an aerobic, multidisciplinary, motor-cognitive, goal-based, and intensive approach for the rehabilitation of patients suffering from PSP. <ref name=":1" /> | ||
* The first therapeutic step in | * The first therapeutic step in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy is identifying and prioritizing the symptoms that can be treated<ref name=":1" />. | ||
=== Historical Perspective === | === Historical Perspective === | ||
This video shows footage of the first diagnosed client and gives a bit of history | This video shows footage of the first diagnosed client and gives a bit of history regarding PSP (3 minutes).{{#ev:youtube|BPt3pTzbcXc}} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 02:59, 24 January 2024
Top Contributors - Angelique Travlos, Lucinda hampton, Jenna Davidson, Jessica Firman, Kim Jackson, Valerie Wallace, Lauren Lopez, Amanda Dawson, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane, Mason Trauger, Vidya Acharya and 127.0.0.1
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) is a form of Parkinsonism. It is an uncommon neurological disorder that can affect movement, gait, balance, speech, swallowing, vision, eye movements, mood, behavior, and cognition.
The disorder's name refers to the disease worsening (progressive) and causing weakness (palsy) by damaging the brain above nerve cell clusters called nuclei (supranuclear). These nuclei predominantly control eye movement[1].
The 5-minute video below is good for an overview of symptoms and diagnosis.
Etiology[edit | edit source]
The cause of progressive supranuclear palsy is unknown.
- Advanced age and environmental factors eg exposure to toxins and heavy metals may be causes.
- Tau protein aggregates may be due: an unconventional infectious agent; random genetic mutations; or some unknown chemical in the food, air, or water.[3]
Tau ligand binding patterns in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Recent studies have reported the prevalence of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy to be 5.8 to 6.5 per 100,000[3]. PSP typically becomes clinically apparent in the 6th decade of life and progresses to death usually within a decade (2-17 years from diagnosis)[4].
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
PSP belongs to the family of tauopathies. PSP is a four-repeat tau proteinopathy. Abnormal tau deposition found in other pathological states and is the basic pathologic finding in some other neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Abnormalities in the protein tau lead to damage in both cortical and subcortical areas of the brain. Histopathologic features of progressive supranuclear palsy are an intracerebral aggregation of the microtubule-associated protein tau with preferential involvement of the subthalamic nucleus, pallidum, striatum, red nucleus, substantia nigra, pontine tegmentum, oculomotor nucleus, medulla, and dentate nucleus.
Definite diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy currently requires neuropathological examination.[5]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Clinical features of PSP include early postural instability with recurrent falls (mostly backwards), speech problems, swallowing difficulties, visual dysfunctions (vertical supranuclear gaze palsy), pseudobulbar palsy, bradykinesia, axial rigidity, and neuropsychological deficits. Falls represent the main cause of reduced independence, morbidity, and mortality in this disorder
Movement disorders [5]
- Bradykinesia, marked micrographia
- Rigidity in patients is more apparent in axial than limb muscles, especially the neck and upper trunk.
- Resistance to passive movement of the neck, possible dystonia of the neck, typically retrocollis.
- Face stiff, immobile, and deeply furrowed (the look of surprise) also due to dystonia.
- May develop pyramidal signs, including hyperreflexia and Babinski signs.
Postural Instability and Falls[5]
- Stiff and broad-based gait, with an inclination to have their knees and trunk extended (as opposed to the flexed posture of idiopathic Parkinson Disease), and arms slightly abducted.
- Pivot quickly when turning, increases the risk of falls, referred to as the "drunken sailor gait." When they fall, it is usually backward due to a lack of postural reflexes.
- As the disease continues to progress people have increased difficulty with movement (many movements become slow and clumsy)[1].
- Eventually, most PSP patients require wheelchair assistance due to balance issues[6].
Visual problems[6], can lead to blurry vision, double vision, light sensitivity, and staring gaze[1].
- Abnormal eye movements develop several years after other movement dysfunctions and often present as an inability to move the eyes up and down.
- Difficulty opening and closing the eyelids, infrequent blinking, and retraction of the eyelids.
- In very advanced stages the eyes may not move at all[1].
Swallowing (dysphagia)
Speech (dysarthria)[1].
Sleep Disturbances.[5]
Personality, behaviour and cognitive changes[6]. Personality changes are often presented as apathy (loss of interest and enthusiasm). Cognitive changes present as difficulties with cognition, attention, planning, and problem solving[7].
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
- There are no known laboratory tests or imaging techniques that can specifically diagnose PSP at this time[8]. A diagnosis is generally made using the patient history in combination with both physical and neurological scans.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Clinically it can be challenging to distinguish PSP from other entities especially when features are not typical.
- Parkinson disease
- Multiple system atrophy (MSA)
- Corticobasal degeneration (CBD)
- Cortical atrophy prominent
Management and Interventions[edit | edit source]
The management of the cognitive, motor, and gait aspects of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy is challenging, and the treatment for individuals suspected to have progressive supranuclear palsy remains symptomatic and supportive, with ongoing clinical trials striving to identify disease-modifying therapies often targeting the underlying tau pathology.[5] There are no effective medical or surgical treatments for PSP.[9]
- There is little known long term benefit to drug agents in this disease, despite its parkinsonian presentation[8]. Occasionally, bradykinesia and stiffness of gait can be altered transiently with levodopa, and botulinum toxin often can decrease involuntary eye closing and results in no long term effects.
- Non-drug treatments for PSP can include assistive walking devices for the prevention of falls (often include counterweights for extensor postures). Often people are prescribed prism glasses that treat the patient’s decreased ability to look down, allowing better visual input for balance and walking[8]. There is evidence of exercise through physiotherapy for the maintenance of strength, coordination, and balance in these patients[10]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
- Progressive Supranuclear Palsy rating scale (PSPRS)[11]
- Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Quality of Life scale (PSP-QoL)[11]
- Neuroprotection in Parkinson Plus Syndromes–Parkinson Plus Scale (NNIPPS-PPS)[11]
- Berg Balance Scale (BBS)[10]
- 6 Minute Walk Test (6MWT)[10]
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The average duration for PSP patient is about 6–8 years. The most important predictors of short survival are the PSP classical variant, early presence of falls, cognitive disorders, and dysphagia. The leading causes of death in PSP patients are pneumonia and sepsis.[12]
Physiotherapy[edit | edit source]
Studies confirm the importance of an aerobic, multidisciplinary, motor-cognitive, goal-based, and intensive approach for the rehabilitation of patients suffering from such a complex disease as PSP[9].
- The potential value of physical therapy is of increasing interest, particularly given evidence of benefit for individuals with Parkinson disease, and a recent trial showed improvement in the Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Rating Scale (PSPRS)[5]
- Physical therapy with particular attention to balance training and “learning to fall” can minimize the potential for injury and provide patients with tools for maneuvering after a fall has occurred.
- The use of a walker is often necessary for safe ambulation and transfers. At late stages, even using a walker is not enough to maintain balance, and patients may need to use a wheelchair exclusively[5].
Since there is no medication available to treat this condition[8], patients are often referred to physiotherapy in order to manage their symptoms. Most physiotherapy interventions for PSP include an exercise regimen that consists of[10]:
- Aerobic exercises
- Transfer/balance training
- Gait training
- Weighted tool can be used to prevent backward falls
- Flexibility training[13]
- Intensive routines
- Goal-oriented tasks
- Visual tracking
- Prism lenses sometimes used to further train gaze[13]
- Motor-cognitive exercises
The study recommends future trials using methods such as the Consensus on Exercise Reporting Template (CERT) to provide a comprehensive description of exercise and physical activity interventions in patients[14]. An exercise program following these guidelines is recommended for about 1-2 hours a day, 5 days a week, in order to show any significant improvements[10].
Concluding Remarks[edit | edit source]
Unlike typical Parkinson Disease, falls begin within the first year of progressive supranuclear palsy, and by year 3, they are common unless precautions are taken to prevent them.[5]
- Downgaze is affected before upgaze, whereas; lateral eye movements are usually preserved in progressive supranuclear palsy.
- Apathy seems to predominate over other neurobehavioral abnormalities in progressive supranuclear palsy.
- Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy develop frontal cognitive impairment.
- The pathology of progressive supranuclear palsy is characterized by widespread neurodegeneration associated with tau protein deposition in subcortical regions.
- Studies confirm the importance of an aerobic, multidisciplinary, motor-cognitive, goal-based, and intensive approach for the rehabilitation of patients suffering from PSP. [5]
- The first therapeutic step in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy is identifying and prioritizing the symptoms that can be treated[5].
Historical Perspective[edit | edit source]
This video shows footage of the first diagnosed client and gives a bit of history regarding PSP (3 minutes).
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Parkinson Canada. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. http://www.parkinson.ca/site/c.kgLNIWODKpF/b.8647261/k.4815/Progressive_Supranuclear_Palsy.htm (accessed 3 May 2017).
- ↑ CurePSP Symptoms and Diagnosis; PSP, CBD and MSA Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qn4VrJRiBOk (last accessed 18.1.2020)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Agarwal S, Gilbert R. Progressive supranuclear palsy. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Apr 11.Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526098/(accessed 17.3.20220
- ↑ Radiopedia PSP Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/progressive-supranuclear-palsy-1(accessed 17.3.2022)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 Agarwal S, Gilbert R. Progressive supranuclear palsy. InStatPearls [Internet] 2019 Mar 27. StatPearls Publishing.available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526098/ (last accessed 18.1.2020)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 US National Library of Medicine. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/progressive-supranuclear-palsy (accessed 3 May 2017).
- ↑ Webmd. Parkinson's and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. http://www.webmd.com/parkinsons-disease/progressive-supranuclear-palsy-psp#1 (accessed 2 May 2017).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Fact Sheet. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Progressive-Supranuclear-Palsy-Fact-Sheet<%22> (accessed 2 May 2017).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Clerici I, Ferrazzoli D, Maestri R, Bossio F, Zivi I, Canesi M, Pezzoli G, Frazzitta G. Rehabilitation in progressive supranuclear palsy: Effectiveness of two multidisciplinary treatments. PloS one. 2017 Feb 3;12(2):e0170927.Available from:https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0170927 (last accessed 18.1.2020)
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Clerici I, Ferrazzoli D, Maestri R, Bossio F, Zivi I, Canesi M, Pezzoli G, Frazzitta G. Rehabilitation in progressive supranuclear palsy: Effectiveness of two multidisciplinary treatments. PloS one. 2017 Feb 3;12(2):e0170927.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Hall DA, Forjaz MJ, Golbe LI, Litvan I, Payan CA, Goetz CG, Leentjens AF, Martinez‐Martin P, Traon AP, Sampaio C, Post B. Scales to Assess Clinical Features of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: MDS Task Force Report. Movement Disorders Clinical Practice. 2015 Jun 1;2(2):127-34.
- ↑ Shoeibi A, Olfati N, Litvan I. Frontrunner in translation: progressive supranuclear palsy. Frontiers in neurology. 2019 Oct 22;10:1125.Available:https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2019.01125/full (accessed 7.10.2023)
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Johns Hopkins Medicine. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/conditions/nervous_system_disorders/progressive_supranuclear_palsy_134,65/ (accessed 2 May 2017).
- ↑ Slade SC, Underwood M, McGinley JL, Morris ME. Exercise and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: the need for explicit exercise reporting. BMC neurology. 2019 Dec 1;19(1):305.